Conversion Of L Atm To J
News Leon
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
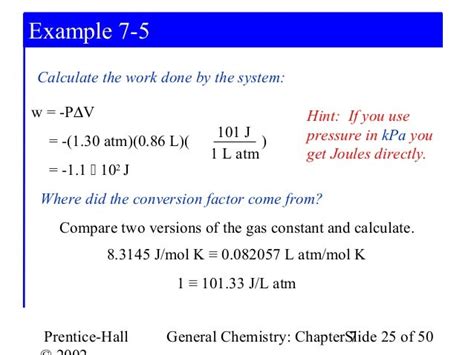
Table of Contents
Converting L·atm to Joules: A Comprehensive Guide
The conversion of liter-atmospheres (L·atm) to Joules (J) is a common task in chemistry and physics, particularly when dealing with thermodynamic calculations involving work done by or on a gas. This conversion is crucial for understanding energy changes in various processes, from piston expansions to chemical reactions. While seemingly simple, a thorough understanding of the underlying principles and potential pitfalls is vital for accurate results. This comprehensive guide delves into the conversion process, explores the relevant concepts, and provides practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding the Units: L·atm and Joules
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the units involved:
-
Liter-atmosphere (L·atm): This unit represents work done by or on a gas. One liter-atmosphere is the work done when a gas expands against a constant external pressure of one atmosphere (atm) by a volume of one liter (L). It's a unit of energy, though not a standard SI unit.
-
Joule (J): This is the SI unit of energy. It's defined as the work done when a force of one Newton (N) acts over a distance of one meter (m). This is a fundamental unit in physics and chemistry, making it the preferred unit for most energy calculations.
The need for conversion arises from the fact that L·atm is not an SI unit, while Joules are. Consistent use of SI units is crucial for accurate calculations and interoperability within the scientific community.
The Conversion Factor: Bridging the Units
The conversion between L·atm and Joules hinges on the relationship between pressure, volume, and work. The conversion factor derives from the definition of these units and the physical constants that relate them.
The key relationship is:
1 L·atm = 101.325 J
This conversion factor arises from the following:
- 1 atm = 101325 Pa (Pascals) – This is the standard atmospheric pressure in Pascals, the SI unit of pressure.
- 1 L = 0.001 m³ (cubic meters) – This is the conversion from liters to cubic meters.
- Work (W) = Pressure (P) × Change in Volume (ΔV) – This fundamental equation from physics defines the work done by a gas during expansion or compression.
By substituting the SI equivalents for atm and L into the work equation and performing the calculation, we arrive at the conversion factor of 101.325 J per L·atm. This means that one liter-atmosphere of work is equivalent to 101.325 Joules of energy.
Practical Application: Converting L·atm to J
The conversion itself is straightforward. To convert a value in L·atm to Joules, simply multiply the value by the conversion factor:
Joules = L·atm × 101.325 J/L·atm
Example:
Let's say a gas expands and does 2.5 L·atm of work. To convert this to Joules:
Joules = 2.5 L·atm × 101.325 J/L·atm = 253.3125 J
Therefore, the gas has done 253.3125 Joules of work.
Potential Sources of Error and Considerations
While the conversion is relatively simple, several factors can contribute to inaccuracies:
-
Significant Figures: Pay close attention to significant figures in your calculations. The conversion factor itself has five significant figures (101.325), so your final answer should reflect the appropriate number of significant figures based on the initial value.
-
Units: Always double-check the units of your input values. Ensure you're working with liters and atmospheres, not milliliters or other pressure units. Incorrect units will lead to grossly inaccurate results.
-
Temperature and Pressure Changes: The conversion factor assumes a constant temperature and pressure. For processes involving significant changes in temperature or pressure, the calculation may be more complex and may require the use of more sophisticated thermodynamic equations, such as the ideal gas law (PV=nRT) in conjunction with the work equation. The ideal gas law helps to account for changes in volume due to temperature and pressure alterations.
-
Non-Ideal Gases: The conversion factor is based on the ideal gas law, which assumes that gas molecules have negligible volume and do not interact with each other. Real gases deviate from ideal behavior, especially at high pressures and low temperatures. For non-ideal gases, more advanced equations of state are needed to accurately calculate the work done.
Advanced Applications and Related Concepts
The conversion of L·atm to Joules is fundamental in various areas of chemistry and physics:
-
Thermochemistry: It's crucial in calculating the heat absorbed or released in chemical reactions that involve changes in gas volume. The work done by or on the system needs to be accounted for in order to obtain the correct enthalpy change (ΔH).
-
Physical Chemistry: Many physical chemistry calculations involving gases require consistent energy units. Converting L·atm to Joules ensures compatibility with the SI system.
-
Engineering: In engineering applications involving gas systems, precise energy calculations are crucial for designing efficient and safe systems. Accurate conversion between L·atm and Joules ensures the reliability of engineering designs.
-
Environmental Science: In studying atmospheric processes, understanding energy changes in the atmosphere is vital. The conversion of L·atm to Joules aids in accurate analysis of atmospheric dynamics.
Conclusion: Mastering the L·atm to J Conversion
Converting liter-atmospheres to Joules is a critical skill for anyone working with thermodynamic calculations involving gases. While the basic conversion is straightforward, a deep understanding of the underlying principles, potential pitfalls, and related concepts is essential for accurate and meaningful results. Always double-check your units, pay attention to significant figures, and consider the limitations of the ideal gas law when dealing with non-ideal gases or significant temperature and pressure changes. By mastering this conversion, you'll enhance your ability to analyze and interpret a wide range of physical and chemical phenomena. Remember to always use the conversion factor of 1 L·atm = 101.325 J for accurate conversions. This thorough understanding will contribute significantly to your success in scientific calculations and problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In A Hypotonic Solution An Animal Cell Will
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Quadrilaterals Have Diagonals That Bisect Each Other
Apr 03, 2025
-
X To The Power Of X Derivative
Apr 03, 2025
-
Positively Charged Center Of An Atom
Apr 03, 2025
-
How To Find Linear Mass Density
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Conversion Of L Atm To J . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
