Difference Between Electric Potential And Electric Potential Energy
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
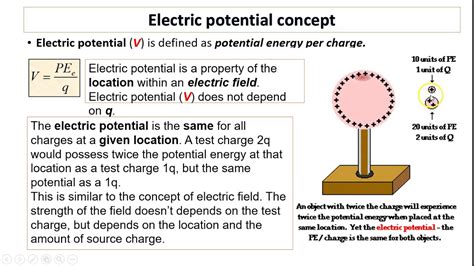
Table of Contents
- Difference Between Electric Potential And Electric Potential Energy
- Table of Contents
- Delving Deep into the Difference Between Electric Potential and Electric Potential Energy
- What is Electric Potential?
- Key characteristics of Electric Potential:
- What is Electric Potential Energy?
- Key characteristics of Electric Potential Energy:
- The Crucial Difference: A Simple Analogy
- Understanding the Relationship: A Deeper Dive
- Practical Applications and Examples
- Distinguishing Features in a Table
- Conclusion: Mastering the Concepts
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Delving Deep into the Difference Between Electric Potential and Electric Potential Energy
Understanding electricity is crucial in today's technologically driven world. However, two fundamental concepts often cause confusion: electric potential and electric potential energy. While closely related, they are distinct concepts representing different aspects of an electric field. This article will thoroughly explore the differences between electric potential and electric potential energy, clarifying their meanings and relationships.
What is Electric Potential?
Electric potential, often denoted by the symbol V, is a scalar quantity that describes the electric potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in an electric field. Imagine it as the "voltage" at a point. It represents the amount of work needed to bring a unit positive charge from infinity (where the electric potential is considered zero) to that specific point. Crucially, it's independent of the charge itself. The electric potential at a point is a property of the electric field itself, not a property of the charge placed within the field.
Key characteristics of Electric Potential:
- Scalar Quantity: Electric potential is a scalar, meaning it only has magnitude, not direction. This simplifies calculations compared to vector quantities.
- Unit of Measurement: The standard unit for electric potential is the volt (V), which is equivalent to joules per coulomb (J/C).
- Reference Point: Electric potential is always relative to a reference point, typically chosen as infinity, where the potential is zero.
- Dependence on Electric Field: The electric potential is directly related to the electric field strength and the distance from the source charge. A stronger electric field will result in a larger potential difference between two points.
- Potential Difference: A more commonly used term is potential difference or voltage, which represents the difference in electric potential between two points. This is what drives the flow of current in a circuit.
What is Electric Potential Energy?
Electric potential energy, denoted by PE or U, is the energy that a charged particle possesses due to its position within an electric field. It's a scalar quantity that represents the work required to move a charged particle from a reference point to its current position against the electric force. Unlike electric potential, which is a property of the field itself, electric potential energy is a property of the charged particle within that field.
Key characteristics of Electric Potential Energy:
- Scalar Quantity: Like electric potential, electric potential energy is a scalar quantity, possessing only magnitude.
- Unit of Measurement: The standard unit for electric potential energy is the joule (J).
- Dependence on Charge and Position: The electric potential energy of a charged particle depends on both the magnitude of its charge (q) and its position within the electric field.
- Relationship to Electric Potential: The electric potential energy (PE) of a point charge (q) at a point with electric potential (V) is given by the simple equation: PE = qV. This equation highlights the direct relationship between the two concepts.
- Work Done: The change in electric potential energy of a charge as it moves between two points is equal to the negative of the work done by the electric field on the charge. This is a consequence of the conservation of energy.
The Crucial Difference: A Simple Analogy
Imagine a water slide. The electric potential is analogous to the height of the slide at a particular point. It's a property of the slide itself, regardless of whether a person is on it or not. A higher point on the slide has a higher potential.
The electric potential energy, on the other hand, is the potential energy a person possesses at a specific point on the slide. This energy depends on both the height of the slide (potential) and the mass of the person (charge). A heavier person at the same height has more potential energy than a lighter person.
The same principle applies to electric potential and electric potential energy. The electric potential is a property of the field, independent of the charge. The electric potential energy depends on both the field's potential and the magnitude of the charge placed within the field.
Understanding the Relationship: A Deeper Dive
The relationship between electric potential and electric potential energy is fundamentally expressed through the equation:
PE = qV
Where:
- PE is the electric potential energy
- q is the charge of the particle
- V is the electric potential at the particle's location.
This equation elegantly showcases that the electric potential energy is directly proportional to both the charge and the electric potential. Doubling the charge will double the potential energy, and doubling the electric potential will also double the potential energy, assuming the charge remains constant.
This relationship is key to understanding how charges behave in electric fields. Charges naturally move from regions of higher potential energy to regions of lower potential energy, much like objects roll downhill. This movement of charge constitutes an electric current.
Practical Applications and Examples
The concepts of electric potential and electric potential energy are fundamental to numerous applications in various fields of science and engineering:
- Circuits and Electronics: Voltage (potential difference) drives the flow of current in electrical circuits. The potential energy difference between two points in a circuit determines the work done by the electric field on the charge carriers.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store energy by accumulating charges on their plates, creating an electric potential difference. The energy stored in a capacitor is directly related to the electric potential energy.
- Batteries: Batteries provide a potential difference, driving the flow of electrons and enabling the operation of electronic devices. The chemical reactions within a battery create an electric potential difference.
- Electrostatics: In electrostatics, the principles of electric potential and potential energy are used to calculate the forces between charges and the work done in moving charges within an electric field.
- Particle Accelerators: Particle accelerators utilize electric fields to accelerate charged particles to very high speeds. The acceleration is driven by the change in electric potential energy as the particles traverse the electric field.
Distinguishing Features in a Table
To summarize the key differences, let's present the information in a table:
| Feature | Electric Potential (V) | Electric Potential Energy (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Scalar | Scalar |
| Unit | Volt (V) | Joule (J) |
| Dependence | Electric field | Charge and electric field |
| Represents | Energy per unit charge | Energy of a charged particle |
| Reference | Typically infinity | Arbitrary; depends on the problem |
Conclusion: Mastering the Concepts
While both electric potential and electric potential energy are essential concepts in understanding electricity, they represent distinct physical quantities. Electric potential is a property of the electric field itself, describing the energy per unit charge, while electric potential energy is a property of the charged particle within the field, representing the particle's energy due to its position. Understanding their relationship, particularly the equation PE = qV, is crucial for comprehending the behavior of charges in electric fields and solving problems in electromagnetism. By grasping these fundamental concepts, you'll gain a solid foundation for delving into more advanced topics in electricity and related fields. Remember the analogy of the water slide: electric potential is the height, and electric potential energy is the energy of the person at that height. This will help you visualize and better understand these key concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 G Equivalent To
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Statement About Unsaturated Fats Is True
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Reproduce By Budding
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Colligative Property
Mar 20, 2025
-
At What Temperature Does Solid Turn To Liquid
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Electric Potential And Electric Potential Energy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
