What Ocean Is West Of Africa
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
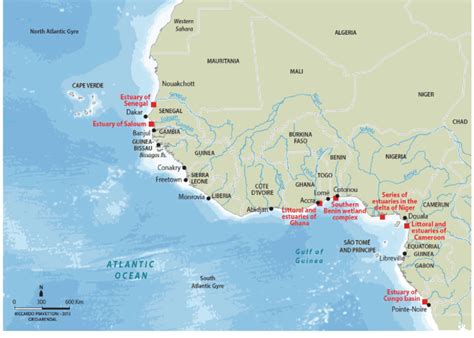
Table of Contents
What Ocean is West of Africa? A Deep Dive into the Atlantic
The answer to the question, "What ocean is west of Africa?" is simple: the Atlantic Ocean. However, a simple answer often belies a deeper story, and this geographical query opens the door to exploring the immense size, diverse ecosystems, and rich history intertwined with this vast body of water. This article will delve into the relationship between Africa and the Atlantic, examining its geographical boundaries, ecological significance, historical impact, and its continuing influence on the continent.
The Atlantic Ocean: A Defining Feature of West Africa
The Atlantic Ocean forms a crucial part of West Africa's identity, shaping its climate, economy, and culture for millennia. Its western shores hug the coastlines of numerous countries, from Morocco in the north to Angola in the south, impacting everything from coastal erosion to the livelihoods of millions. The sheer scale of the ocean is staggering; its vast expanse influences weather patterns, ocean currents, and the distribution of marine life across the globe.
Geographical Boundaries and Coastal Features
The Atlantic's western edge against Africa is remarkably diverse. It doesn't present a uniform shoreline; instead, it boasts a fascinating array of geographical features:
- Coastal Plains: Many West African nations possess extensive coastal plains, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting densely populated areas. These plains are often susceptible to flooding and erosion, however, making coastal management a critical issue.
- Estuaries and Lagoons: Numerous estuaries and lagoons dot the coastline, providing vital habitats for a wide range of species and acting as natural harbors. The Niger Delta, for instance, is a prime example of a vast estuarine system supporting a unique biodiversity.
- Cliffs and Headlands: In contrast to the plains, some sections of the West African coastline are characterized by dramatic cliffs and headlands, offering stunning scenery but presenting challenges for coastal development.
- Islands: The Atlantic is also home to several significant islands off the West African coast, such as Cape Verde, São Tomé and Príncipe, and the Canary Islands. These islands have their own unique cultures and ecosystems, shaped by their proximity to the African continent and the influences of the Atlantic.
The Ecological Importance of the Atlantic to West Africa
The Atlantic Ocean plays a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance of West Africa. Its influence extends far beyond the immediate coastline, affecting everything from rainfall patterns to the distribution of plant and animal life.
Marine Biodiversity and Fisheries
The waters off the West African coast are incredibly rich in biodiversity. This supports thriving fisheries, providing sustenance and livelihoods for millions of people. However, overfishing and unsustainable fishing practices pose a significant threat to this vital resource. The delicate balance of the marine ecosystem is under pressure, highlighting the need for responsible management and conservation efforts.
Key species found in the region include:
- Pelagic fish: Tuna, sardines, and mackerel are economically important species, supporting significant fishing industries.
- Demersal fish: Cod, haddock, and other bottom-dwelling fish are also abundant in certain areas.
- Shellfish: Shrimp, crabs, and other shellfish contribute significantly to the coastal economies.
- Marine mammals: Whales, dolphins, and seals are found in the Atlantic off the coast of West Africa, although their populations are often threatened by human activities.
Coastal Ecosystems and Mangroves
The coastal ecosystems of West Africa, including mangrove forests, seagrass beds, and coral reefs, are crucial for maintaining biodiversity and protecting the coastline from erosion. These ecosystems provide vital nurseries for fish and other marine species, and they act as natural buffers against storms and rising sea levels. However, these ecosystems are facing increasing threats from deforestation, pollution, and coastal development.
Influence on Climate and Weather Patterns
The Atlantic Ocean plays a dominant role in shaping the climate of West Africa. The warm currents flowing along the coast influence rainfall patterns, creating a diverse range of climates from arid deserts in the north to tropical rainforests in the south. The ocean also moderates temperatures, preventing extreme temperature fluctuations in coastal areas. However, climate change is altering these patterns, leading to increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods.
The Historical Impact of the Atlantic on West Africa
The history of West Africa is inextricably linked to the Atlantic Ocean. The ocean has served as both a highway for trade and a source of both opportunity and exploitation.
Transatlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic Ocean played a tragic role in the history of West Africa as the primary route for the transatlantic slave trade. Millions of Africans were forcibly transported across the ocean to the Americas, leaving an indelible mark on the continent's history and culture. The legacy of this horrific period continues to impact West African societies today.
Maritime Trade and Exploration
Prior to the slave trade, and after its abolition, the Atlantic served as a vital artery for trade between West Africa and other parts of the world. Goods such as gold, ivory, and spices were traded across the ocean, fostering economic development and cultural exchange. European exploration of the Atlantic also led to the establishment of colonies and trading posts along the West African coast, profoundly shaping the region's political landscape.
The Impact of Colonialism and Globalization
The arrival of Europeans and the subsequent colonization of West African nations had a profound impact on the region's relationship with the Atlantic. Colonial powers exploited the continent's resources, contributing to economic imbalances that persist today. Globalization has also significantly impacted West Africa's relationship with the Atlantic, leading to increased trade and investment, but also posing challenges in terms of environmental sustainability and economic inequality.
The Atlantic Ocean Today: Challenges and Opportunities
The Atlantic Ocean continues to play a crucial role in the lives of West Africans, presenting both challenges and opportunities.
Sustainable Development and Conservation
Balancing economic development with environmental sustainability is a major challenge facing West African nations. Overfishing, pollution, and coastal erosion pose significant threats to the region's marine ecosystems. Sustainable development strategies are crucial to ensure that the benefits of the Atlantic are shared equitably and that the ocean's resources are managed responsibly for future generations.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change is exacerbating existing challenges in West Africa. Rising sea levels, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and changes in ocean currents pose serious threats to coastal communities and ecosystems. Adaptation and mitigation strategies are vital to reduce the impacts of climate change on the region.
Maritime Security and Piracy
The Atlantic Ocean is also a scene of maritime security challenges. Piracy and other illegal activities threaten shipping lanes and coastal communities. International cooperation and improved maritime security measures are essential to address these concerns.
Economic Opportunities
Despite the challenges, the Atlantic Ocean also presents significant economic opportunities for West Africa. Sustainable tourism, offshore renewable energy, and responsible fisheries management can contribute to economic growth and create jobs. Investing in infrastructure and promoting sustainable development is key to unlocking these opportunities.
Conclusion: A Complex and Vital Relationship
The Atlantic Ocean's relationship with West Africa is complex and multifaceted. It has shaped the continent’s history, its environment, and its future prospects. Understanding this deep connection is crucial for fostering sustainable development, addressing environmental challenges, and ensuring the equitable sharing of the ocean’s resources. As West African nations continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by the Atlantic, a commitment to responsible stewardship of this vital resource will be essential for the region's prosperity and stability. The future of West Africa is inextricably linked to the health and well-being of the Atlantic Ocean.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A 1 1 Ratio
Mar 19, 2025
-
5 Paragraph Essay Benefits Of Exercise
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Bone Does Not Articulate With Any Other Bone
Mar 19, 2025
-
Square Root Of 3 Divided By 3
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Undergoes Solvolysis In Methanol Most Rapidly
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Ocean Is West Of Africa . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
