What Is A Result Of Drinking Too Much Alcohol Milady
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
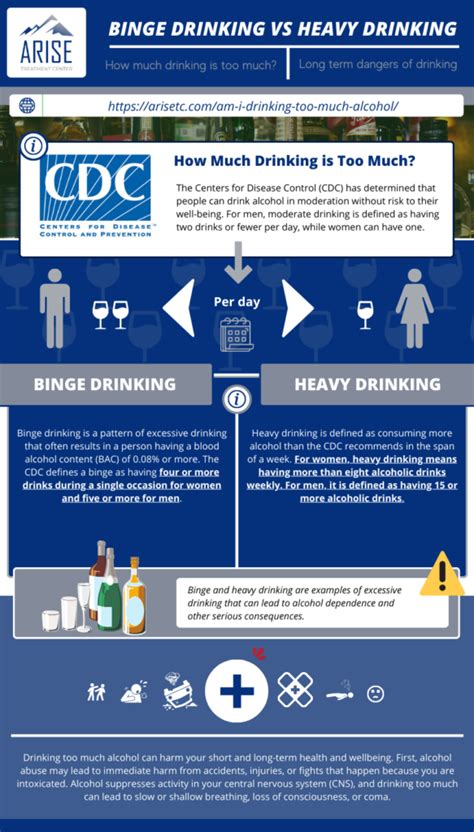
Table of Contents
The Devastating Consequences of Excessive Alcohol Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide
Excessive alcohol consumption, often termed as alcohol abuse or alcohol dependence, carries a multitude of serious health consequences affecting nearly every system in the body. This article will delve into the devastating effects of drinking too much alcohol, exploring the short-term and long-term ramifications across various aspects of physical and mental well-being. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed choices and promoting a healthy lifestyle.
Short-Term Effects: Immediate Dangers of Excessive Drinking
Even a single episode of binge drinking – defined as consuming a large amount of alcohol in a short period – can lead to immediate and potentially life-threatening consequences. These short-term effects can vary depending on factors such as the amount consumed, the individual's tolerance, and their overall health.
Immediate Physical Effects:
- Intoxication: This is the most common short-term effect, characterized by impaired coordination, slurred speech, dizziness, and slowed reaction times. Severe intoxication can lead to unconsciousness, vomiting, and aspiration pneumonia (inhaling vomit into the lungs).
- Dehydration: Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it increases urine production. This leads to dehydration, causing headaches, fatigue, and dry mouth. Severe dehydration can be dangerous, especially in hot environments.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These are common side effects, often triggered by the irritation of alcohol on the stomach lining. Severe vomiting can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
- Disrupted Sleep: While alcohol may initially induce sleep, it significantly disrupts sleep patterns, leading to poor quality sleep and daytime fatigue.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: Impaired judgment, coordination, and reaction time dramatically increase the risk of accidents, including falls, car crashes, and injuries.
Immediate Mental and Behavioral Effects:
- Impaired Judgment: Alcohol significantly impairs judgment, leading to risky behaviors and poor decision-making. This can result in regrettable actions and dangerous situations.
- Aggression and Violence: Alcohol can lower inhibitions and increase aggression, contributing to domestic violence, assaults, and other violent acts.
- Mood Swings: Alcohol can lead to unpredictable mood swings, ranging from euphoria to anger and depression.
- Memory Impairment (Blackouts): Excessive alcohol consumption can cause temporary memory loss, known as a blackout. Individuals may not remember events that occurred while intoxicated.
Long-Term Effects: The Crushing Weight of Chronic Alcohol Abuse
Chronic alcohol abuse – the prolonged and excessive consumption of alcohol – leads to a cascade of devastating long-term consequences affecting nearly every organ system. These effects are often cumulative and irreversible.
Cardiovascular System:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Chronic alcohol use significantly increases the risk of hypertension, a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- Heart Disease: Alcohol abuse damages the heart muscle, increasing the risk of cardiomyopathy (weakening of the heart muscle), heart failure, and irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias).
- Stroke: Alcohol can increase the risk of stroke by raising blood pressure and contributing to blood clot formation.
Liver Disease:
- Fatty Liver Disease: Excessive alcohol consumption leads to the accumulation of fat in the liver, causing inflammation and damage.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: This is an inflammation of the liver caused by alcohol, leading to liver cell damage and scarring.
