Why Europe Is Called The Peninsula Of Peninsulas
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
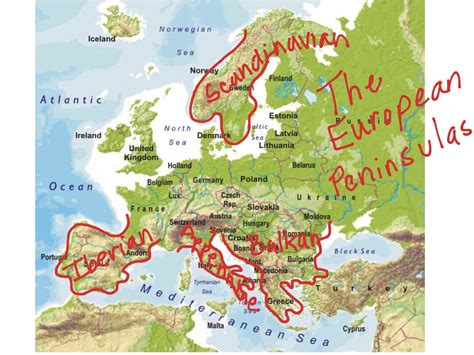
Table of Contents
- Why Europe Is Called The Peninsula Of Peninsulas
- Table of Contents
- Europe: The Peninsula of Peninsulas – A Geographical Deep Dive
- The Defining Feature: A Highly Indented Coastline
- Major Peninsulas: The Building Blocks of Europe's Geography
- Minor Peninsulas: Adding Complexity to the Landscape
- Geological Processes: Shaping the Peninsula of Peninsulas
- Tectonic Plate Movement: The Foundation of Europe's Structure
- Glacial Activity: Carving the Coastline
- Erosion and Sedimentation: Sculpting the Details
- The Impact on Human History and Culture
- Isolation and Interaction: A Balancing Act
- Seafaring and Trade: A Maritime Legacy
- Defense and Conquest: Geographical Advantages and Disadvantages
- Conclusion: A Continent Defined by its Shape
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Europe: The Peninsula of Peninsulas – A Geographical Deep Dive
Europe, a continent steeped in history, culture, and vibrant landscapes, is often described as the "peninsula of peninsulas." This intriguing moniker isn't just a poetic flourish; it's a geographically accurate reflection of the continent's unique morphology. Understanding why Europe earns this title requires delving into its complex coastline, its geological formations, and the intricate interplay of land and sea that shaped its history and identity.
The Defining Feature: A Highly Indented Coastline
Europe's coastline is exceptionally complex, far more so than many other continents. This high degree of indentation is the primary reason for its "peninsula of peninsulas" designation. Instead of a relatively straight or gently curved shoreline, Europe is characterized by numerous projections of land into the sea – peninsulas – each with its own distinct characteristics and geological history. These peninsulas, in turn, often feature smaller peninsulas, creating a fractal-like pattern of landmasses extending into the surrounding waters.
Major Peninsulas: The Building Blocks of Europe's Geography
Several major peninsulas form the backbone of Europe's geography, each contributing significantly to the continent's diverse landscapes and cultures. These include:
-
Iberian Peninsula: Home to Spain and Portugal, this large peninsula is separated from the rest of Europe by the Pyrenees Mountains. Its varied geography encompasses everything from sun-drenched Mediterranean coasts to rugged mountain ranges. The Iberian Peninsula itself features smaller peninsulas, such as Galicia in the northwest.
-
Italian Peninsula: Boot-shaped and easily recognizable, the Italian Peninsula stretches into the Mediterranean Sea. Its central spine is dominated by the Apennine Mountains, influencing the climate and shaping the distribution of various landscapes. The peninsula features its own smaller peninsulas and coastal projections.
-
Balkan Peninsula: A complex and historically significant region, the Balkan Peninsula extends south into the Mediterranean and Aegean Seas. This area is characterized by its rugged mountains, its diverse ethnicities and cultures, and its historically significant role in the interaction between Europe and Asia.
-
Scandinavian Peninsula: Shared by Norway and Sweden, this vast peninsula stretches northwards, encompassing fjords, mountains, and vast forests. Its unique geography is shaped by glaciers and the dramatic forces of the Ice Age. The Scandinavian Peninsula itself exhibits a number of smaller peninsulas and coastal inlets.
-
Jutland Peninsula: Located in northern Europe, the Jutland Peninsula is a relatively flat region shared by Denmark and Germany. Its unique geography impacted the historical development of the region, influencing trade routes and settlement patterns.
