Which Of The Following Is A Nonrenewable Source Of Energy
News Leon
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
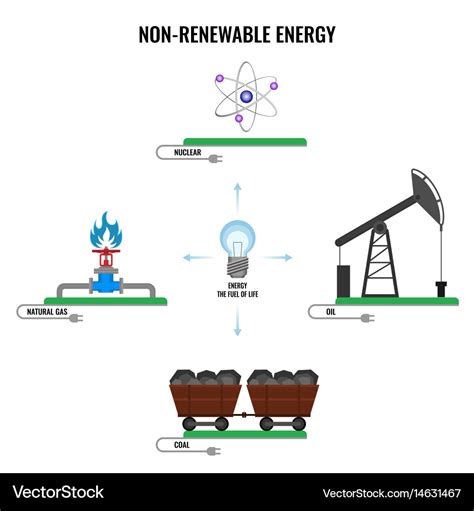
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Nonrenewable Source of Energy? Understanding Finite Resources
The world runs on energy. From the electricity powering our homes to the fuel propelling our vehicles, energy is the lifeblood of modern civilization. But where does this energy come from? Understanding the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources is crucial, not only for our present comfort but for the sustainability of our future. This article delves deep into the nature of nonrenewable energy sources, exploring their characteristics, impacts, and the ongoing search for alternatives.
What are Nonrenewable Energy Sources?
Nonrenewable energy sources are natural resources that are finite and cannot be replenished within a human timescale. Once they are used up, they are gone. This depletion has significant environmental and economic consequences, driving the urgent need for global transitions towards renewable energy alternatives. The key characteristic distinguishing nonrenewable sources is their limited supply. They formed over millions of years through geological processes, and their consumption significantly outpaces their natural rate of formation.
Key Characteristics of Nonrenewable Energy Sources:
- Finite Supply: The defining feature. These resources exist in fixed quantities, and their extraction and consumption lead to eventual depletion.
- Long Formation Times: Millions of years were needed for the formation of these resources through geological processes.
- Environmental Impact: Their extraction and combustion often result in significant pollution, contributing to climate change and other environmental problems.
- Geopolitical Implications: The uneven distribution of nonrenewable resources across the globe creates geopolitical complexities and dependencies.
Types of Nonrenewable Energy Sources:
Several types fall under the umbrella of nonrenewable energy. Each has its unique characteristics, applications, and associated environmental impacts. Let's explore them in detail:
1. Fossil Fuels: The Dominant Players
Fossil fuels – coal, oil (petroleum), and natural gas – are the most widely used nonrenewable energy sources globally. They've powered industrialization and continue to fuel much of the world's economy. However, their use comes with considerable drawbacks.
a) Coal: The Ancient Fuel
Coal, formed from ancient plant matter subjected to intense pressure and heat over millions of years, is a relatively abundant fossil fuel. It's primarily used for electricity generation in power plants.
- Advantages: Abundant and relatively inexpensive (though this is becoming less true as extraction becomes more difficult).
- Disadvantages: High carbon emissions, contributing significantly to climate change; air and water pollution from mining and combustion; land degradation from mining operations.
b) Oil (Petroleum): The Versatile Resource
Oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, found in underground reservoirs. It's incredibly versatile, used as fuel for transportation (gasoline, diesel), heating, and in the production of plastics and other petrochemicals.
- Advantages: High energy density; versatility in applications.
- Disadvantages: Significant greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change; oil spills pose significant environmental risks; geopolitical instability linked to oil production and distribution.
c) Natural Gas: A Cleaner-Burning Alternative (Relatively Speaking)
Natural gas, primarily methane, is found alongside oil and in independent reservoirs. It’s often considered a "cleaner" fossil fuel than coal or oil because it produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions when burned. However, it still contributes to climate change and poses environmental risks.
- Advantages: Relatively cleaner burning than coal and oil (lower carbon emissions per unit of energy); efficient for electricity generation and heating.
- Disadvantages: Methane leakage during extraction and transportation contributes significantly to global warming; potential for groundwater contamination; risks associated with pipeline infrastructure.
2. Nuclear Energy: A Controversial Choice
Nuclear energy harnesses the power of atomic fission to generate electricity. It's a low-carbon source, but carries substantial risks and challenges.
- Advantages: Low greenhouse gas emissions; high energy density; relatively small land footprint compared to other energy sources.
- Disadvantages: Risk of nuclear accidents (Chernobyl, Fukushima); challenges in nuclear waste disposal (long-term storage required); potential for nuclear proliferation.
The Environmental Impact of Nonrenewable Energy: A Dire Situation
The extensive use of nonrenewable energy sources has had profound and often detrimental impacts on the environment:
- Climate Change: The combustion of fossil fuels releases vast quantities of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), driving global warming and climate change. This leads to rising sea levels, more frequent and intense extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems.
- Air Pollution: Burning fossil fuels releases pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM), which harm human health and contribute to acid rain and smog.
- Water Pollution: Extraction and processing of fossil fuels can contaminate water sources with heavy metals, chemicals, and other pollutants. Oil spills cause devastating damage to marine ecosystems.
- Land Degradation: Coal mining causes significant land degradation, destroying habitats and impacting biodiversity. Oil and gas extraction can also disrupt ecosystems and landscapes.
The Search for Alternatives: The Urgent Need for Transition
The environmental and economic consequences of relying on nonrenewable energy sources are becoming increasingly clear. The global community is actively pursuing a transition towards renewable energy sources. This transition is multifaceted and involves:
- Investing in Renewable Energy Technologies: Solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy are becoming increasingly cost-competitive and efficient.
- Improving Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through better building design, more efficient appliances, and improved transportation systems is crucial.
- Developing Smart Grids: Modernizing electricity grids to better integrate renewable energy sources and manage energy demand.
- Implementing Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Technologies that capture CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial facilities and store them underground are being developed, but their large-scale deployment faces significant challenges.
- Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Government policies and regulations are essential to incentivize the transition to renewable energy and phase out the use of fossil fuels. Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, can help to internalize the environmental costs of carbon emissions.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Requires Change
The continued reliance on nonrenewable energy sources is unsustainable. The environmental impacts are severe and growing, threatening the planet's ecosystems and human well-being. A rapid and comprehensive transition to renewable energy is not just desirable but absolutely necessary to ensure a sustainable future. This transition requires a multifaceted approach, involving technological innovation, policy changes, and a fundamental shift in societal attitudes towards energy consumption. The choices we make today will determine the quality of life for generations to come. Understanding the limitations and consequences of nonrenewable energy sources is the first step towards building a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world. The question, "Which of the following is a nonrenewable source of energy?" should prompt not just identification, but also a commitment to action.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Are Complementary Bases In Dna
Mar 31, 2025
-
Classify The Following As A Homogeneous Or A Heterogeneous Mixture
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Physical Quantity Does The Slope Represent
Mar 31, 2025
-
An Object Becomes Positively Charged By Gaining Protons
Mar 31, 2025
-
Right Hand Rule For Angular Velocity
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Nonrenewable Source Of Energy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
