The Urinary Bladder Is Composed Of What Epithelium
News Leon
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
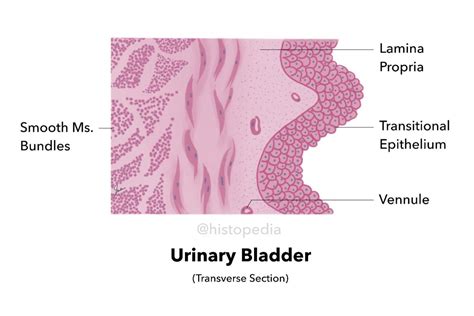
Table of Contents
The Urinary Bladder: A Deep Dive into its Epithelial Composition
The urinary bladder, a crucial component of the urinary system, serves as a temporary reservoir for urine produced by the kidneys before its excretion from the body. Understanding its intricate structure, particularly the type of epithelium that lines it, is vital for comprehending its function and the various pathological conditions that can affect it. This article delves deep into the epithelial composition of the urinary bladder, exploring its unique characteristics, adaptations, and significance in maintaining urinary tract health.
The Transitional Epithelium: A Unique Adaptation
The urinary bladder's lining is not composed of a simple, uniform epithelium like many other organs. Instead, it's characterized by a remarkable transitional epithelium, also known as urothelium. This specialized epithelium is uniquely adapted to withstand the significant changes in volume and pressure that the bladder undergoes during the filling and emptying cycle. Unlike simple squamous or columnar epithelia, transitional epithelium exhibits remarkable plasticity, allowing it to stretch considerably without compromising its integrity.
Characteristics of Transitional Epithelium
Several key characteristics distinguish transitional epithelium:
-
Stratified Structure: The urothelium is a stratified epithelium, meaning it consists of multiple layers of cells. This multi-layered structure contributes to its strength and resilience. The number of layers varies depending on the bladder's state of distention.
-
Cell Shape Variability: The defining feature of transitional epithelium is the variability in cell shape depending on the bladder's filling status. When the bladder is empty, the cells appear dome-shaped or cuboidal, forming many layers. As the bladder fills and expands, the cells flatten and become thinner, reducing the number of apparent layers. This remarkable adaptability allows for efficient storage of urine without compromising the epithelial barrier.
-
Umbrella Cells: The apical layer of the urothelium is composed of large, flattened cells known as umbrella cells. These specialized cells are crucial for the bladder's barrier function. Their apical surface is covered with asymmetric unit membranes (AUMs), also known as plaques, which are unique structures that prevent the passage of water and solutes. These AUMs contain specialized proteins, such as uroplakin, that contribute to the impermeability of the urothelium. The tight junctions between umbrella cells further enhance the barrier properties.
-
Underlying Cell Layers: Beneath the umbrella cells lie several layers of intermediate and basal cells. These cells provide structural support and contribute to the regeneration and maintenance of the urothelium. The basal cells are actively involved in cell division, replenishing the upper layers.
The Role of Uroplakin in Bladder Function
Uroplakin is a family of transmembrane proteins specifically expressed in umbrella cells. These proteins are essential for the formation and maintenance of the AUMs, which are crucial for the bladder's barrier function. Uroplakin plays a critical role in preventing the back-diffusion of urea and other substances from urine into the underlying tissues, maintaining osmotic balance and preventing tissue damage. Mutations in uroplakin genes have been implicated in various bladder pathologies, highlighting its importance.
Beyond the Barrier: Other Functions of Urothelium
While the barrier function is paramount, the urothelium's role extends beyond simple impermeability. It also contributes to:
-
Protection against Urine Components: Urine contains various potentially harmful substances, including toxins and irritants. The urothelium acts as a protective barrier, preventing these substances from damaging the underlying tissues.
-
Sensory Perception: The urothelium contains sensory nerve endings that detect changes in bladder volume and pressure. This sensory information is transmitted to the central nervous system, triggering the urge to urinate.
-
Immune Modulation: The urothelium interacts with the immune system, playing a role in host defense against pathogens. It expresses various immune-related molecules that can modulate the immune response and prevent infection.
Clinical Significance of Urothelial Dysfunction
Dysfunction of the transitional epithelium can lead to various clinical conditions, including:
-
Bladder Infections (UTIs): Compromised barrier function of the urothelium can increase susceptibility to urinary tract infections. Bacteria can penetrate the urothelium more easily, leading to inflammation and infection.
-
Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome (IC/BPS): This chronic bladder condition is characterized by persistent pelvic pain and urinary urgency and frequency. While the exact etiology is unknown, some research suggests that alterations in urothelial function play a significant role.
-
Bladder Cancer: The majority of bladder cancers originate from the urothelium. Exposure to carcinogens, such as those found in cigarette smoke, can damage the urothelium, increasing the risk of cancer development.
-
Neurogenic Bladder: Conditions affecting the nervous system can disrupt the normal function of the bladder, leading to neurogenic bladder. This can result in urinary retention, incontinence, or both.
Maintaining Urinary Bladder Health
Maintaining the health of the urinary bladder and its urothelium is vital for overall urinary tract health. Several lifestyle factors can contribute to maintaining bladder health:
-
Hydration: Adequate fluid intake helps to flush out bacteria and other irritants from the urinary tract.
-
Diet: A balanced diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, can contribute to overall health and may reduce the risk of bladder infections.
-
Hygiene: Proper hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after urination, can help to prevent the spread of bacteria to the urinary tract.
-
Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a significant risk factor for bladder cancer. Quitting smoking significantly reduces this risk.
-
Regular Urination: Avoiding prolonged urine retention can reduce the risk of bladder infections and stones.
Advanced Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of the urothelium and its role in urinary tract health and disease. Areas of active investigation include:
-
Development of novel therapies for bladder diseases: Research is focused on developing new treatments for conditions such as IC/BPS and bladder cancer that target the urothelium.
-
Understanding the mechanisms of urothelial regeneration: Research is exploring the process of urothelial regeneration to develop strategies for repairing damaged urothelium.
-
Identifying biomarkers for bladder cancer: Researchers are searching for biomarkers in urine or urothelial cells that can help in early detection and diagnosis of bladder cancer.
-
Investigating the role of the urothelium in the response to various drugs and therapies: Research is exploring how the urothelium affects the efficacy and toxicity of various medications.
Conclusion
The urinary bladder's transitional epithelium, or urothelium, is a remarkable and complex structure uniquely adapted to its demanding function. Its intricate composition and specialized cells ensure the bladder's efficient storage of urine while protecting the underlying tissues. Understanding the structure, function, and clinical significance of the urothelium is crucial for advancing the diagnosis and treatment of various bladder diseases. Continued research into the intricacies of this specialized epithelium promises to enhance our understanding of urinary tract health and lead to the development of more effective therapies for bladder conditions. The urothelium’s critical role in maintaining urinary health underscores the need for continued research and focused efforts on preventative measures to ensure optimal bladder function throughout life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Not True About The Cell Membrane
Mar 29, 2025
-
Example Of Request Letter For Permission
Mar 29, 2025
-
Largest Foramen In The Human Skeleton
Mar 29, 2025
-
In Humans The Diploid Number Of Chromosomes Is
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Nephrons Are Contained In Each Kidney
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Urinary Bladder Is Composed Of What Epithelium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
