Which Heart Chamber Has The Thickest Wall
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
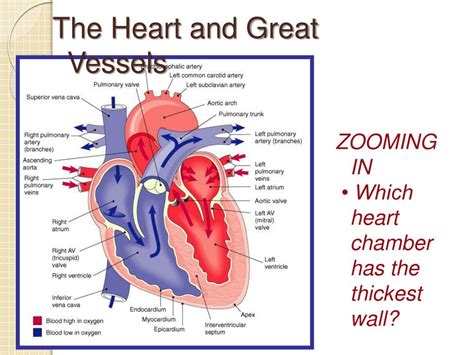
Table of Contents
Which Heart Chamber Has the Thickest Wall? Understanding Cardiac Anatomy and Function
The human heart, a marvel of biological engineering, is a powerful pump responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. Its four chambers – the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle – each play a crucial role in this process. But one chamber stands out for its robust construction: the left ventricle. This article delves deep into the reasons behind the left ventricle's significantly thicker wall, exploring the anatomical and physiological factors that contribute to its unique structure and vital function.
The Anatomy of the Heart: A Closer Look
Before understanding why the left ventricle boasts the thickest wall, let's establish a basic understanding of the heart's anatomy. The heart is divided into four chambers:
- Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood returning from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Right Ventricle: Receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs via the pulmonary artery for oxygenation.
- Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
- Left Ventricle: Receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps it to the rest of the body via the aorta, the body's largest artery.
Each chamber's structure reflects its specific function. The atria, receiving chambers, have relatively thin walls. The ventricles, pumping chambers, have thicker walls, especially the left ventricle. This difference in wall thickness is not arbitrary; it's a direct consequence of the differing pressures and volumes each chamber must handle.
Why the Left Ventricle Needs the Thickest Wall
The left ventricle's significantly thicker wall is a testament to its demanding role in the circulatory system. It needs this robust structure to perform the following crucial tasks:
-
Higher Pressure Pumping: The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body, except for the lungs. This requires significantly higher pressure than the right ventricle's pulmonary circulation. The systemic circulation, served by the left ventricle, involves much greater resistance due to the extensive network of blood vessels throughout the body. This higher pressure necessitates a stronger, thicker muscular wall to generate the necessary force.
-
Greater Force of Contraction: To overcome the systemic vascular resistance and propel blood throughout the entire body, the left ventricle must contract with considerably more force than the right ventricle. This increased contractile force directly correlates with the thickness of its myocardial wall. The thicker the wall, the greater the number of muscle fibers, allowing for stronger contractions.
-
Maintaining Systemic Blood Pressure: The left ventricle is responsible for maintaining systemic blood pressure, the pressure exerted by circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Consistent blood pressure is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to all tissues and organs. The thicker left ventricular wall ensures adequate pressure generation to maintain this vital function.
-
Sustained Workload: The left ventricle continuously pumps blood throughout life, facing a constant and considerable workload. This sustained workload requires robust structural integrity and the ability to withstand the continuous pressure and stress. The thick wall provides the necessary structural support and resilience.
Comparing Left and Right Ventricular Wall Thickness
The difference in wall thickness between the left and right ventricles is readily apparent. The left ventricle's wall can be up to three times thicker than the right ventricle's. This significant difference highlights the disparity in their functional demands. The right ventricle only needs to pump blood to the lungs, a relatively short distance, requiring less pressure and force. In contrast, the left ventricle must pump blood throughout the entire body, demanding significantly higher pressure and forceful contractions.
The Myocardium: The Heart's Muscular Engine
The walls of the heart's chambers are primarily composed of cardiac muscle tissue, also known as the myocardium. The myocardium of the left ventricle is considerably thicker and more robust than that of the other chambers. This difference in myocardial thickness is crucial for generating the power required for systemic circulation. The arrangement and density of cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) within the myocardium also contribute to the left ventricle's superior pumping capacity.
Clinical Implications of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
While a thick left ventricular wall is essential for normal physiological function, excessive thickening, known as left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), can be a sign of underlying cardiovascular problems. LVH can result from various conditions, including:
- Hypertension: Chronically elevated blood pressure forces the left ventricle to work harder, leading to thickening of its wall.
- Aortic Stenosis: Narrowing of the aortic valve increases the resistance the left ventricle faces when pumping blood, causing hypertrophy.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A genetic condition characterized by thickening of the left ventricular wall independent of other cardiovascular conditions.
LVH can significantly impair the heart's ability to function effectively, potentially leading to heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. Therefore, monitoring left ventricular wall thickness is crucial in diagnosing and managing cardiovascular diseases.
Technological Advancements in Assessing Left Ventricular Function
Various advanced imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and cardiac CT scans, allow for precise assessment of left ventricular wall thickness and function. These technologies provide detailed visualizations of the heart's structure and help physicians diagnose and monitor conditions affecting the left ventricle.
Lifestyle Factors and Left Ventricular Health
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in preserving the health of the left ventricle. Factors such as:
- Regular Exercise: Strengthens the heart muscle and improves cardiovascular health.
- Balanced Diet: Reduces the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Decreases strain on the cardiovascular system.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Protects against cardiovascular diseases.
Contribute significantly to the overall well-being of the heart, including the left ventricle. These lifestyle choices can help prevent conditions that might lead to LVH and other cardiac complications.
Conclusion: The Left Ventricle – A Powerful Pump
The left ventricle's remarkably thick wall is a testament to its crucial role in the circulatory system. Its robust structure is essential for generating the high pressure and forceful contractions required to pump oxygenated blood throughout the entire body. Understanding the anatomical and physiological factors that contribute to the left ventricle's unique characteristics is crucial for appreciating the complexity and efficiency of the human cardiovascular system. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical attention are vital for preserving the health and functionality of this vital organ. The left ventricle, with its powerful contractions and thick muscular wall, truly exemplifies the incredible power and precision of the human heart. Further research into the intricate workings of the left ventricle and the development of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic strategies will continue to enhance our understanding and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. The continuing advancements in cardiology promise to further improve the lives of individuals affected by heart conditions, ensuring a healthier future for all. The robust and powerful left ventricle remains a vital component of human survival, driving the life-sustaining flow of oxygenated blood to every corner of the body. It serves as a powerful reminder of the exquisite intricacy and efficiency of the human circulatory system, making it a captivating subject for both medical professionals and those simply curious about the workings of their own bodies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Sphere Has How Many Vertex
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Ne
Mar 15, 2025
-
Tool Used To Detect Electric Charge
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In A Single Molecule Of H2o
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Nucleophile
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Heart Chamber Has The Thickest Wall . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
