Which Of The Following Is A Mineralocorticoid
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
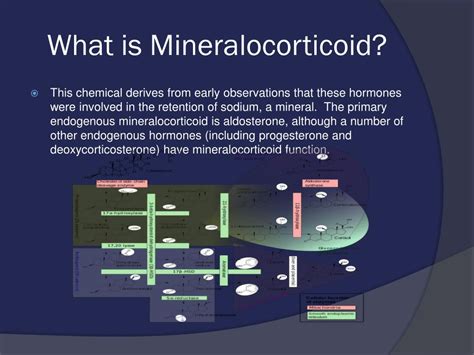
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Mineralocorticoid? Understanding Steroid Hormones
Steroid hormones are vital signaling molecules in the body, influencing a wide range of physiological processes. Among these, mineralocorticoids hold a critical role in regulating electrolyte balance, particularly sodium and potassium, which are essential for maintaining fluid homeostasis and blood pressure. This article delves into the fascinating world of mineralocorticoids, clarifying their function and distinguishing them from other steroid hormones. We’ll explore which of several potential hormones are indeed classified as mineralocorticoids and examine the crucial impact these hormones have on overall health.
Understanding Steroid Hormones: A Brief Overview
Before focusing on mineralocorticoids, it's crucial to understand the broader context of steroid hormones. These lipid-soluble hormones are synthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal glands, gonads, and placenta. Their hydrophobic nature allows them to easily cross cell membranes and interact with intracellular receptors, initiating changes in gene expression. Steroid hormones are broadly classified into several groups based on their primary functions:
1. Glucocorticoids: Regulators of Metabolism and Stress Response
Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, are primarily involved in glucose metabolism, regulating blood sugar levels, suppressing inflammation, and modulating the body's response to stress. They play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis during periods of physical or psychological stress.
2. Mineralocorticoids: Guardians of Electrolyte Balance
Mineralocorticoids, the focus of this article, are primarily responsible for regulating the balance of electrolytes, mainly sodium and potassium, in the body. This regulation is essential for maintaining proper fluid balance, blood pressure, and cardiovascular function. The most prominent mineralocorticoid is aldosterone.
3. Androgens: Influencers of Male Characteristics
Androgens, like testosterone, are primarily involved in the development and maintenance of male secondary sexual characteristics. They play a role in muscle growth, bone density, and libido. While typically associated with males, androgens are also present in females, although at much lower levels.
4. Estrogens and Progestogens: Key Players in Female Reproduction
Estrogens, such as estradiol, and progestogens, such as progesterone, are crucial for female reproductive health. They are responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in females, the regulation of the menstrual cycle, and the maintenance of pregnancy.
Mineralocorticoids: A Deep Dive into Aldosterone and its Actions
The primary mineralocorticoid in humans is aldosterone. It's produced in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex and exerts its effects primarily in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the kidneys. Here's a detailed look at its mechanism of action:
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS): A Feedback Loop for Blood Pressure Regulation
Aldosterone secretion is tightly regulated by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). This intricate feedback loop responds to changes in blood volume and pressure. When blood pressure drops, the kidneys release renin, an enzyme that initiates a cascade of events leading to the production of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II stimulates the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone.
How Aldosterone Works:
- Sodium Retention: Aldosterone acts on the kidneys to increase the reabsorption of sodium ions (Na+) from the filtrate back into the bloodstream.
- Potassium Excretion: Simultaneously, it promotes the excretion of potassium ions (K+) in the urine.
- Water Balance: The increased sodium reabsorption leads to an increase in water reabsorption, due to osmotic pressure, effectively increasing blood volume and blood pressure.
Clinical Significance of Aldosterone Imbalance
Disruptions in aldosterone production or action can lead to significant health consequences:
- Hyperaldosteronism (Conn's Syndrome): Excessive aldosterone production leads to hypertension (high blood pressure), hypokalemia (low potassium levels), and metabolic alkalosis.
- Hypoaldosteronism (Addison's Disease): Insufficient aldosterone production causes hypotension (low blood pressure), hyperkalemia (high potassium levels), and metabolic acidosis. This is often associated with adrenal insufficiency affecting other steroid hormone production as well.
Differentiating Mineralocorticoids from Other Steroids: Key Distinctions
While aldosterone is the primary mineralocorticoid, other steroid hormones can exhibit some mineralocorticoid activity, albeit often weaker and less specific than aldosterone. Understanding these subtle differences is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment of endocrine disorders.
The Role of 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 (11β-HSD2)
A crucial enzyme, 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (11β-HSD2), plays a key role in preventing glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, from binding to mineralocorticoid receptors. Cortisol, though not a mineralocorticoid, has some affinity for mineralocorticoid receptors. 11β-HSD2 converts cortisol into cortisone, a biologically inactive metabolite, thus preventing it from competing with aldosterone for receptor binding. Deficiency in 11β-HSD2 can lead to apparent mineralocorticoid excess, even without increased aldosterone production.
Other Steroids with Weak Mineralocorticoid Activity
Some steroids, including deoxycorticosterone (DOC) and cortisone, possess some mineralocorticoid activity. However, their effects are significantly weaker compared to aldosterone. This weak activity is generally not clinically significant unless there are underlying conditions that significantly alter the balance of steroid hormones.
Answering the Question: Which of the Following is a Mineralocorticoid?
Based on the information presented, the primary mineralocorticoid is undeniably aldosterone. While other steroids may exhibit some mineralocorticoid activity, aldosterone is the most potent and specific regulator of sodium and potassium balance in the body. The other options, depending on the specific list provided, will generally fall into the categories of glucocorticoids, androgens, or estrogens/progestogens, which have distinct and separate physiological functions.
Conclusion: The Importance of Mineralocorticoid Regulation
Mineralocorticoids, primarily aldosterone, are essential for maintaining electrolyte balance, blood pressure, and overall cardiovascular health. The complex interplay of the RAAS and enzymes like 11β-HSD2 ensures tight regulation of aldosterone levels. Disruptions in this delicate balance can lead to serious health consequences. Understanding the function and distinction of mineralocorticoids from other steroid hormones is critical for medical professionals in diagnosing and treating endocrine disorders and managing cardiovascular health. Further research continues to unravel the complexities of the steroid hormone system and its intricate role in human physiology. Continued awareness of these hormones and their intricate relationship with other body systems is critical for promoting health and wellbeing.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not An Intrusive Igneous Body
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Extensive Property Of Matter
Mar 26, 2025
-
Mating Animals Of Different Breeds Is Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Resting Phase Of The Cell Cycle Is Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Surveyor Is Using A Magnetic Compass 6 1
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Mineralocorticoid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
