Which Of The Following Is An Essential Fatty Acid
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
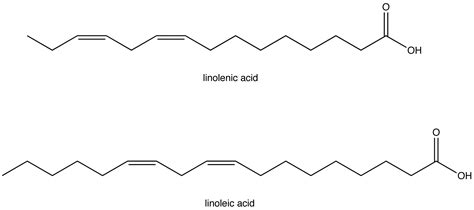
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is an Essential Fatty Acid? Understanding EFAs and Their Importance
Essential fatty acids (EFAs) are a crucial part of a healthy diet, playing a vital role in numerous bodily functions. Unlike other fatty acids, our bodies cannot produce EFAs, making it essential to obtain them through our diet. But which fatty acids actually fall under this critical category? This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of EFAs, exploring their types, benefits, and sources, helping you understand why they’re essential for optimal health.
Understanding Essential Fatty Acids: The Basics
Essential fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are vital for various physiological processes. The term "essential" emphasizes their necessity for survival; our bodies can't synthesize them, so we must consume them from food. Deficiencies can lead to serious health problems, highlighting their importance in maintaining overall well-being.
There are two main families of EFAs:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Known for their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3s are crucial for brain health, cardiovascular health, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Omega-6 fatty acids: While also important, omega-6 fatty acids need to be balanced with omega-3s. An imbalance, with excessive omega-6 intake, can contribute to inflammation.
Identifying EFAs: A Closer Look at the Chemical Structures
The "omega" designation refers to the location of the last double bond in the fatty acid chain. Omega-3 fatty acids have their last double bond three carbons from the omega (methyl) end of the molecule. Similarly, omega-6 fatty acids have their last double bond six carbons from the omega end. This seemingly minor difference in molecular structure has profound effects on their biological activity and impact on our health.
Key Players: Specific Essential Fatty Acids
While the omega-3 and omega-6 categories encompass multiple fatty acids, several stand out due to their abundance and significant health benefits.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
-
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): This is the parent omega-3 fatty acid, meaning the body can convert it into other, more biologically active omega-3s, although this conversion is often inefficient. ALA is found primarily in plant-based foods.
- Sources: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and canola oil.
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): EPA is a more potent omega-3 fatty acid, directly contributing to various health benefits. While the body can convert ALA to EPA, the conversion rate is low. Therefore, direct consumption from fatty fish is recommended.
- Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, sardines, and anchovies.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): DHA is another highly active omega-3 fatty acid crucial for brain function, eye health, and reducing inflammation. Like EPA, DHA is efficiently obtained through direct consumption.
- Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, sardines, and anchovies. Also found in smaller amounts in algae.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids:
-
Linoleic acid (LA): This is the parent omega-6 fatty acid, acting as a precursor to other omega-6s like arachidonic acid. While essential, maintaining a healthy balance with omega-3s is crucial.
- Sources: Vegetable oils like soybean oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, and safflower oil. Also found in nuts and seeds.
-
Arachidonic acid (AA): This omega-6 fatty acid is involved in inflammation, but it also plays a role in other bodily functions. The balance between AA and EPA/DHA is critical for optimal health. AA is synthesized from LA in the body.
- Sources: Meat, poultry, and eggs.
The Importance of a Balanced Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio
The ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids in the diet is crucial for overall health. The modern Western diet often contains a significantly higher proportion of omega-6 fatty acids compared to omega-3s. This imbalance can contribute to chronic inflammation, potentially increasing the risk of various health problems such as heart disease, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer.
Striving for a balanced ratio, ideally closer to 1:1 or even favoring omega-3s, is vital. This can be achieved by:
- Increasing omega-3 intake: Incorporate more fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts into your diet.
- Reducing omega-6 intake: Limit the consumption of processed foods, vegetable oils high in omega-6s, and fried foods.
Health Benefits of Essential Fatty Acids
The benefits of consuming sufficient EFAs are extensive and impact various aspects of health:
Cardiovascular Health:
- Reduced blood pressure: Omega-3 fatty acids can help lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Improved cholesterol levels: They can help improve triglyceride levels and increase HDL ("good") cholesterol.
- Reduced blood clotting: Omega-3s help prevent blood clot formation, reducing the risk of stroke.
Brain Health:
- Improved cognitive function: Omega-3s, particularly DHA, are essential for brain structure and function, supporting cognitive performance and memory.
- Reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases: Studies suggest that adequate omega-3 intake may help reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative conditions.
Mental Health:
- Reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety: Some research indicates that omega-3s may help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Eye Health:
- Improved vision: DHA is a critical component of the retina, essential for maintaining healthy vision and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Immune Function:
- Modulation of inflammation: EFAs play a key role in regulating the immune response, helping to reduce excessive inflammation.
Skin Health:
- Improved skin hydration and elasticity: EFAs are vital for maintaining healthy skin, reducing dryness and promoting elasticity.
Dietary Sources of Essential Fatty Acids: A Practical Guide
Incorporating EFAs into your diet is relatively straightforward. Here's a practical guide to include these essential nutrients:
Excellent Sources of Omega-3s:
- Fatty fish: Aim for at least two servings per week of fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, sardines, and anchovies.
- Flaxseeds: Add flaxseeds to your yogurt, smoothies, or salads. Grind them before consumption to improve absorption.
- Chia seeds: Similar to flaxseeds, chia seeds can be added to various dishes.
- Walnuts: Enjoy walnuts as a snack or add them to salads and baked goods.
- Canola oil: Use canola oil for cooking or as a salad dressing (in moderation).
Good Sources of Omega-6s (consume in moderation):
- Nuts and seeds: These contain LA, but consume them in moderation to maintain a healthy balance with omega-3s.
- Vegetable oils: Use these sparingly, opting for olive oil as a primary cooking oil.
Important Considerations:
- Supplementation: If you struggle to meet your EFA requirements through diet alone, consider supplementing with high-quality omega-3 supplements, particularly EPA and DHA. However, always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
- Food preparation: Avoid frying foods, as high heat can damage the beneficial fatty acids. Opt for baking, grilling, or steaming instead.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While EFAs are essential for health, excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids can be detrimental. A skewed omega-6 to omega-3 ratio can contribute to chronic inflammation, so moderation is key.
Also, individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medication should exercise caution when consuming high amounts of omega-3s, as they can increase the risk of bleeding. Consult your doctor before making significant dietary changes, particularly if you have any underlying health conditions.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Essential Fatty Acids for Optimal Health
Essential fatty acids are indispensable for numerous bodily functions, impacting cardiovascular health, brain function, mental well-being, and more. By understanding the different types of EFAs, their sources, and the importance of maintaining a balanced omega-3 to omega-6 ratio, you can take proactive steps to optimize your health and well-being. Remember to incorporate a variety of EFA-rich foods into your diet and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your intake or have underlying health conditions. Prioritizing EFAs is an investment in your long-term health and vitality.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Cannot Be A Probability
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is A Metaloids Considered A Noble Gas
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does As Have
Mar 26, 2025
-
Select The Correct Statement About Cardiac Output
Mar 26, 2025
-
Why Is Dna Replication Called Semiconservative
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is An Essential Fatty Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
