Which Of The Following Statements Is True Regarding Goal-setting Theory
News Leon
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
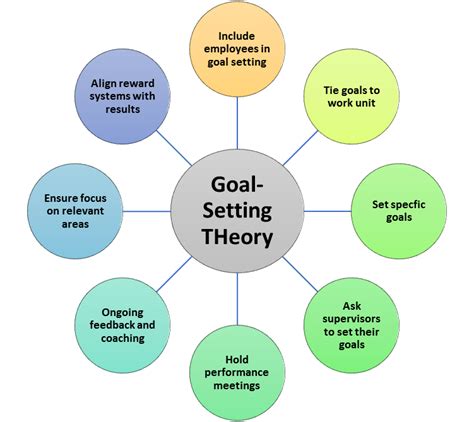
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Statements is True Regarding Goal-Setting Theory?
Goal-setting theory, a cornerstone of organizational behavior and performance management, proposes that specific and challenging goals lead to higher performance than vague or easy ones. However, the nuances of this theory are often overlooked. This article will delve into the core tenets of goal-setting theory, examining common misconceptions and clarifying the conditions under which its principles hold true. We will analyze several statements regarding the theory, identifying the accurate ones and explaining why others are inaccurate or require further qualification.
Understanding Goal-Setting Theory: The Fundamentals
Before we analyze the truthfulness of various statements, it's crucial to establish a solid understanding of goal-setting theory's foundational principles. Developed primarily by Edwin Locke and Gary Latham, this theory posits that:
-
Goal Specificity: Vague goals like "do your best" are significantly less effective than specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. A specific goal clearly defines what needs to be accomplished, leaving no room for ambiguity.
-
Goal Difficulty: Challenging goals, while demanding more effort, consistently result in higher performance than easy goals. This is because challenging goals encourage greater effort, persistence, and the development of more effective strategies.
-
Goal Commitment: Individuals must be committed to the goals for them to be effective. Commitment stems from factors like understanding the goal's importance, having the necessary resources, and believing in one's ability to achieve the goal (self-efficacy).
-
Feedback: Regular feedback on progress towards the goal is crucial. Feedback allows for adjustments in strategies, increases motivation, and reinforces commitment.
-
Task Complexity: The impact of goal-setting is influenced by task complexity. For complex tasks, the process of goal-setting might involve breaking down the task into smaller, more manageable subgoals.
Analyzing Statements Regarding Goal-Setting Theory
Now let's examine some statements about goal-setting theory and determine their accuracy:
Statement 1: Goal-setting theory suggests that the more challenging the goal, the higher the performance, regardless of other factors.
FALSE. While challenging goals generally lead to higher performance, this is not universally true. This statement ignores crucial factors like goal commitment, feedback, and task complexity. An overly challenging goal, without sufficient support or resources, can lead to frustration, decreased motivation, and ultimately, lower performance. The optimal level of goal difficulty is a balance between challenge and achievability, taking individual capabilities and contextual factors into consideration.
Statement 2: Specific goals always lead to better performance than general goals.
TRUE (with qualifications). Research overwhelmingly supports the superior effectiveness of specific goals compared to general goals. Specific goals provide clear direction, making it easier to monitor progress and adjust strategies as needed. However, the effectiveness of specific goals depends on the individual's commitment and the availability of resources. A highly specific but unattainable goal might have a detrimental effect.
Statement 3: Goal-setting theory is solely dependent on the individual's intrinsic motivation.
FALSE. While intrinsic motivation—the desire to engage in an activity for its own sake—plays a role, goal-setting theory acknowledges the significance of both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Extrinsic motivators, such as rewards and recognition, can significantly enhance commitment to goals and drive performance. A comprehensive approach to goal-setting considers both types of motivation.
Statement 4: Feedback is unnecessary if the goal is clearly defined and challenging enough.
FALSE. Feedback is a crucial component of goal-setting theory. Even with a well-defined and challenging goal, regular feedback is necessary to track progress, identify potential obstacles, and make necessary adjustments to strategies. Feedback provides valuable information, enhances motivation, and reinforces commitment. Without feedback, individuals might become discouraged or adopt inefficient approaches.
Statement 5: Goal-setting theory applies equally to all types of tasks and individuals.
FALSE. While the core principles of goal-setting theory are widely applicable, its effectiveness can vary depending on the nature of the task and the individual's characteristics. For example, highly creative tasks might benefit less from highly specific goals, as they require flexibility and exploration. Similarly, individuals with low self-efficacy might need more support and less challenging goals to build confidence and achieve success. The optimal application of goal-setting theory requires considering individual differences and task characteristics.
Expanding on Key Aspects of Goal-Setting Theory
Let's delve deeper into some critical aspects of goal-setting theory that often get overlooked:
The Role of Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy, or an individual's belief in their ability to succeed, significantly influences goal commitment and performance. Individuals with high self-efficacy are more likely to set challenging goals, persist in the face of obstacles, and ultimately achieve higher performance. Conversely, individuals with low self-efficacy might avoid challenging goals or give up easily. Goal-setting interventions should consider bolstering self-efficacy through training, mentoring, and providing opportunities for successful experiences.
The Importance of Participation in Goal Setting
Participative goal setting, where individuals actively participate in defining their goals, often leads to higher commitment and performance than assigned goals. Participation fosters a sense of ownership and increases the likelihood that individuals will invest the necessary effort to achieve their goals. However, participation alone is not sufficient; the goals must still be specific, challenging, and achievable.
The Influence of Organizational Context
The organizational context significantly impacts the effectiveness of goal-setting. Factors such as organizational culture, leadership support, resource availability, and the clarity of roles and responsibilities influence an individual's ability to achieve their goals. A supportive and encouraging organizational environment is crucial for fostering goal commitment and maximizing performance.
The Consideration of Multiple Goals
Individuals often pursue multiple goals simultaneously. The interaction between these goals can influence their overall effectiveness. For instance, conflicting goals can lead to reduced performance, while compatible goals can enhance motivation and achievement. Effective goal-setting requires careful consideration of the potential interactions between multiple goals.
Practical Applications and Conclusion
Goal-setting theory provides a powerful framework for enhancing individual and organizational performance. However, its successful application requires a nuanced understanding of its principles and the contextual factors that influence its effectiveness. Managers and individuals should strive to set SMART goals, foster goal commitment, provide regular feedback, and consider individual differences and task complexity.
To summarize, understanding goal-setting theory extends beyond simple adherence to SMART goals. It involves a comprehensive understanding of human motivation, the interplay between intrinsic and extrinsic rewards, the impact of self-efficacy, and the crucial role of feedback and organizational support. By appreciating these complexities, we can harness the full potential of goal-setting theory to achieve remarkable outcomes. The statements analyzed earlier highlight the importance of avoiding oversimplification and embracing a more nuanced, holistic approach to effective goal setting. Remember that the key to success lies in creating a synergistic relationship between challenging goals, supportive environments, and empowered individuals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Friction A Non Conservative Force
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Graphs Represents A One To One Function
Apr 03, 2025
-
Is B2 2 Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic
Apr 03, 2025
-
Capital Of Karnataka State In India
Apr 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Substances Should Not Be Filtered
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Statements Is True Regarding Goal-setting Theory . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
