What Is The Formula For Magnesium Acetate
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
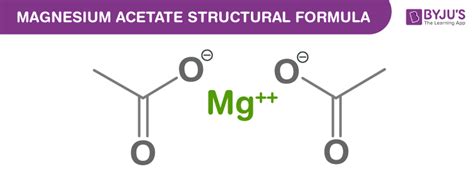
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for Magnesium Acetate? Unlocking the Chemistry of this Versatile Compound
Magnesium acetate, a seemingly simple chemical compound, plays a surprisingly diverse role in various applications, from medicine to environmental remediation. Understanding its chemical formula is the key to unlocking its properties and potential uses. This comprehensive guide delves into the formula, properties, production, and diverse applications of magnesium acetate. We will also explore its safety considerations and future prospects.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: Mg(CH₃COO)₂
The chemical formula for magnesium acetate is Mg(CH₃COO)₂. This formula concisely communicates the composition of the compound:
- Mg: Represents one magnesium atom (Mg²⁺), a divalent alkaline earth metal known for its role in various biological processes.
- (CH₃COO)₂: Represents two acetate ions (CH₃COO⁻). Each acetate ion is a negatively charged organic molecule, the conjugate base of acetic acid (vinegar). The subscript "2" indicates two acetate ions are needed to balance the 2+ charge of the magnesium ion.
This ionic structure is critical to understanding magnesium acetate's properties and behavior. The strong electrostatic attraction between the positively charged magnesium ion and the negatively charged acetate ions creates a stable crystalline structure.
Properties of Magnesium Acetate: A Closer Look
Magnesium acetate exhibits several key properties that influence its applications:
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Typically exists as a white crystalline powder or colorless crystals.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, readily dissolving to form a clear solution. This high solubility is vital for many of its applications, allowing for easy handling and distribution.
- Melting Point: Possesses a relatively low melting point, around 320°C (608°F). This property is important during manufacturing and processing.
- Hygroscopic Nature: Magnesium acetate is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. This characteristic should be considered when storing and handling the compound to prevent clumping or degradation.
Chemical Properties:
- Ionic Compound: Its ionic nature contributes to its solubility in polar solvents like water.
- Weakly Acidic: While derived from acetic acid, magnesium acetate solutions exhibit a slightly acidic pH due to the hydrolysis of the acetate ion.
- Reactivity: Relatively stable under normal conditions, but can react with strong acids and bases. It's important to consider these potential reactions when using magnesium acetate in different chemical environments.
- Biodegradability: An important aspect is its biodegradability, making it an environmentally friendly compound compared to some other magnesium salts.
Production of Magnesium Acetate: Methods and Processes
Magnesium acetate is generally produced through various methods, all of which involve combining a source of magnesium ions with a source of acetate ions:
Common Production Methods:
-
Reaction of Magnesium Oxide/Hydroxide with Acetic Acid: This is a common and straightforward method. Magnesium oxide (MgO) or magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)₂] reacts with acetic acid (CH₃COOH) to form magnesium acetate and water. This reaction is typically carried out in an aqueous solution, followed by purification and crystallization.
MgO + 2CH₃COOH → Mg(CH₃COO)₂ + H₂O Mg(OH)₂ + 2CH₃COOH → Mg(CH₃COO)₂ + 2H₂O -
Reaction of Magnesium Carbonate with Acetic Acid: Magnesium carbonate (MgCO₃) can also react with acetic acid to produce magnesium acetate, carbon dioxide, and water.
MgCO₃ + 2CH₃COOH → Mg(CH₃COO)₂ + CO₂ + H₂O -
Neutralization Reaction: The reaction of magnesium hydroxide with acetic acid is essentially a neutralization reaction, where the acidic properties of acetic acid are balanced by the basic properties of magnesium hydroxide.
The choice of production method depends on factors such as cost, availability of raw materials, and desired purity of the final product. Purification techniques, such as recrystallization and filtration, are often employed to ensure a high-quality magnesium acetate product.
Diverse Applications of Magnesium Acetate: A Wide Spectrum of Uses
The unique properties of magnesium acetate make it a versatile compound with a wide array of applications:
Medical Applications:
- Magnesium Supplementation: Magnesium is an essential mineral for various bodily functions, and magnesium acetate can be used as a dietary supplement to address magnesium deficiency.
- Pharmaceutical Excipient: It serves as an excipient in some pharmaceutical formulations, playing a role in tablet binding or as a stabilizing agent.
Industrial Applications:
- Textile Industry: Used as a mordant in dyeing and printing textiles, improving dye fixation and colorfastness.
- Water Treatment: Its ability to absorb moisture makes it potentially useful in certain water treatment applications, particularly for controlling humidity.
- Catalyst: Can be used as a catalyst in some chemical reactions, although this application is less common compared to its other uses.
- Flame Retardant: Although less commonly used compared to other flame retardants, its potential in this application is being explored due to its relatively lower toxicity profile.
Environmental Applications:
- Dust Suppression: Magnesium acetate is increasingly used as a dust suppressant on unpaved roads and construction sites. Its hygroscopic nature helps bind dust particles, reducing air pollution and improving air quality. This application leverages its ability to retain moisture, effectively controlling dust without the environmental drawbacks associated with some other dust suppressants.
- Soil Remediation: It's being explored for its potential in soil remediation, helping to improve soil structure and potentially reduce the mobility of certain contaminants. This application relies on its ability to interact with soil components and modify their properties.
- Wastewater Treatment: Its potential applications in wastewater treatment are being studied, as its properties might help with certain aspects of contaminant removal or control.
Other Applications:
- Food Additive: Magnesium acetate is approved for use as a food additive in some countries, primarily as a source of magnesium in fortified foods.
- Animal Feed: In animal feed, it can be included as a magnesium supplement to support animal health and growth.
Safety Considerations and Handling Precautions
While generally considered safe, appropriate handling procedures should be followed when working with magnesium acetate:
- Eye and Skin Contact: Avoid direct contact with eyes and skin. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and eye protection during handling.
- Inhalation: Avoid inhalation of dust. Work in well-ventilated areas.
- Ingestion: Do not ingest. Keep away from children and pets.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from incompatible substances. Proper storage helps prevent degradation and maintains the quality of the product.
It's crucial to consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the manufacturer for detailed safety information specific to the particular product.
Future Prospects and Research: Exploring New Avenues
Ongoing research explores new and potential applications of magnesium acetate:
- Biomedical Applications: Research is exploring its potential in targeted drug delivery and other biomedical applications.
- Sustainable Materials: Its biodegradability makes it an attractive component for developing environmentally friendly materials.
- Advanced Agricultural Applications: Research continues into its potential use as a soil amendment in agriculture to improve crop yield and soil health.
The versatility of magnesium acetate suggests a promising future in diverse fields, driven by both its chemical properties and its environmentally friendly nature.
Conclusion: A Versatile Compound with a Bright Future
Magnesium acetate, with its simple formula Mg(CH₃COO)₂, belies its remarkable versatility. Its unique properties – high solubility, biodegradability, and hygroscopic nature – underpin its diverse applications across medical, industrial, and environmental sectors. Understanding its formula, properties, and production methods is crucial to fully appreciating its importance and potential for future innovations. While generally safe, proper handling procedures are necessary. Ongoing research continues to unveil new applications, solidifying its place as a valuable chemical compound with a bright future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Bonding Involves The Unequal Sharing Of Electrons
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Earths Layers Is The Thinnest
Mar 19, 2025
-
Three Particles Are Fixed On An X Axis
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Sulfur A Metal Or Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 19, 2025
-
Identify The Geometric Mean Of 6 And 24
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For Magnesium Acetate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
