Identify The Geometric Mean Of 6 And 24 .
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
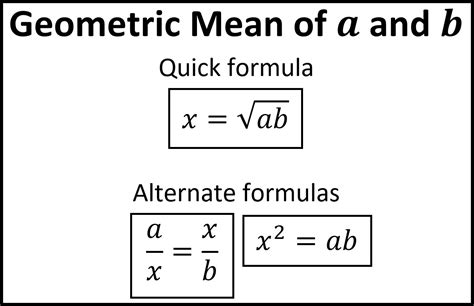
Table of Contents
Identifying the Geometric Mean of 6 and 24: A Comprehensive Guide
The geometric mean (GM) is a crucial concept in mathematics and statistics, offering a unique way to calculate the central tendency of a set of numbers, particularly when dealing with multiplicative relationships or rates of change. Unlike the arithmetic mean (average), which sums numbers and divides by the count, the geometric mean multiplies the numbers and then finds the nth root, where n is the count of numbers. This article delves deep into understanding the geometric mean, focusing on calculating the geometric mean of 6 and 24, and exploring its broader applications and significance.
Understanding the Geometric Mean
The geometric mean is a type of average that indicates the central tendency or typical value of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). It's particularly useful when dealing with:
- Rates of change: Calculating average growth rates over time.
- Proportions: Finding the average of ratios or proportions.
- Positive numbers: The geometric mean is only defined for positive numbers. Negative numbers introduce complexities in the calculation.
- Financial analysis: Determining average investment returns.
The formula for calculating the geometric mean (GM) of 'n' positive numbers (x₁, x₂, ..., xₙ) is:
GM = ⁿ√(x₁ * x₂ * ... * xₙ)
This means you multiply all the numbers together and then take the nth root, where 'n' is the number of values. For two numbers, the formula simplifies to:
GM = √(x₁ * x₂)
Calculating the Geometric Mean of 6 and 24
Let's apply this knowledge to find the geometric mean of 6 and 24. Using the simplified formula for two numbers:
GM = √(6 * 24)
-
Multiply the numbers: 6 * 24 = 144
-
Find the square root: √144 = 12
Therefore, the geometric mean of 6 and 24 is 12.
Geometric Mean vs. Arithmetic Mean: A Key Distinction
It's important to understand the difference between the geometric mean and the arithmetic mean. While both are measures of central tendency, they serve different purposes and yield different results.
Let's compare the two means for the numbers 6 and 24:
- Arithmetic Mean (AM): (6 + 24) / 2 = 15
- Geometric Mean (GM): √(6 * 24) = 12
Notice the difference? The arithmetic mean is larger than the geometric mean in this case. This is generally true when the numbers in the set are not all equal. The arithmetic mean is more sensitive to outliers, while the geometric mean is less influenced by extreme values.
Geometric Mean and Proportions: A Deeper Dive
The geometric mean has a unique relationship with proportions. Consider the numbers 6 and 24. We can express their relationship as a proportion: 6/12 = 12/24 = 1/2. The geometric mean, 12, perfectly bridges the gap between these two numbers, maintaining the proportional relationship. This characteristic makes the geometric mean incredibly useful in situations involving ratios or proportions.
Applications of the Geometric Mean
The geometric mean finds applications across numerous fields:
1. Finance: Calculating Average Investment Returns
In finance, the geometric mean is used to calculate the average rate of return on an investment over multiple periods. This is because it accounts for the compounding effect of returns. Using the arithmetic mean to calculate average investment returns can overestimate the actual average return, especially over longer periods with fluctuating returns.
2. Statistics: Analyzing Data with Multiplicative Relationships
The geometric mean is valuable in statistical analysis when dealing with data that exhibits multiplicative relationships, such as growth rates or ratios. It provides a more accurate representation of the central tendency than the arithmetic mean in such scenarios.
3. Engineering and Science: Averaging Measurements
In engineering and science, the geometric mean is used to average measurements that have a multiplicative relationship, ensuring the result accurately reflects the data's inherent nature. For instance, when calculating the average diameter of a cylindrical object, the geometric mean might be more appropriate than the arithmetic mean.
4. Image Processing and Computer Graphics: Calculating Average Brightness
The geometric mean is employed in image processing and computer graphics for calculating the average brightness of pixels in an image. It provides a more accurate representation of the overall brightness, particularly in images with varying levels of contrast.
5. Biology: Calculating Average Growth Rates
In biology, the geometric mean is often used to compute the average growth rate of populations over time. This method takes into account the compounding effect of growth, offering a more precise measure of average growth compared to the arithmetic mean.
6. Music and Acoustics: Calculating Average Frequencies
In music and acoustics, the geometric mean is used to calculate the average frequency of musical notes or sound waves. This is because the relationship between musical notes often follows a logarithmic scale, and the geometric mean effectively handles this type of data.
7. Environmental Science: Averaging Pollution Levels
In environmental science, the geometric mean can be used to calculate average pollution levels, where different types of pollutants might interact multiplicatively. This offers a more robust measure compared to simply averaging pollution levels directly.
Limitations of the Geometric Mean
While the geometric mean offers many advantages, it does have some limitations:
- Positive numbers only: It cannot be used with negative numbers or zero.
- Sensitivity to zero values: Even a single zero value will result in a geometric mean of zero, regardless of other values.
- Less intuitive than the arithmetic mean: It is less familiar to many people, requiring a more detailed understanding of its calculation and interpretation.
- Complex calculations for larger datasets: While readily calculated for small sets, for large datasets, specialized software or tools might be needed.
Conclusion
The geometric mean is a powerful tool for calculating central tendency, particularly in situations involving multiplicative relationships, rates of change, and proportions. Its ability to handle compounding effects and to represent central tendency accurately within proportional relationships makes it invaluable in various fields, from finance and statistics to engineering and environmental science. Understanding the geometric mean, as demonstrated through the example of calculating the geometric mean of 6 and 24, is essential for anyone working with data that requires a precise and nuanced understanding of central tendency. While the arithmetic mean remains a fundamental tool, the geometric mean provides a crucial alternative, better suited to specific data characteristics and problem contexts. Remember to consider the limitations of the geometric mean and choose the appropriate method based on the specific application and data characteristics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does Prokaryotic Cells Have Membrane Bound Organelles
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Figure Shows Three Paths Connecting Points A And B
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Types Of Bonds Found In Nucleic Acids Are
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Central Part Of The Atom Is Called The
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Figure Shows A Conical Pendulum In Which The Bob
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Identify The Geometric Mean Of 6 And 24 . . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
