Charge Of Alpha Particle In Coulombs
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
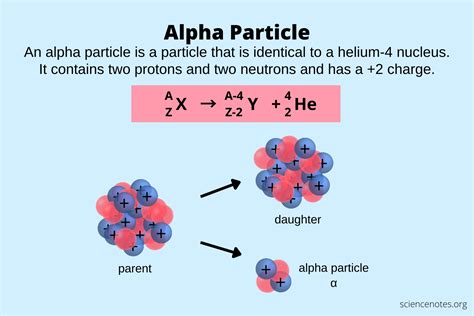
Table of Contents
- Charge Of Alpha Particle In Coulombs
- Table of Contents
- The Charge of an Alpha Particle in Coulombs: A Deep Dive
- Understanding the Alpha Particle
- Key Properties of Alpha Particles:
- Calculating the Charge in Coulombs
- The Significance of the Alpha Particle's Charge
- Ionization and its Consequences:
- Applications Leveraging the Alpha Particle's Charge:
- Comparing Alpha Particle Charge to Other Subatomic Particles
- The Role of Charge in Alpha Decay
- Safety Considerations and Radiation Protection
- Further Exploration: Advanced Concepts
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Charge of an Alpha Particle in Coulombs: A Deep Dive
The alpha particle, a fundamental component in the field of nuclear physics, holds a significant place in our understanding of atomic structure and radioactive decay. This article delves deep into the specifics of the alpha particle's charge, expressed in Coulombs, exploring its origins, implications, and applications in various scientific disciplines. We'll also touch upon related concepts to build a comprehensive understanding of this crucial subatomic particle.
Understanding the Alpha Particle
Before delving into the charge itself, let's establish a foundational understanding of what an alpha particle actually is. An alpha particle is essentially a helium nucleus, consisting of two protons and two neutrons tightly bound together. Its relatively large mass and positive charge are key characteristics that distinguish it from other forms of radiation. This tightly bound structure makes alpha particles relatively stable and predictable in their behavior.
Key Properties of Alpha Particles:
- Composition: 2 protons and 2 neutrons
- Charge: +2e (where 'e' represents the elementary charge)
- Mass: Approximately 4 atomic mass units (amu)
- Penetration Power: Low; easily stopped by a sheet of paper or a few centimeters of air.
- Ionizing Power: High; readily interacts with matter, causing ionization.
Calculating the Charge in Coulombs
The charge of an alpha particle is +2e, where 'e' represents the elementary charge, the fundamental unit of electric charge. The elementary charge has a value of approximately 1.602 x 10⁻¹⁹ Coulombs. Therefore, to calculate the charge of an alpha particle in Coulombs, we simply multiply the elementary charge by 2:
Charge of alpha particle = 2 * e = 2 * (1.602 x 10⁻¹⁹ C) = 3.204 x 10⁻¹⁹ Coulombs
This seemingly small value has profound implications in various scientific contexts, from nuclear reactions to medical applications.
The Significance of the Alpha Particle's Charge
The positive charge of the alpha particle is pivotal to its interactions with matter. Its relatively large charge compared to other types of radiation, such as beta particles (electrons), contributes to its high ionizing power.
Ionization and its Consequences:
As an alpha particle travels through a medium (like air or tissue), its positive charge attracts electrons from nearby atoms. This process, known as ionization, creates ions – charged atoms – along the alpha particle's path. These ions can disrupt chemical bonds, causing damage to biological molecules and potentially leading to cellular damage. This high ionizing power is exploited in certain medical treatments, but it also presents a significant risk in terms of radiation exposure.
Applications Leveraging the Alpha Particle's Charge:
The distinctive properties of alpha particles, particularly their charge and ionizing power, find applications in several fields:
- Smoke detectors: Alpha particles ionize air, creating a small electric current. Smoke particles disrupt this current, triggering the alarm.
- Radioactive Dating: The decay of certain radioactive isotopes, which often involves alpha particle emission, is utilized to determine the age of materials such as rocks and artifacts. The rate of alpha decay is predictable and constant.
- Radiation Therapy (Targeted Alpha Therapy): Certain radioactive isotopes that emit alpha particles are used in targeted cancer therapy. The high ionizing power of alpha particles, concentrated over a short range, can effectively destroy cancerous cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Nuclear Physics Research: Studying alpha particle interactions and decay helps physicists understand nuclear forces and the structure of atomic nuclei. Alpha decay is a crucial aspect of nuclear stability and radioactivity.
Comparing Alpha Particle Charge to Other Subatomic Particles
To gain a better understanding of the alpha particle's charge, let's compare it to other subatomic particles:
| Particle | Charge (Coulombs) | Mass (amu) |
|---|---|---|
| Proton | +1.602 x 10⁻¹⁹ | ~1 |
| Neutron | 0 | ~1 |
| Electron | -1.602 x 10⁻¹⁹ | ~0 |
| Alpha Particle | +3.204 x 10⁻¹⁹ | ~4 |
The table highlights that the alpha particle's charge is twice that of a proton, making it a highly charged particle for its size. Its relatively large mass also contributes to its unique behavior and interaction with matter.
The Role of Charge in Alpha Decay
Alpha decay is a type of radioactive decay where an unstable atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle. This process is governed by the strong nuclear force and the electromagnetic force. The positive charge of the alpha particle plays a crucial role in the decay process. The repulsion between the positively charged alpha particle and the remaining nucleus provides the energy needed for the alpha particle to overcome the strong nuclear force and escape the nucleus. The energy released in this process is characteristic of the decaying isotope and is a key factor in determining the stability of various elements.
Safety Considerations and Radiation Protection
Given the high ionizing power of alpha particles, safety precautions are essential when handling alpha-emitting materials. While alpha particles have low penetration power, internal exposure can be significantly harmful. If alpha-emitting substances are ingested or inhaled, the ionizing radiation can cause severe damage to internal organs. Therefore, proper handling procedures, including using protective equipment and maintaining a safe distance, are crucial to minimize risk.
Further Exploration: Advanced Concepts
This article provided a foundational understanding of the charge of an alpha particle in Coulombs. For a deeper exploration, consider researching the following advanced concepts:
- Quantum Tunneling: This quantum mechanical phenomenon explains how the alpha particle can escape the nucleus despite the strong nuclear force.
- Nuclear Shell Model: This model helps predict the stability and decay modes of different nuclei, including alpha decay.
- Geiger-Müller Counter: This instrument detects ionizing radiation, including alpha particles, by measuring the ionization it produces.
- Specific Activity: This measure describes the amount of radioactivity per unit mass of a substance, often expressed in Becquerels (Bq) or Curies (Ci).
- Linear Energy Transfer (LET): This parameter quantifies the rate at which energy is deposited by ionizing radiation as it travels through matter. Alpha particles have a high LET due to their charge and mass.
Conclusion
The charge of an alpha particle, precisely 3.204 x 10⁻¹⁹ Coulombs, is a fundamental property with far-reaching consequences. Understanding this charge, along with the particle's other properties, is essential to comprehending nuclear physics, radioactive decay, and the various applications and safety considerations related to alpha radiation. The concepts explored in this article serve as a starting point for further exploration into the fascinating world of subatomic particles and nuclear phenomena. This knowledge is crucial for advancements in various scientific and technological domains, highlighting the enduring importance of understanding this seemingly small but incredibly significant charge.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Electron Configuration Of Nickel
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Statement Is Incorrect For The Following Reaction Profile
Mar 19, 2025
-
Difference Between Electric Potential And Electric Potential Energy
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is 200 In Decimal Form
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Ocean Is West Of Africa
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Charge Of Alpha Particle In Coulombs . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
