What Is The Electron Configuration Of Nickel
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
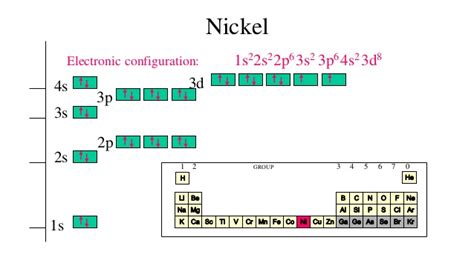
Table of Contents
What is the Electron Configuration of Nickel? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Nickel, a silvery-white metal known for its strength and resistance to corrosion, holds a fascinating place in the periodic table. Understanding its electron configuration is key to unlocking its unique properties and chemical behavior. This comprehensive guide will delve into the electron configuration of nickel, exploring its underlying principles, variations, and implications.
Understanding Electron Configuration
Before diving into nickel's specific configuration, let's establish a foundational understanding of the concept. Electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in the various energy levels (shells) and sublevels (subshells) within an atom. This arrangement is governed by the principles of quantum mechanics, which dictate how electrons fill orbitals based on their energy levels.
Key Principles Governing Electron Configuration
- Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. This is like filling a container from the bottom up – the lowest levels are filled before higher ones.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, and these electrons must have opposite spins (represented as +1/2 and -1/2). Think of it as each apartment in a building accommodating only two residents with different characteristics.
- Hund's Rule: Within a subshell, electrons will individually occupy each orbital before doubling up in any single orbital. Imagine each orbital as a separate seat – everyone gets their own seat before anyone shares.
These principles ensure stability and predictability in electron configurations. They help us understand why certain elements react the way they do and what their properties are.
Nickel's Electron Configuration: The Basics
Nickel (Ni) has an atomic number of 28, meaning it has 28 protons and, in its neutral state, 28 electrons. Its electron configuration is typically written as:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁸
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: The first energy level (shell) contains one subshell (s), which holds a maximum of two electrons.
- 2s² 2p⁶: The second energy level contains an s subshell (2 electrons) and a p subshell (6 electrons).
- 3s² 3p⁶: The third energy level also contains an s subshell (2 electrons) and a p subshell (6 electrons).
- 4s² 3d⁸: The fourth energy level starts with an s subshell (2 electrons) and then the 3d subshell (8 electrons). Note the slightly unusual order: the 4s subshell fills before the 3d subshell, even though the 3d subshell is at a lower principal quantum number (n=3). This is due to subtle energy level differences.
The Significance of the 3d Subshell
The 3d subshell is crucial to understanding nickel's properties. The eight electrons in this subshell are responsible for many of nickel's characteristics, including its magnetic properties and catalytic activity. The partially filled d-orbital allows for a range of oxidation states and complex formation, impacting its reactivity and applications.
Orbital Diagram for Nickel
A more visual representation of the electron configuration uses orbital diagrams. For nickel, it would look like this:
- 1s: ↑↓
- 2s: ↑↓
- 2p: ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓
- 3s: ↑↓
- 3p: ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓
- 4s: ↑↓
- 3d: ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑↓ ↑↓
Exceptions and Variations in Electron Configuration
While the standard electron configuration is generally accurate, it's important to note that variations can occur, especially in the context of ionization or when nickel forms compounds.
Nickel Ions and their Electron Configurations
When nickel loses electrons to form ions (cations), it typically loses the 4s electrons first, followed by 3d electrons. For example:
- Ni²⁺: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁸ (loss of two 4s electrons)
- Ni³⁺: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁷ (loss of two 4s electrons and one 3d electron)
The specific electron configuration of nickel ions depends on the oxidation state and the chemical environment.
Influence of Ligands in Coordination Complexes
In coordination complexes, the interaction of nickel with ligands (molecules or ions bound to the central metal atom) can significantly alter the electron configuration. Ligand field theory describes how these interactions affect the energies of the d orbitals, potentially causing electron rearrangement. This leads to variations in magnetic properties and other characteristics.
Nickel's Properties and their Relation to Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of nickel directly influences its physical and chemical properties:
Magnetic Properties
The partially filled 3d subshell is responsible for nickel's ferromagnetic properties. The unpaired electrons in the 3d orbitals interact with each other, leading to a spontaneous alignment of magnetic moments, resulting in strong magnetism. This property is crucial in various applications, including magnets and magnetic recording materials.
Catalytic Activity
Nickel's partially filled d-orbitals enable it to act as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. It can readily accept or donate electrons, facilitating the formation and breaking of chemical bonds. This catalytic activity is exploited in industrial processes such as hydrogenation and carbonylation.
Metallic Bonding and Conductivity
The valence electrons (those in the outermost shell) participate in metallic bonding, which accounts for nickel's high electrical and thermal conductivity. These electrons are delocalized, creating a "sea" of electrons that readily move throughout the metal lattice.
Oxidation States
Nickel exhibits multiple oxidation states, primarily +2 and +3, but can also exist in +1, +4, and even higher oxidation states in specific chemical environments. The availability of the d-electrons dictates the number of electrons that can be donated or shared during the formation of chemical bonds.
Applications of Nickel and its Electron Configuration Relevance
The unique properties stemming from its electron configuration make nickel incredibly versatile. It's utilized in numerous applications:
Alloys
Nickel is a crucial component in various alloys, enhancing their strength, corrosion resistance, and other desirable properties. Stainless steel, for instance, owes its durability partly to the presence of nickel. Nickel alloys are employed in high-temperature applications and in industries requiring corrosion resistance.
Catalysis
Nickel catalysts are used extensively in chemical processes like hydrogenation (adding hydrogen to unsaturated compounds), hydrocracking (breaking down large hydrocarbon molecules), and carbonylation (introducing carbon monoxide into molecules). The ability to readily donate or accept electrons is vital to its function as a catalyst.
Batteries
Nickel-based batteries, such as nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, are used in portable electronic devices and electric vehicles. Nickel's electrochemical properties contribute to the batteries' energy storage and discharge characteristics.
Coatings and Plating
Nickel plating is used to protect metals from corrosion and enhance their appearance. The process involves depositing a layer of nickel onto a substrate, offering both aesthetic and protective benefits.
Magnetic Applications
Nickel's ferromagnetism makes it essential in producing magnets and magnetic recording materials. The strong magnetic properties are leveraged in various applications, including hard drives, speakers, and other magnetic devices.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Metal
Nickel's electron configuration is not merely a theoretical concept; it's the key to understanding its rich physical and chemical properties. The partially filled 3d subshell is the driving force behind its magnetism, catalytic activity, and ability to form various compounds. The intricate interplay of its electrons explains its wide array of applications, making it an indispensable element in modern technology and industry. Further research into the intricacies of nickel's electron configuration continues to unlock new possibilities and applications for this multifaceted metal.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Sigma And Pi Bonds In Co2
Mar 19, 2025
-
A Floating Ice Block Is Pushed Through A Displacement
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Event Had An Enormous Effect On Us Workplace Safety
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Formula For Magnesium Acetate
Mar 19, 2025
-
Converse Of Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Electron Configuration Of Nickel . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