- Cirrhosis: This is the late-stage scarring of the liver, resulting from chronic alcohol abuse. Cirrhosis is irreversible and can lead to liver failure, requiring a liver transplant.
Gastrointestinal System:
- Gastritis: Alcohol irritates the stomach lining, causing inflammation and gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining).
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, which can lead to severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Severe pancreatitis can be life-threatening.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Alcohol weakens the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus, causing heartburn and damage to the esophagus.
- Increased Risk of Certain Cancers: Alcohol significantly increases the risk of several types of cancer, including mouth, throat, esophageal, liver, breast, and colorectal cancers.
Nervous System:
- Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome: This is a severe neurological disorder caused by thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency, often associated with chronic alcohol abuse. It can lead to confusion, memory loss, and paralysis of eye muscles.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Damage to the nerves in the arms and legs, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Seizures: Excessive alcohol consumption can trigger seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of epilepsy or alcohol withdrawal.
Mental Health:
- Depression and Anxiety: Alcohol abuse is strongly linked to an increased risk of depression and anxiety disorders. Alcohol may initially provide temporary relief from these conditions, but long-term use exacerbates them.
- Alcohol Dependence (Alcoholism): Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to alcohol dependence, a chronic relapsing brain disease characterized by compulsive alcohol seeking and use, despite harmful consequences.
- Increased Risk of Suicide: Individuals with alcohol dependence have a significantly higher risk of suicide.
Other Effects:
- Weakened Immune System: Alcohol weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Alcohol interferes with the absorption and utilization of essential nutrients, leading to various nutritional deficiencies.
- Reproductive Issues: In women, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to menstrual irregularities, infertility, and an increased risk of miscarriage. In men, it can lead to decreased testosterone levels and erectile dysfunction.
- Dental Problems: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to gum disease and tooth decay.
- Skin Problems: Alcohol can dehydrate the skin, leading to dryness, wrinkles, and other skin problems.
Alcohol Withdrawal: A Dangerous Process
Stopping alcohol consumption abruptly after prolonged heavy use can trigger a dangerous condition known as alcohol withdrawal. Symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening and include:
- Anxiety and Irritability: These are common early symptoms.
- Tremors (Shaking): These are often noticeable in the hands.
- Sweating and Increased Heart Rate: These are signs of the body's physiological response to alcohol withdrawal.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia and vivid nightmares are common.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These can be severe.
- Seizures: In severe cases, alcohol withdrawal can lead to seizures, which are a medical emergency.
- Delirium Tremens (DTs): This is a severe and life-threatening complication of alcohol withdrawal, characterized by confusion, hallucinations, and seizures. DTs require immediate medical attention.
Seeking Help and Support
If you or someone you know is struggling with excessive alcohol consumption, it's crucial to seek help. There are many resources available to support individuals in overcoming alcohol dependence, including:
- Medical Professionals: Doctors and other healthcare professionals can provide medical assessments, manage withdrawal symptoms, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
- Therapists and Counselors: Therapy can help individuals address the underlying psychological and emotional issues that contribute to alcohol abuse.
- Support Groups: Organizations like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and other support groups offer peer support and a sense of community.
- Rehabilitation Centers: Inpatient rehabilitation programs provide intensive treatment in a structured environment.
It's important to remember that recovery from alcohol dependence is possible with proper treatment and support. Seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices about Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption carries severe and potentially fatal consequences. Understanding the short-term and long-term effects is crucial for making informed choices about alcohol consumption. If you are concerned about your alcohol use, seeking help from a healthcare professional or support group is essential. Remember, prioritizing your health and well-being is paramount. Choosing a healthy lifestyle that includes responsible alcohol consumption, or abstinence altogether, significantly reduces the risk of these devastating effects. Prioritizing your health and seeking help when needed are essential steps towards a healthier and happier future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Homogeneous Mixture Of Two Or More Substances
Mar 26, 2025
-
Reaction Of Ethanol And Acetic Acid
Mar 26, 2025
-
Proverbs Of The Day With Meaning
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Sodium
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Urinary Bladder Is Composed Of What Epithelium
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Result Of Drinking Too Much Alcohol Milady . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
