Classify The Following As A Homogeneous Or A Heterogeneous Mixture
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
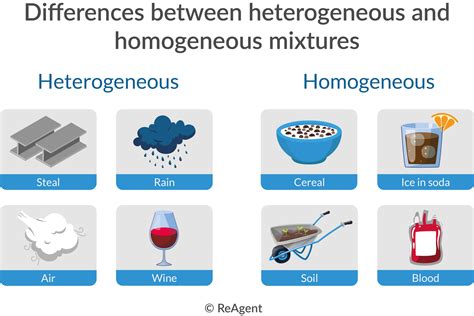
Table of Contents
Classifying Mixtures: Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous
Understanding the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures is fundamental to chemistry and many other scientific disciplines. This comprehensive guide will delve into the definitions, provide clear examples, and explore the characteristics that distinguish these two types of mixtures. We'll also address some nuanced cases that might initially seem confusing. By the end, you'll be able to confidently classify a wide range of mixtures.
What is a Mixture?
Before diving into the specifics of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, let's establish a clear understanding of what a mixture is. A mixture is a substance composed of two or more components that are not chemically bonded. This means the individual components retain their own chemical properties. Crucially, mixtures can be separated into their constituent parts by physical methods, such as filtration, distillation, evaporation, or chromatography. This contrasts with compounds, where the components are chemically bonded and require chemical reactions for separation.
Homogeneous Mixtures: Uniformity at the Microscopic Level
A homogeneous mixture is one that has a uniform composition throughout. This means that at a microscopic level, the components are evenly distributed, and you won't be able to distinguish the individual components with the naked eye or even with a typical optical microscope. The properties of a homogeneous mixture are consistent regardless of the sample size you take.
Key Characteristics of Homogeneous Mixtures:
- Uniform composition: The components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture.
- Single phase: A homogeneous mixture exists in a single phase (solid, liquid, or gas). You won't see distinct layers or regions of different composition.
- Invisible components: The individual components are not visually distinguishable.
- Consistent properties: Properties like density, color, and taste remain constant throughout the mixture.
Examples of Homogeneous Mixtures:
- Air: A mixture of primarily nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and trace amounts of other gases. While the gases have different properties, they are evenly dispersed, making air a homogeneous mixture.
- Saltwater: When salt (NaCl) dissolves completely in water, it forms a homogeneous mixture. The salt ions are evenly distributed throughout the water.
- Sugar water: Similar to saltwater, dissolved sugar in water creates a homogeneous solution.
- Brass: An alloy of copper and zinc, brass is a solid homogeneous mixture.
- Stainless steel: This metal alloy is another example of a solid homogeneous mixture consisting of iron, chromium, and other elements.
- Vinegar: A solution of acetic acid in water.
- Many commercially available drinks: Clear sodas, juices (before any pulp settles), and certain types of tea are typically homogeneous mixtures.
Heterogeneous Mixtures: A Lack of Uniformity
In contrast to homogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous mixtures exhibit a non-uniform composition. This means that the components are not evenly distributed, and you can visually distinguish the different parts. Different samples taken from a heterogeneous mixture will likely have different properties.
Key Characteristics of Heterogeneous Mixtures:
- Non-uniform composition: The components are not evenly distributed.
- Multiple phases: A heterogeneous mixture often exists in multiple phases, meaning you can see distinct regions with different compositions.
- Visible components: The individual components are visibly distinguishable.
- Inconsistent properties: Properties may vary depending on the sample location.
Examples of Heterogeneous Mixtures:
- Sand and water: The sand particles are clearly visible and settle at the bottom, creating distinct layers.
- Oil and water: Oil and water do not mix; they form two separate layers.
- Salad: A mixture of various vegetables and other ingredients, each retaining its identity and position.
- Soil: A complex mixture of minerals, organic matter, water, and air, with varying compositions at different locations within the soil sample.
- Granite: A rock composed of visibly distinct crystals of different minerals (quartz, feldspar, mica).
- Concrete: A mixture of cement, sand, gravel, and water. You can easily see the individual components.
- Pizza: A classic example, with visible layers and components like crust, sauce, cheese, and toppings.
- Trail mix: A heterogeneous mixture of nuts, seeds, dried fruits, and chocolates, each easily discernible.
- Blood: A suspension of various cells and platelets in plasma.
- Milk: Although it might appear homogeneous at first glance, milk is actually a heterogeneous mixture containing fat globules, proteins, and water. These components are not evenly distributed at a microscopic level.
Nuanced Cases and Considerations
Some mixtures can be tricky to classify definitively. The scale of observation is crucial. A mixture that appears homogeneous at a macroscopic level (with the naked eye) might be revealed as heterogeneous at a microscopic level (under a powerful microscope).
Colloids: A Special Case
Colloids are a type of mixture that blur the line between homogeneous and heterogeneous. They appear homogeneous to the naked eye, but under magnification, you can see distinct particles dispersed throughout the medium. These particles are larger than molecules but small enough to remain suspended, preventing immediate settling. Examples include milk (as mentioned earlier), fog, and ink. While exhibiting some characteristics of homogeneous mixtures, their microscopic heterogeneity sets them apart.
Suspensions: Clearly Heterogeneous
Suspensions are clearly heterogeneous mixtures. They contain larger particles that settle out over time if left undisturbed. Examples include muddy water and a mixture of sand and water.
Practical Applications and Importance
Understanding the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures has significant implications across various fields:
- Chemistry: Classifying mixtures is essential for designing separation techniques, understanding reaction kinetics, and predicting the properties of materials.
- Materials Science: The properties of materials often depend on whether they are homogeneous or heterogeneous mixtures. This influences their applications in engineering and manufacturing.
- Environmental Science: Analyzing the composition of air and water samples often requires distinguishing between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures to assess environmental quality.
- Food Science: Understanding the nature of food mixtures helps in processing, preservation, and quality control.
- Medicine: Many pharmaceutical formulations are mixtures, and their homogeneity is crucial for consistent dosage and efficacy.
Conclusion: Mastering Mixture Classification
Distinguishing between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures is a foundational concept in science. By understanding the key characteristics—uniformity of composition, the number of phases, and the visibility of components—you can confidently classify a wide range of mixtures. Remember that the scale of observation can influence classification, and some mixtures like colloids present nuanced cases. Mastering this distinction will enhance your understanding of the world around us and its intricate chemical composition. Continuously practicing identification through diverse examples will solidify your understanding and expertise in this important area of chemistry and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Short Term Unsecured Promissory Note Issued By A Company Is
Apr 01, 2025
-
Adjacent Angles Whose Sum In 180 Degrees
Apr 01, 2025
-
Lewis Dot Structure For Magnesium Chloride
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Group Of Related Records Is Called A Table
Apr 01, 2025
-
Provides Long Term Energy Storage For Animals
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Classify The Following As A Homogeneous Or A Heterogeneous Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
