Sigma And Pi Bonds In Co2
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
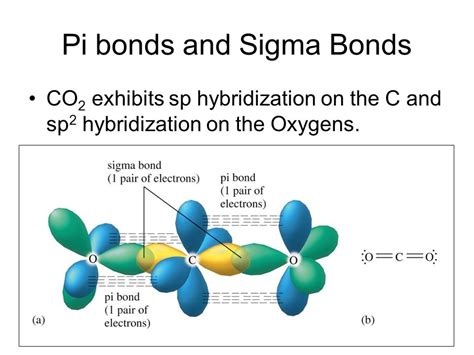
Table of Contents
Sigma and Pi Bonds in CO2: A Deep Dive into Molecular Structure and Bonding
Carbon dioxide (CO2), a ubiquitous compound in our atmosphere and a crucial component of the carbon cycle, presents a fascinating case study in chemical bonding. Its linear structure and unique properties are directly attributable to the interplay of sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds formed between the carbon and oxygen atoms. This article will delve deep into the nature of these bonds within the CO2 molecule, exploring their formation, characteristics, and implications for the molecule's overall behavior.
Understanding Sigma (σ) and Pi (π) Bonds
Before we dissect the bonding in CO2, let's establish a fundamental understanding of sigma and pi bonds. These terms describe different types of covalent bonds, arising from the overlap of atomic orbitals.
Sigma Bonds (σ Bonds)
A sigma bond is formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals. This means the electron density is concentrated along the internuclear axis – the imaginary line connecting the two bonded nuclei. Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent bond and are typically the first bond formed between two atoms. They are crucial for establishing the basic framework of a molecule. They allow for free rotation around the bond axis.
Pi Bonds (π Bonds)
A pi bond (π bond) is formed by the sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, specifically p orbitals. The electron density is concentrated above and below the internuclear axis, creating two regions of electron density. Pi bonds are weaker than sigma bonds and are typically formed after a sigma bond has been established between the same two atoms. They are characterized by restricted rotation around the bond axis; rotation would disrupt the sideways overlap.
The Lewis Structure of CO2 and its Implications
The Lewis structure of CO2 illustrates the arrangement of valence electrons and provides a starting point for understanding the bonding. Carbon, with four valence electrons, forms double bonds with each of the two oxygen atoms (each oxygen having six valence electrons). This is represented as O=C=O.
This Lewis structure, however, provides a simplified representation. It doesn't directly show the three-dimensional arrangement of orbitals and the nature of the sigma and pi bonds. To understand this more fully, we need to consider the valence bond theory and hybridization.
Hybridization in CO2: sp Hybridization
The carbon atom in CO2 undergoes sp hybridization. This means that one s orbital and one p orbital combine to form two sp hybrid orbitals. These two sp hybrid orbitals are oriented at an angle of 180°, leading to the linear geometry of the CO2 molecule.
Each sp hybrid orbital on carbon then overlaps head-on with a p orbital from each oxygen atom, forming two sigma (σ) bonds. This accounts for two of the four bonds in the Lewis structure.
The remaining two p orbitals on the carbon atom and two unhybridized p orbitals on each oxygen atom participate in the formation of two pi (π) bonds. Each pi bond involves the sideways overlap of a p orbital on carbon with a p orbital on an oxygen atom. These are located above and below the molecular axis.
Delving Deeper: Molecular Orbital Theory Perspective
While valence bond theory with hybridization provides a good understanding of the bonding in CO2, molecular orbital theory (MOT) provides a more comprehensive picture. MOT considers the combination of all atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals that span the entire molecule.
In CO2, the sp hybrid orbitals on carbon combine with the p orbitals of the oxygen atoms, generating bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Similarly, the unhybridized p orbitals on carbon and oxygen interact to create further bonding and antibonding pi molecular orbitals.
According to MOT, the resulting molecular orbitals are filled with electrons according to the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule. The bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy and are filled first. The filled bonding molecular orbitals contribute to the stability of the CO2 molecule.
Bond Order and Bond Length in CO2
The bond order in CO2 is 2 for each C=O bond. This signifies the presence of a double bond, which is a combination of one sigma and one pi bond. The presence of the two pi bonds shortens the carbon-oxygen bond length compared to a single bond. The bond length in CO2 is approximately 116 pm, reflecting the strength of the double bonds.
Properties of CO2 arising from Sigma and Pi Bonds
The sigma and pi bonds in CO2 significantly influence its physical and chemical properties:
Linear Geometry and Polarity:
The sp hybridization and the linear arrangement of atoms result in the molecule possessing a symmetrical structure. This symmetry cancels out the individual bond dipoles, leading to a nonpolar molecule despite the polar nature of individual C=O bonds.
Bond Strength and Reactivity:
The presence of double bonds (one sigma and one pi bond) leads to a relatively strong C=O bond. The pi bond is weaker than the sigma bond, but it still adds significantly to the overall bond strength. This strength contributes to the relative stability of CO2 and its relatively low reactivity under standard conditions.
Vibrational Modes and Spectroscopy:
The unique bonding arrangement in CO2 leads to distinct vibrational modes that can be detected using infrared (IR) spectroscopy. These vibrational modes provide further experimental evidence for the presence of both sigma and pi bonds. Specific frequencies observed in the IR spectrum support the assignment of a linear structure and the presence of double bonds.
Role in the Carbon Cycle:
The stability and reactivity of CO2, dictated by its sigma and pi bonding arrangement, are critical to its role in the carbon cycle. The molecule is relatively unreactive in the atmosphere, but it plays a vital role in photosynthesis and respiration where enzymes facilitate its reaction. The breaking and forming of bonds are crucial for its involvement in biological and geological processes.
Comparison with Related Molecules: CO and O2
Understanding the bonding in CO2 becomes even more insightful when comparing it to similar molecules like carbon monoxide (CO) and oxygen (O2).
CO: CO has a triple bond (one sigma and two pi bonds), making it even more strongly bonded and less reactive than CO2. The triple bond also contributes to the higher bond strength.
O2: Oxygen (O2) has a double bond, but its bonding is more complex than that of CO2. While it also features a sigma and a pi bond, the electronic configuration and paramagnetism make it quite different in its chemical properties.
Conclusion: The Significance of Sigma and Pi Bonds in CO2
The presence and interplay of sigma and pi bonds in CO2 are fundamental to its molecular structure, properties, and reactivity. The sp hybridization of carbon dictates the linear geometry, while the double bonds create a molecule with high bond strength and relative stability, crucial for its role in the atmosphere and biological systems. Understanding the intricacies of these bonds allows for a profound appreciation of CO2's behavior and significance in the wider world. Further studies focusing on the intricacies of sigma and pi bond interactions in CO2 continue to advance our knowledge of molecular behavior. Advanced spectroscopic techniques, computational modeling and theoretical studies offer ongoing insight into these fascinating interactions. The interplay of sigma and pi bonds demonstrates the complexity of chemical bonding and its role in determining molecular features and biological processes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Sulfur A Metal Or Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 19, 2025
-
Identify The Geometric Mean Of 6 And 24
Mar 19, 2025
-
Three Coplanar Lines That Intersect In A Common Point
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Boron Solid Liquid Or Gas
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is Molar Mass Of Iron
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sigma And Pi Bonds In Co2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
