Which Of The Following Statements Correctly Describes Gene Linkage
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
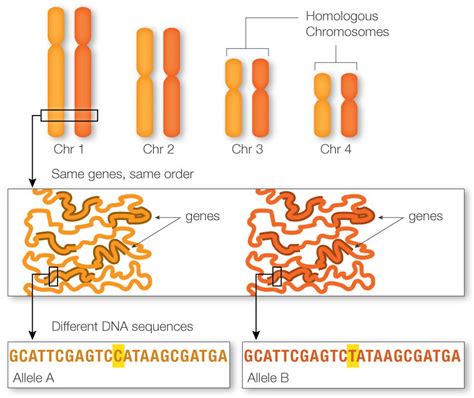
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Statements Correctly Describes Gene Linkage?
Gene linkage is a fundamental concept in genetics, explaining the inheritance patterns of genes located on the same chromosome. Understanding gene linkage is crucial for comprehending various genetic phenomena, including the construction of genetic maps and the prediction of inheritance patterns in offspring. This article will delve into the concept of gene linkage, exploring its definition, mechanisms, and implications. We'll analyze several statements about gene linkage, determining their accuracy and providing a comprehensive understanding of this vital genetic principle.
Understanding Gene Linkage: The Basics
Genes residing on the same chromosome are said to be linked. Unlike independently assorting genes, linked genes tend to be inherited together during meiosis, the process of cell division that produces gametes (sperm and egg cells). This occurs because linked genes are physically close to each other on the chromosome, meaning they're less likely to be separated during the process of crossing over (recombination).
Independent Assortment vs. Gene Linkage
Independent assortment, described by Mendel's Second Law, states that during gamete formation, alleles for different genes segregate independently of each other. This applies to genes located on different chromosomes. However, gene linkage demonstrates that genes located close together on the same chromosome often defy independent assortment, exhibiting a tendency to be inherited together.
The Role of Crossing Over
Crossing over, also known as recombination, is a crucial event during meiosis. It involves the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes (pairs of chromosomes, one from each parent). While crossing over can separate linked genes, the frequency of separation depends on the distance between them. Genes that are physically close together have a lower probability of being separated by crossing over, whereas genes that are farther apart have a higher probability.
Analyzing Statements About Gene Linkage
Now let's examine several statements about gene linkage and determine which correctly describes the concept:
Statement 1: Linked genes are always inherited together.
Accuracy: False. While linked genes tend to be inherited together, crossing over can separate them. The frequency of separation depends on the distance between the genes.
Statement 2: Gene linkage violates Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment.
Accuracy: Partially True. Gene linkage appears to violate Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment for genes on the same chromosome. However, it's more accurate to say it modifies it. The law applies perfectly to genes on separate chromosomes.
Statement 3: The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the higher the probability of recombination between them.
Accuracy: False. The opposite is true. The closer two genes are, the lower the probability of recombination. Physical proximity reduces the chance of a crossover event separating them.
Statement 4: Gene mapping uses recombination frequencies to estimate the distances between genes on a chromosome.
Accuracy: True. This is a core principle of gene mapping. The recombination frequency (the percentage of recombinant offspring) is directly proportional to the distance between genes. A higher recombination frequency indicates a greater distance. This relationship allows geneticists to create genetic maps showing the relative positions of genes on chromosomes.
Statement 5: Linked genes always exhibit a 1:1:1:1 phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross.
Accuracy: False. A 1:1:1:1 ratio is characteristic of independent assortment. Linked genes will show a deviation from this ratio, with a higher proportion of parental phenotypes (phenotypes matching the parents) and a lower proportion of recombinant phenotypes. The exact ratio depends on the distance between the linked genes.
Statement 6: The strength of linkage between two genes is inversely proportional to the distance between them.
Accuracy: True. The further apart two genes are, the weaker the linkage because the probability of crossing over increases, leading to more recombinant offspring. Conversely, genes that are very close together are strongly linked and show a low recombination frequency.
Statement 7: Recombination frequency can be used to construct genetic maps.
Accuracy: True. Recombination frequencies are fundamental to constructing genetic maps. By analyzing the frequency of recombinant offspring in crosses involving linked genes, geneticists can estimate the relative distances between genes on a chromosome. One map unit (centimorgan) represents a 1% recombination frequency.
Statement 8: Gene linkage is only observed in diploid organisms.
Accuracy: False. While gene linkage is readily observed in diploid organisms (organisms with two sets of chromosomes), the principle applies to any organism with multiple genes located on the same chromosome, including haploid organisms.
Statement 9: All genes on the same chromosome are always linked.
Accuracy: False. While genes on the same chromosome tend to be linked, the strength of linkage varies depending on the distance between them. Genes that are very far apart on the same chromosome might exhibit near-independent assortment due to frequent crossing over.
Statement 10: The detection of linked genes provides evidence against the idea of independent assortment.
Accuracy: True. The observation of linked genes directly contradicts the prediction of independent assortment for genes on the same chromosome. The deviation from expected Mendelian ratios in dihybrid crosses is strong evidence for gene linkage.
Applications of Gene Linkage
Understanding gene linkage has several significant applications:
-
Genetic Mapping: As previously mentioned, gene linkage is crucial for creating genetic maps that illustrate the relative positions of genes on chromosomes. These maps are invaluable for understanding genome organization and for identifying genes associated with specific traits or diseases.
-
Disease Gene Identification: Linkage analysis is a powerful tool for identifying genes responsible for inherited diseases. By studying the inheritance patterns of markers (DNA sequences with known locations) linked to disease genes, researchers can narrow down the chromosomal region containing the disease-causing gene.
-
Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS): In agriculture, MAS utilizes linked markers to select desirable traits in plants and animals. By identifying markers linked to genes for yield, disease resistance, or other traits, breeders can efficiently select individuals with the desired characteristics.
-
Evolutionary Studies: The analysis of gene linkage patterns can provide insights into evolutionary relationships between species. Changes in linkage patterns over time can reflect evolutionary events such as chromosomal rearrangements or gene duplications.
Conclusion
Gene linkage is a critical concept in genetics, demonstrating that the inheritance of genes on the same chromosome is often non-random. While crossing over can separate linked genes, the frequency of separation depends on the distance between them. Understanding the intricacies of gene linkage is essential for genetic mapping, disease gene identification, and various applications in agriculture and evolutionary biology. Statements that accurately describe gene linkage emphasize the relationship between gene distance and recombination frequency, the deviation from independent assortment, and the application of linkage analysis in genetic mapping. Remember, while genes on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together, the strength of linkage is variable and depends on the distance separating them. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding requires considering both the concept of linkage and the influence of crossing over.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Select The Correct Statement About Plant Life Cycles
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Phosphoric Acid
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Type Of Joint Is In The Skull
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Implicit Cost Of Production
Apr 03, 2025
-
Select The Sentence That Is Punctuated Correctly
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Statements Correctly Describes Gene Linkage . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
