Why Heart Is On Left Side
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
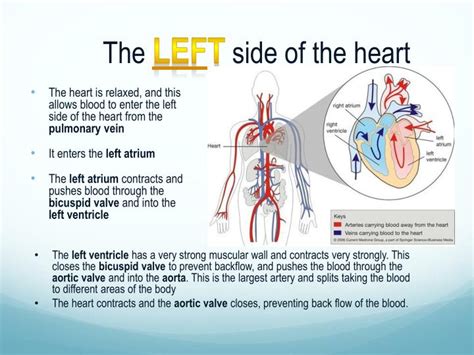
Table of Contents
Why Is the Heart on the Left Side? A Deep Dive into Cardiac Asymmetry
The human heart, a tireless engine of life, resides predominantly on the left side of the chest cavity. This seemingly simple fact belies a complex story interwoven with developmental biology, evolutionary pressures, and the intricate mechanics of our circulatory system. While seemingly straightforward, the question of why the heart is on the left side opens a fascinating window into the remarkable processes that shape our anatomy and physiology. This article will explore the multifaceted reasons behind this leftward positioning, delving into the intricacies of embryonic development, the impact of situs solitus (normal organ placement), and the potential consequences of situs inversus (reversed organ placement).
The Genesis of Asymmetry: Embryonic Development and the Left-Right Axis
The journey towards a left-sided heart begins long before birth, in the intricate dance of cellular signaling during embryonic development. Early in embryonic development, the seemingly symmetrical embryo must establish a clear left-right axis. This crucial step determines the placement of internal organs, including the heart, lungs, liver, and spleen. This process isn't a simple matter of chance; instead, it's a carefully orchestrated molecular cascade driven by a complex interplay of signaling pathways.
The Role of the Nodal Cilium: A Tiny Motor Driving Asymmetry
A pivotal player in this process is the nodal cilia, a tiny hair-like structure found on the surface of cells in the node, a crucial region of the early embryo. These cilia, beating in a coordinated clockwise motion, create a leftward flow of fluid. This leftward flow is not merely a passive movement; it's a vital signal, transporting morphogens – signaling molecules that influence cell fate and development. These morphogens, such as Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and Activin, are differentially distributed, with higher concentrations on the left side of the embryo.
Downstream Signaling Pathways: Translating Fluid Flow into Organ Placement
This asymmetrical distribution of morphogens triggers a cascade of downstream signaling events, activating specific genes on the left side and suppressing them on the right. This differential gene expression dictates the development and positioning of various organs. One crucial pathway involves the Nodal gene, which is activated by the leftward flow and plays a critical role in establishing left-right asymmetry in the developing heart.
Defects in this intricate signaling system can result in serious congenital heart defects and other conditions involving organ reversal or malposition. These conditions highlight the critical importance of proper left-right axis determination.
Situs Solitus: The Usual Arrangement
The normal arrangement of organs, with the heart predominantly on the left, is termed situs solitus. This arrangement is the most common and allows for the efficient function of the circulatory and respiratory systems. The left-sided position of the heart optimizes its interaction with the lungs, maximizing oxygen uptake and efficient circulation throughout the body.
Advantages of a Left-Sided Heart in Situs Solitus
The left-sided heart in situs solitus offers several key advantages:
- Efficient Blood Flow: The placement of the heart allows for efficient blood flow to and from the lungs, optimizing gas exchange. The aorta, the major artery carrying oxygenated blood from the heart, is ideally positioned to distribute this oxygenated blood efficiently throughout the body.
- Optimal Venous Return: The position of the vena cava, the major vein returning deoxygenated blood to the heart, is optimized for efficient blood return to the heart. This efficient venous return supports optimal cardiac output and systemic circulation.
- Space Optimization: The left-sided position of the heart is efficient in terms of thoracic space utilization, allowing other organs to be optimally positioned within the chest cavity.
Situs Inversus: A Mirror Image of Normal Anatomy
In contrast to situs solitus, situs inversus is a rare condition where the major visceral organs are reversed or mirrored. In situs inversus totalis, the heart is predominantly located on the right side, and other organs are correspondingly reversed. Interestingly, individuals with situs inversus often lead relatively normal lives, demonstrating the remarkable adaptability of the human body.
Functioning Despite the Reversal: The Remarkable Adaptability of the Body
Despite the reversed organ placement, the circulatory and other systems in situs inversus usually function normally. The circulatory system adapts to the reversed anatomy, maintaining efficient blood flow and oxygen delivery. This adaptation underscores the inherent flexibility and robustness of the cardiovascular system.
The Mystery of Situs Inversus: Unraveling the Genetic and Environmental Factors
The exact causes of situs inversus remain an area of ongoing research. Genetic mutations affecting the left-right axis determination pathways are known to be involved. However, environmental factors may also play a role. This highlights the interplay of genetics and the environment in shaping human anatomy.
The Evolutionary Perspective: Did Natural Selection Favor a Left-Sided Heart?
While the mechanisms of left-right asymmetry during development are well-studied, the evolutionary reasons for the prevalence of situs solitus remain less clear. One hypothesis suggests that the leftward position of the heart might offer subtle advantages in terms of biomechanics and efficient blood flow.
Hypotheses Regarding Evolutionary Advantages
Several theories attempt to explain the evolutionary advantage of a left-sided heart:
- Reduced Torque: The leftward displacement of the heart might reduce the rotational torque on the circulatory system, improving efficiency.
- Improved Venous Return: The leftward positioning might enhance venous return to the heart, improving cardiac output.
- Space Optimization: A left-sided heart might be advantageous in terms of space utilization within the thoracic cavity, optimizing the arrangement and function of other vital organs.
Further research is needed to fully elucidate the evolutionary pressures that led to the establishment of the left-sided heart as the predominant configuration in humans.
Conclusion: A Complex Symphony of Development and Evolution
The question of why the heart is on the left side is far from trivial. It's a question that delves into the fascinating intricacies of embryonic development, the remarkable adaptability of the human body, and the evolutionary pressures that have shaped our anatomy. The meticulous choreography of molecular signaling pathways, the critical role of the nodal cilia, and the remarkable resilience of the cardiovascular system in cases of situs inversus all contribute to this captivating story. While the precise evolutionary pressures remain a subject of ongoing investigation, the process of left-right axis determination and the resultant left-sided heart are testaments to the elegant complexity of human biology. Future research focusing on genetic influences, environmental factors, and the biomechanics of the circulatory system will continue to shed light on this fundamental aspect of human anatomy. The study of situs inversus, while rare, provides invaluable insights into the underlying mechanisms governing organ placement and the robustness of our biological systems. Understanding these processes is crucial for advancing our knowledge of congenital heart defects and other related conditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Oxidation Number Of Carbon In Co
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is Friction A Non Conservative Force
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Graphs Represents A One To One Function
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is B2 2 Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic
Apr 03, 2025
-
Capital Of Karnataka State In India
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Heart Is On Left Side . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
