The Angle Of Elevation To The Top Of A Building
News Leon
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
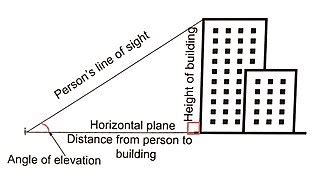
Table of Contents
The Angle of Elevation to the Top of a Building: A Comprehensive Guide
The angle of elevation is a fundamental concept in trigonometry with practical applications in various fields, from surveying and construction to navigation and astronomy. Understanding how to calculate and apply the angle of elevation is crucial for solving real-world problems, especially those involving heights and distances. This article provides a detailed explanation of the angle of elevation, focusing specifically on its application in determining the height of a building. We'll explore different methods, including the use of trigonometry, practical considerations, and potential sources of error.
Understanding the Angle of Elevation
The angle of elevation is the angle formed between the horizontal line of sight and the line of sight to an object above the horizontal. Imagine you're standing on the ground looking up at the top of a building. The angle you make by tilting your head upwards is the angle of elevation. This angle is always measured from the horizontal upwards. It's crucial to distinguish this from the angle of depression, which is the angle measured downwards from the horizontal.
Key Terminology:
- Angle of Elevation: The acute angle formed between the horizontal and the line of sight to an object above the horizontal.
- Horizontal Line: A straight line parallel to the ground.
- Line of Sight: The imaginary line connecting the observer's eye to the object being viewed.
- Height: The vertical distance from the ground to the top of the object.
- Distance: The horizontal distance from the observer to the base of the object.
Calculating the Angle of Elevation and Building Height Using Trigonometry
Trigonometry provides the mathematical tools for calculating the angle of elevation and the height of a building given certain measurements. The key trigonometric functions involved are:
- Tangent (tan): The tangent of an angle is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side in a right-angled triangle. In the context of the angle of elevation to a building, the opposite side is the height of the building, and the adjacent side is the horizontal distance from the observer to the building.
Formula:
tan(angle of elevation) = height / distance
This formula allows us to calculate any of the three variables if we know the other two.
Example Calculation:
Let's say you are standing 50 meters away from a building. Using a clinometer or similar device, you measure the angle of elevation to the top of the building to be 30 degrees. To find the height (h) of the building, we can use the following calculation:
tan(30°) = h / 50
h = 50 * tan(30°)
Using a calculator, we find that tan(30°) ≈ 0.577. Therefore:
h = 50 * 0.577 ≈ 28.85 meters
Therefore, the height of the building is approximately 28.85 meters.
Different Methods for Measuring the Angle of Elevation
Several methods can be employed to measure the angle of elevation, each with its own level of accuracy and practicality:
1. Clinometer: A clinometer is a simple, handheld instrument specifically designed for measuring angles of elevation and depression. It typically uses a protractor and a weighted plumb bob to determine the angle. Clinometers are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them suitable for many applications.
2. Theodolite: A theodolite is a more sophisticated surveying instrument that provides highly accurate measurements of angles of elevation and azimuth (horizontal angle). Theodolites are commonly used in professional surveying and construction projects where precision is paramount.
3. Smartphone Apps: Many smartphone apps utilize the phone's built-in accelerometer and gyroscope to measure angles of elevation. While convenient, the accuracy of these apps can vary depending on the app's quality and the phone's calibration.
Practical Considerations and Potential Sources of Error
While the trigonometric calculations provide a theoretical basis for determining the height of a building, several factors can influence the accuracy of the measurements in real-world scenarios:
-
Measurement Errors: Inaccurate measurements of the distance or angle of elevation will directly affect the calculated height. Using precise measuring tools and techniques is crucial to minimize these errors.
-
Observer's Height: The calculation assumes the observer's eye is at ground level. If the observer is standing on an elevated platform, the observer's height must be added to the calculated height of the building.
-
Curvature of the Earth: Over long distances, the curvature of the Earth can affect the accuracy of the measurements. This effect is typically negligible for shorter distances.
-
Atmospheric Refraction: The bending of light as it passes through the atmosphere can slightly alter the measured angle of elevation. This effect is more pronounced over longer distances and in varying atmospheric conditions.
Advanced Applications and Extensions
The principles of angle of elevation have broad applications beyond simply measuring building heights:
-
Surveying: Surveyors use angle of elevation measurements to create topographic maps and determine the elevation of various points in the landscape.
-
Navigation: Pilots and sailors use angle of elevation measurements to determine their altitude and distance to landmarks.
-
Astronomy: Astronomers use angle of elevation measurements to track the positions of celestial objects.
-
Construction: Engineers and architects use angle of elevation measurements to ensure the proper placement and alignment of structures.
-
Forensics: Angle of elevation calculations can assist in reconstructing accident scenes or crime scenes.
Conclusion: Mastering the Angle of Elevation
The angle of elevation is a powerful tool for determining heights and distances. Understanding the underlying trigonometric principles, employing accurate measurement techniques, and being aware of potential sources of error are crucial for obtaining reliable results. Whether you're a student learning trigonometry, a surveyor mapping terrain, or an architect designing a building, mastering the angle of elevation ensures precision and accuracy in your work. By considering the practical aspects and employing appropriate instruments and methods, you can confidently tackle real-world problems involving height and distance calculations, making this fundamental concept a valuable asset across various disciplines. The more experience you gain, the more proficient you'll become in accurately calculating and applying the angle of elevation to various scenarios. Remember that practice is key to mastering this essential concept in trigonometry and its practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Does Count Do In Python
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Represents Beta Decay
Mar 30, 2025
-
Can Ammonia Be Decomposed By A Chemical Change
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Measure Of Its Complement
Mar 30, 2025
-
An Object Of Mass M Is Thrown Vertically Upward
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Angle Of Elevation To The Top Of A Building . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
