Which Type Of Electromagnetic Wave Has The Shortest Wavelength
News Leon
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
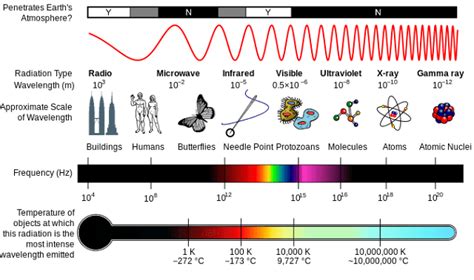
Table of Contents
Which Type of Electromagnetic Wave Has the Shortest Wavelength?
The electromagnetic spectrum is a vast and fascinating expanse, encompassing a wide range of wave types, each with its unique properties and applications. From the long wavelengths of radio waves to the incredibly short wavelengths of gamma rays, these waves play crucial roles in our understanding of the universe and our daily lives. But which type of electromagnetic wave boasts the shortest wavelength? The answer, unequivocally, is gamma rays.
Understanding the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Before delving into the specifics of gamma rays, it's essential to establish a firm grasp of the electromagnetic spectrum itself. This spectrum represents the entire range of electromagnetic radiation, ordered by frequency and wavelength. These two properties are inversely proportional; as frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa. The spectrum, broadly categorized, includes:
-
Radio Waves: These waves possess the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies, used extensively in communication technologies like radio broadcasting, television, and Wi-Fi.
-
Microwaves: Shorter than radio waves, microwaves are utilized in radar systems, microwave ovens, and satellite communication. Their shorter wavelength allows for more focused transmission and reception.
-
Infrared Radiation: This type of electromagnetic radiation is felt as heat and is responsible for the warmth we receive from the sun. It's widely used in thermal imaging, remote controls, and various industrial applications.
-
Visible Light: The only portion of the electromagnetic spectrum visible to the human eye, visible light ranges from violet (shortest wavelength) to red (longest wavelength).
-
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Shorter than visible light, UV radiation is invisible to the human eye but can cause sunburn and damage to DNA. It's also utilized in sterilization processes and forensic investigations.
-
X-rays: These high-energy waves have even shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than UV radiation. They are widely used in medical imaging and material analysis due to their ability to penetrate soft tissue.
-
Gamma Rays: At the far end of the spectrum, gamma rays possess the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. They are extremely high-energy and highly penetrating.
Gamma Rays: The Champions of Short Wavelengths
Gamma rays stand out due to their exceptionally short wavelengths, typically ranging from less than 10 picometers (pm) to less than 10 femtometers (fm). This translates to frequencies exceeding 10<sup>19</sup> Hz. To put this into perspective, a picometer is one trillionth of a meter, and a femtometer is one quadrillionth of a meter. These unbelievably short wavelengths and correspondingly high energies make gamma rays incredibly powerful and potentially dangerous.
The Origin of Gamma Rays
Gamma rays originate from a variety of sources, both terrestrial and extraterrestrial. Some common sources include:
-
Nuclear Reactions: Nuclear fission and fusion processes, such as those occurring in nuclear power plants and stars, are significant sources of gamma radiation. These reactions release immense amounts of energy, a substantial portion of which is emitted as gamma rays.
-
Radioactive Decay: Certain radioactive isotopes undergo decay processes that release gamma rays as they transition to a more stable state. This radioactive decay is utilized in various medical applications, such as cancer treatment.
-
Cosmic Sources: Beyond Earth, gamma rays are emitted from a wide range of cosmic sources, including supernovae (exploding stars), quasars (extremely luminous and distant celestial objects), and pulsars (rapidly rotating neutron stars). The study of these cosmic gamma rays provides invaluable insights into the high-energy processes occurring in the universe.
The Properties of Gamma Rays
Several key properties distinguish gamma rays from other types of electromagnetic radiation:
-
High Energy: The most defining characteristic of gamma rays is their incredibly high energy. Their short wavelengths and high frequencies directly correlate with their high energy content. This high energy allows them to penetrate matter effectively.
-
Penetrating Power: Due to their high energy, gamma rays possess remarkable penetrating power. They can easily pass through many materials, including soft tissue, making them challenging to shield against. This necessitates specialized shielding materials, such as lead or concrete, to mitigate the risks associated with gamma radiation exposure.
-
Ionizing Radiation: Gamma rays are a form of ionizing radiation, meaning they can strip electrons from atoms, creating ions. This ionization can damage biological molecules like DNA, potentially leading to cell death or mutations. This is why exposure to high levels of gamma radiation is harmful to living organisms.
-
Wave-Particle Duality: Like all electromagnetic radiation, gamma rays exhibit wave-particle duality, meaning they behave as both waves and particles. They can be described as streams of high-energy photons, the fundamental particles of light.
Applications of Gamma Rays
Despite their potential hazards, gamma rays have numerous beneficial applications in various fields:
-
Medical Imaging and Therapy: Gamma rays are utilized in medical imaging techniques, such as gamma cameras, and in cancer therapy through techniques like gamma knife radiosurgery. These applications leverage the penetrating power and high energy of gamma rays to diagnose and treat diseases.
-
Industrial Applications: Gamma rays are employed in industrial processes for sterilization, material analysis, and quality control. Their ability to penetrate materials makes them useful for detecting flaws in welds or examining the internal structure of objects.
-
Scientific Research: Gamma-ray astronomy is a significant branch of astronomy that studies celestial sources of gamma radiation. This research provides crucial information about the most energetic processes in the universe.
Comparing Gamma Rays to Other High-Frequency Waves
While other high-frequency electromagnetic waves, such as X-rays, also possess short wavelengths, gamma rays consistently hold the title of having the shortest. The difference isn't merely a matter of degree; it reflects a significant distinction in their origins and energy levels. X-rays are typically generated through interactions with electrons, while gamma rays originate from nuclear transitions or other high-energy processes within the nucleus of an atom. This fundamental difference in origin leads to the significantly higher energy and shorter wavelengths of gamma rays.
The Importance of Understanding Gamma Rays
Understanding the properties and characteristics of gamma rays is crucial for several reasons:
-
Safety Precautions: Awareness of the dangers of gamma radiation is vital to ensure appropriate safety measures are taken when working with or near gamma ray sources. This includes the use of specialized shielding and monitoring equipment.
-
Technological Advancements: The applications of gamma rays in medicine, industry, and scientific research are constantly evolving, leading to advancements in various fields.
-
Understanding the Universe: The study of cosmic gamma rays provides invaluable insights into the high-energy processes and structures within our universe, helping us to understand the universe's evolution and composition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gamma rays undoubtedly possess the shortest wavelengths among all types of electromagnetic waves. Their incredibly short wavelengths and high energies have far-reaching implications, impacting various aspects of science, technology, and medicine. Understanding their properties and applications is critical for both safety and technological advancement, allowing us to harness their power responsibly while mitigating potential risks. The continuing exploration of gamma rays promises to reveal further insights into the universe and advance technological capabilities even further.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Initialize A Tuple In Python
Apr 02, 2025
-
Find The Acceleration When The Velocity Is 0
Apr 02, 2025
-
Are Metals Solid At Room Temperature
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Correctly Describes Gene Linkage
Apr 02, 2025
-
Complete The Complementary Strand Of Dna
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Type Of Electromagnetic Wave Has The Shortest Wavelength . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
