What Is The Molecular Mass Of Calcium Carbonate
News Leon
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
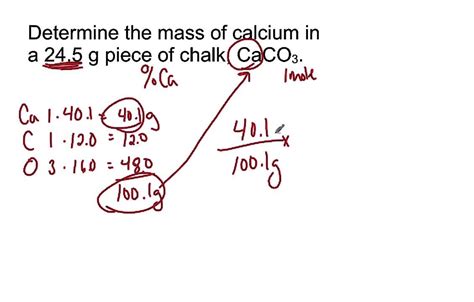
Table of Contents
What is the Molecular Mass of Calcium Carbonate? A Deep Dive into Atomic Weights and Chemical Formulas
Calcium carbonate, a ubiquitous compound found in chalk, limestone, marble, and even seashells, plays a crucial role in various geological and biological processes. Understanding its molecular mass is fundamental to numerous scientific calculations and applications, from stoichiometry in chemistry to geological estimations of mineral deposits. This article will comprehensively explore the molecular mass of calcium carbonate, delving into the atomic weights of its constituent elements and explaining the methods used to calculate it. We'll also touch upon its practical significance across different scientific fields.
Understanding Atomic Weights and the Periodic Table
Before we calculate the molecular mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), it's vital to grasp the concept of atomic weight. The atomic weight of an element, also known as its standard atomic weight, is the average mass of atoms of an element, taking into account the relative abundance of its isotopes. These values are meticulously determined and are found on the periodic table of elements – a cornerstone of chemistry.
The periodic table provides crucial information, including:
- Element Symbol: A shorthand representation of the element (e.g., Ca for calcium, C for carbon, O for oxygen).
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This uniquely identifies the element.
- Atomic Weight (or Atomic Mass): The average mass of an atom of the element, expressed in atomic mass units (amu). One amu is approximately the mass of a proton or a neutron.
For our calculation, we need the atomic weights of calcium (Ca), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). These values are readily available from any standard periodic table. Note that these values might slightly vary depending on the source and the level of precision, but the differences are typically negligible for most calculations.
Calculating the Molecular Mass of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO₃)
Calcium carbonate's chemical formula, CaCO₃, tells us that one molecule of calcium carbonate consists of:
- One calcium atom (Ca): Its atomic weight is approximately 40.08 amu.
- One carbon atom (C): Its atomic weight is approximately 12.01 amu.
- Three oxygen atoms (O): Its atomic weight is approximately 16.00 amu. Since there are three oxygen atoms, their total contribution to the molecular mass is 3 * 16.00 amu = 48.00 amu.
To calculate the molecular mass of CaCO₃, we simply sum the atomic weights of its constituent atoms:
Molecular Mass (CaCO₃) = Atomic weight (Ca) + Atomic weight (C) + 3 * Atomic weight (O)
Molecular Mass (CaCO₃) ≈ 40.08 amu + 12.01 amu + 48.00 amu ≈ 100.09 amu
Therefore, the molecular mass of calcium carbonate is approximately 100.09 atomic mass units (amu). This value is widely accepted and used in various chemical calculations. It's important to note that this is an average molecular mass due to the presence of isotopes.
The Significance of Molecular Mass in Chemistry and Beyond
The molecular mass of calcium carbonate is not just a theoretical value; it holds significant practical implications across multiple scientific disciplines:
1. Stoichiometric Calculations:
In chemistry, stoichiometry deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. Knowing the molecular mass of CaCO₃ is crucial for performing stoichiometric calculations, such as determining the amount of calcium carbonate needed to react completely with a specific amount of another substance, or predicting the yield of a reaction.
2. Determining Concentrations:
In analytical chemistry, the molecular mass is used to determine the concentration of calcium carbonate in a solution. For instance, if you know the mass of CaCO₃ dissolved in a known volume of solution, you can calculate its molar concentration (moles per liter).
3. Geology and Mineralogy:
Geologists and mineralogists use the molecular mass of CaCO₃ to estimate the amount of calcium carbonate present in rocks and minerals. This information is essential for understanding the composition of geological formations and their formation processes. For example, calculating the percentage of CaCO₃ in limestone samples helps in assessing their suitability for various industrial applications.
4. Environmental Science:
In environmental science, understanding the molecular mass of CaCO₃ is important in studying the calcium carbonate cycle in the environment, including its role in ocean acidification and carbon sequestration. Calculations involving the mass of CaCO₃ deposited or dissolved in various ecosystems are pivotal for assessing environmental changes.
5. Material Science and Engineering:
Calcium carbonate is used in various industrial applications, such as in the production of cement, paper, and plastics. Knowledge of its molecular mass is essential for controlling the properties of these materials and optimizing their production processes.
6. Biochemistry and Physiology:
In biological systems, calcium carbonate plays crucial roles, such as in the formation of bones and shells. Understanding its molecular mass is essential for studying these biological processes and the mechanisms involved.
Further Considerations: Isotopes and Isotopic Abundance
The molecular mass we calculated (100.09 amu) is an average molecular mass. This is because the elements calcium, carbon, and oxygen each exist as a mixture of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This leads to slightly different masses for each isotope. The atomic weights given on the periodic table reflect the weighted average of these isotopes, based on their natural abundance. For extremely precise calculations, considering the individual isotopic masses and their abundances might be necessary, but for most applications, the average molecular mass is sufficient.
Conclusion: The Importance of Precision and Context
The molecular mass of calcium carbonate, approximately 100.09 amu, is a fundamental piece of information with far-reaching implications in various scientific disciplines. Its accurate calculation, based on the atomic weights of its constituent elements, is essential for numerous applications, from stoichiometric calculations and concentration determinations to geological estimations and environmental assessments. While the average molecular mass is sufficient for most purposes, understanding the nuances of isotopic variations adds a deeper level of precision for specialized applications. The accurate use of this value underscores the importance of meticulous calculations and careful consideration of the context within which it is applied. This foundational understanding enables deeper insights and more accurate predictions across a wide array of scientific fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Pairs Of Ions Represent Isoelectronic Species
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Calculate E Not Cell
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Part Of The Ear Looks Like A Snail Shell
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Agno3
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Of 68 Is 17
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molecular Mass Of Calcium Carbonate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
