Which Of The Following Are Examples Of Polysaccharides
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
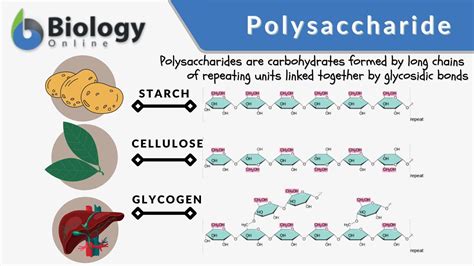
Table of Contents
Which of the Following are Examples of Polysaccharides? A Deep Dive into Carbohydrate Chemistry
Polysaccharides are a crucial class of carbohydrates, playing vital roles in biological systems. Understanding what constitutes a polysaccharide and recognizing common examples is fundamental to grasping their biological significance. This comprehensive article will delve into the definition of polysaccharides, exploring various examples and highlighting their diverse functions in nature. We'll clarify which of several substances qualify as polysaccharides and explain why.
Understanding Polysaccharides: The Building Blocks of Complex Carbohydrates
Polysaccharides, also known as glycans, are large, complex carbohydrates composed of long chains of monosaccharide units (simple sugars) linked together by glycosidic bonds. These chains can be branched or unbranched, and the specific monosaccharide units and their arrangement determine the polysaccharide's properties and functions. Unlike monosaccharides (like glucose and fructose) and disaccharides (like sucrose and lactose), which are relatively small and readily soluble in water, polysaccharides are typically large, insoluble molecules.
Key characteristics of polysaccharides:
- High molecular weight: They are macromolecules, meaning they have very large molecular weights compared to monosaccharides and disaccharides.
- Insoluble in water: Their large size and complex structure prevent them from dissolving readily in water.
- Structural or storage function: Polysaccharides primarily serve as structural components in cells or as energy storage molecules.
- Variety of monosaccharide units: They can be composed of a single type of monosaccharide (homopolysaccharides) or multiple types (heteropolysaccharides).
- Glycosidic bonds: Monosaccharide units are linked through glycosidic bonds, which are covalent bonds formed between the hydroxyl groups of adjacent sugar molecules.
Common Examples of Polysaccharides: A Detailed Exploration
Let's examine several substances and determine whether they classify as polysaccharides:
1. Starch: Yes, starch is a polysaccharide. It's a crucial energy storage polysaccharide in plants. Starch consists of two main components:
- Amylose: A linear chain of α-D-glucose units linked by α(1→4) glycosidic bonds.
- Amylopectin: A branched chain of α-D-glucose units with α(1→4) glycosidic bonds in the linear chains and α(1→6) bonds at the branch points.
The branching in amylopectin allows for efficient storage and rapid mobilization of glucose when needed by the plant. Starch is easily digestible by humans and serves as a significant source of dietary energy.
2. Glycogen: Yes, glycogen is a polysaccharide. Known as animal starch, glycogen is the primary energy storage polysaccharide in animals. Similar to amylopectin, it's a highly branched structure composed of α-D-glucose units linked by α(1→4) and α(1→6) glycosidic bonds. However, glycogen is even more highly branched than amylopectin, allowing for faster glucose release when energy demands increase. It's stored primarily in the liver and muscles.
3. Cellulose: Yes, cellulose is a polysaccharide. This is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, forming the major structural component of plant cell walls. Cellulose is a linear polymer of β-D-glucose units linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds. This subtle difference in the glycosidic bond (β instead of α) significantly alters its properties. Unlike starch and glycogen, cellulose is indigestible by humans due to the inability of our digestive enzymes to break down β(1→4) glycosidic bonds. Herbivores, however, possess specialized microorganisms in their digestive tracts that can break down cellulose.
4. Chitin: Yes, chitin is a polysaccharide. This is a structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of arthropods (insects, crustaceans) and the cell walls of some fungi. Chitin is a linear polymer of N-acetylglucosamine units linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds. Its structure is similar to cellulose, but the presence of the N-acetyl group confers unique properties, contributing to its strength and rigidity.
5. Sucrose: No, sucrose is not a polysaccharide. Sucrose is a disaccharide, composed of one glucose molecule and one fructose molecule linked by a glycosidic bond. It's a common table sugar and a readily soluble sweetener. As a disaccharide, it's far smaller and simpler than polysaccharides.
6. Glucose: No, glucose is not a polysaccharide. Glucose is a monosaccharide, the simplest form of carbohydrate. It's a key energy source for cells and serves as the building block for many polysaccharides.
7. Fructose: No, fructose is not a polysaccharide. Like glucose, fructose is a monosaccharide. It's found in fruits and honey and is also a component of sucrose.
8. Maltose: No, maltose is not a polysaccharide. Maltose is a disaccharide, formed by two glucose molecules linked by an α(1→4) glycosidic bond. It's produced during the breakdown of starch.
9. Hyaluronic Acid: Yes, hyaluronic acid is a polysaccharide. This is a glycosaminoglycan (GAG), a type of heteropolysaccharide found in the extracellular matrix of connective tissues. It's composed of repeating disaccharide units of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine. Hyaluronic acid plays a vital role in hydration, lubrication, and tissue repair.
10. Heparin: Yes, heparin is a polysaccharide. Another glycosaminoglycan, heparin is an anticoagulant found in the mast cells of many tissues. It’s a highly sulfated heteropolysaccharide consisting of repeating units of uronic acid and glucosamine. Its complex structure contributes to its ability to inhibit blood clotting.
The Diverse Functions of Polysaccharides: Beyond Energy Storage
Polysaccharides are not simply energy stores; they have a wide range of functions within living organisms:
Structural Roles:
- Cellulose: Forms the rigid cell walls of plants, providing structural support.
- Chitin: Provides structural support in the exoskeletons of arthropods and cell walls of fungi.
- Peptidoglycan: A component of bacterial cell walls, providing structural integrity.
Energy Storage:
- Starch: The primary energy storage polysaccharide in plants.
- Glycogen: The primary energy storage polysaccharide in animals.
Other Functions:
- Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs): Such as hyaluronic acid and heparin, these polysaccharides have various roles including lubrication, hydration, and regulation of cellular processes.
- Cell signaling and recognition: Specific polysaccharides on cell surfaces play crucial roles in cell-cell recognition and communication.
- Immune system modulation: Some polysaccharides act as antigens, triggering immune responses.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Polysaccharide Diversity
This detailed exploration highlights the critical role of polysaccharides in biology. Recognizing the differences between polysaccharides, disaccharides, and monosaccharides is crucial for understanding their respective functions. From the energy-storing capabilities of starch and glycogen to the structural integrity provided by cellulose and chitin, polysaccharides are indispensable molecules in living systems. Their diverse structures and functions underscore their significance in biological processes. By appreciating the variations in their composition and linkages, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexity and beauty of biological chemistry. Remember, the key to identifying a polysaccharide lies in its polymeric structure, consisting of many monosaccharide units joined by glycosidic bonds, resulting in a large, often insoluble molecule that serves structural or energy storage functions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Definition Of Order Of A Reaction
Mar 25, 2025
-
Distilled Water Does Not Conduct A Current
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Projectile Is Fired Horizontally From A Gun
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Europe Is Called The Peninsula Of Peninsulas
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Mineralocorticoid
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Are Examples Of Polysaccharides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