Minor Peninsulas: Adding Complexity to the Landscape
Beyond the major peninsulas, a multitude of smaller peninsulas contribute to Europe's intricate coastline. These include the Crimean Peninsula, the Peloponnese Peninsula in Greece, the Bretagne Peninsula in France, and numerous others along the coasts of the Baltic, North, and Mediterranean Seas. These smaller projections of land, although less prominent than the larger peninsulas, further contribute to the fragmented and highly indented nature of Europe's coastline.
Geological Processes: Shaping the Peninsula of Peninsulas
The formation of Europe's peninsulas is a complex geological story spanning millions of years. The interplay of tectonic plate movement, volcanic activity, erosion, and glacial action has shaped the continent's unique morphology.
Tectonic Plate Movement: The Foundation of Europe's Structure
The movement of tectonic plates has been instrumental in creating Europe's mountainous regions and defining the shape of its peninsulas. The collision of the Eurasian and African plates, for example, contributed to the uplift of the Alps and the Pyrenees Mountains, directly influencing the formation of the Iberian and Italian peninsulas. The ongoing geological activity in this region also contributed to the formation of numerous islands and volcanic features.
Glacial Activity: Carving the Coastline
The Ice Ages profoundly shaped Europe's landscape, particularly its coastline. Glacial activity carved out deep fjords and valleys, adding to the complexity of the coastline, especially in Scandinavia and the British Isles. The advance and retreat of glaciers also contributed to the formation of various landforms, such as moraines and eskers, which further contribute to the intricate detail of Europe's coastal geography.
Erosion and Sedimentation: Sculpting the Details
Erosion and sedimentation processes have played a continuous role in shaping Europe's peninsulas. The action of waves, rivers, and wind has sculpted the coastlines, creating cliffs, beaches, and estuaries. Sediment deposited by rivers has also contributed to the formation of plains and deltas, further influencing the shape and character of the peninsulas.
The Impact on Human History and Culture
The "peninsula of peninsulas" nature of Europe has profoundly impacted the course of human history and the development of its diverse cultures.
Isolation and Interaction: A Balancing Act
The peninsular nature of Europe led to both isolation and interaction among different populations. The mountainous regions and the seas separating the various peninsulas created natural barriers, fostering the development of distinct cultures and languages. However, the same seas also provided pathways for trade and cultural exchange, leading to a complex interplay of isolation and connection.
Seafaring and Trade: A Maritime Legacy
Europe's extensive coastline made seafaring a significant part of its history. The numerous ports and harbors along the peninsulas facilitated trade and exploration, shaping the economic development and cultural exchange across the continent. The Mediterranean Sea, in particular, played a crucial role in connecting different parts of Europe and fostering the development of powerful maritime empires.
Defense and Conquest: Geographical Advantages and Disadvantages
The peninsular structure of Europe also played a significant role in matters of defense and conquest. The natural barriers created by seas and mountains provided defense against invasion, but also facilitated the formation of isolated kingdoms and city-states. The strategic importance of the various peninsulas, and the control over coastal regions, became crucial factors in the conflicts that shaped European history.
Conclusion: A Continent Defined by its Shape
Europe's description as the "peninsula of peninsulas" is more than just a catchy phrase; it's a concise yet accurate summary of the continent's unique geographic features. The intricate coastline, shaped by millions of years of geological processes, has profoundly impacted the development of European cultures, economies, and political landscapes. Understanding this unique geography is essential for comprehending Europe's rich history and its place in the world. The numerous peninsulas, large and small, have shaped its destiny, contributing to its intricate tapestry of nations, languages, and cultural traditions. The complex interplay of land and sea has not only defined Europe’s physical characteristics but has also profoundly influenced its historical, cultural, and even political development. Therefore, the phrase "peninsula of peninsulas" is not merely a geographical description; it’s a powerful metaphor encapsulating the very essence of this remarkable continent.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 4 Percent Of 50
Mar 26, 2025
-
Difference Between A Democracy And A Dictatorship
Mar 26, 2025
-
In Dna Adenine Always Pairs With
Mar 26, 2025
-
Net Ionic Equation For Hcl Naoh
Mar 26, 2025
-
Bundles Of Axons Within The Central Nervous System Are Called
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Europe Is Called The Peninsula Of Peninsulas . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
