Which Of The Following Has The Least Resistance
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
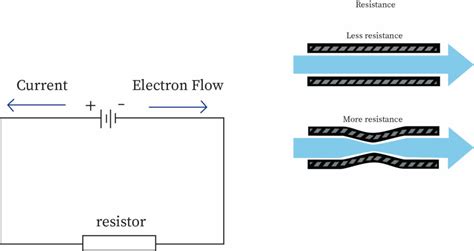
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Has the Least Resistance? A Deep Dive into Material Properties and Electrical Conductivity
The question, "Which of the following has the least resistance?" is deceptively simple. To answer it accurately, we need to understand the factors influencing electrical resistance and explore the properties of various materials. This isn't just about memorizing facts; it's about grasping the fundamental principles of electricity and how they dictate material behavior. This article will delve into the physics behind resistance, analyze various materials, and provide a robust understanding of this crucial concept.
Understanding Electrical Resistance
Before we compare materials, let's define what electrical resistance is. Resistance is the opposition a material offers to the flow of electric current. It's measured in ohms (Ω), and a higher resistance means a smaller current will flow for a given voltage (Ohm's Law: V = IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance). Several factors contribute to a material's resistance:
1. Material Type: The Intrinsic Property
The most significant factor is the intrinsic nature of the material. Different materials have different atomic structures and electron configurations, leading to vastly different abilities to conduct electricity. Metals, for instance, are excellent conductors because their outermost electrons are loosely bound and can move freely, forming a "sea" of electrons. Conversely, insulators, like rubber or glass, tightly bind their electrons, hindering current flow and exhibiting high resistance. Semiconductors fall somewhere in between, possessing conductivity that can be controlled through various means.
2. Length: The Longer, the Higher the Resistance
The length of the conductor directly impacts resistance. A longer conductor provides a longer path for electrons to travel, increasing the likelihood of collisions and scattering, thereby increasing resistance. Imagine a long, narrow pipe versus a short, wide one – the longer pipe offers more resistance to water flow, similarly, a longer wire offers more resistance to electron flow.
3. Cross-Sectional Area: The Wider, the Lower the Resistance
The cross-sectional area of the conductor is inversely proportional to resistance. A larger cross-sectional area provides more space for electrons to flow, reducing the likelihood of collisions and hence reducing resistance. Using the pipe analogy again, a wider pipe allows more water to flow with less resistance; similarly, a thicker wire allows more electrons to flow with less resistance.
4. Temperature: Heat Increases Resistance (Generally)
Temperature significantly influences resistance, especially in metals. As temperature rises, the atoms in the conductor vibrate more vigorously. These increased vibrations impede the flow of electrons, leading to higher resistance. This relationship is generally linear for metals at moderate temperatures. However, some materials, like semiconductors, exhibit a more complex relationship between temperature and resistance.
Comparing Materials: A Hierarchy of Resistance
Now, let's analyze the resistance characteristics of various materials. This analysis won't provide a definitive "least resistance" answer without specifying the materials in question but will equip you to make that determination when provided with options.
1. Metals: The Champions of Conductivity
Metals, as mentioned earlier, are characterized by their low resistance. This stems from the availability of free electrons in their atomic structure. The best conductors among metals include:
- Silver (Ag): Often considered the best conductor of electricity, possessing the lowest resistivity.
- Copper (Cu): Widely used in electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity and relative affordability.
- Gold (Au): Excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for high-end applications.
- Aluminum (Al): Lighter than copper and a decent conductor, making it a cost-effective option for power transmission lines.
2. Semiconductors: Conductivity Under Control
Semiconductors, such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge), possess electrical conductivity between that of metals and insulators. Their resistance can be precisely controlled by doping – introducing impurities – to either increase (n-type) or decrease (p-type) the number of charge carriers. This makes them crucial in electronic devices like transistors and integrated circuits.
3. Insulators: Resistance at its Peak
Insulators, such as rubber, glass, and plastics, have exceptionally high resistance, meaning electrons have difficulty moving through them. This property is essential for safety in electrical applications, preventing current leakage and shocks. Their tightly bound electrons severely limit the flow of charge carriers.
4. Superconductors: Resistance Vanishes!
Superconductors are exceptional materials that exhibit zero electrical resistance below a critical temperature. This phenomenon opens up exciting possibilities for lossless power transmission and other advanced technologies, although maintaining these low temperatures requires significant effort.
Factors influencing the “Least Resistance” Determination
Determining which material has the least resistance depends critically on the context. It’s not simply a matter of picking a material from a list; we need to consider factors like:
- Specific Materials: A list comparing silver, copper, and rubber is straightforward. Silver wins. However, comparing specific alloys or composite materials requires more detailed knowledge of their resistivity.
- Temperature: Resistance changes with temperature, sometimes dramatically. At extremely low temperatures, even poor conductors can exhibit surprisingly low resistance, while at high temperatures, excellent conductors experience increased resistance.
- Length and Cross-Sectional Area: Even the best conductor will have high resistance if it's extremely long and thin. Conversely, a mediocre conductor could exhibit low resistance if it is short and wide.
- Purity: Impurities within a material can significantly increase its resistance. The purer the metal, the lower the resistance.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The concept of least resistance has far-reaching implications in various applications:
- Electrical Wiring: Copper is the most common material in electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity, affordability, and ease of handling. Aluminum is sometimes used for high-voltage transmission lines due to its lower density and cost-effectiveness despite its slightly higher resistance.
- Electronics: Semiconductors are the bedrock of modern electronics, allowing for precise control of current flow and the construction of transistors, integrated circuits, and other essential components.
- Safety: Insulators are critical for ensuring safety in electrical systems, preventing shocks and short circuits.
- Superconducting technologies: Research and development in superconductors continue to explore new applications, potentially revolutionizing energy transmission and various other technologies.
Conclusion: Understanding Context is Key
The question of which material possesses the least resistance isn't a simple one-size-fits-all answer. While silver generally exhibits the lowest resistivity among common materials, other factors like temperature, dimensions, and material purity significantly affect the overall resistance. Understanding the interplay of these factors is crucial for selecting appropriate materials for various electrical and electronic applications. Remember, the concept of least resistance goes beyond simply memorizing a list; it’s about mastering the fundamental physics that govern electrical conductivity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Pairs Of Ions Represent Isoelectronic Species
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Calculate E Not Cell
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Part Of The Ear Looks Like A Snail Shell
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Agno3
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Of 68 Is 17
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Has The Least Resistance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
