What Set Of Reflections Would Carry Hexagon Abcdef Onto Itself
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
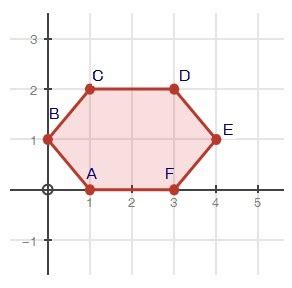
Table of Contents
What Set of Reflections Would Carry Hexagon ABCDEF onto Itself?
Understanding the symmetries of a regular hexagon, like ABCDEF, involves exploring the transformations that map the hexagon onto itself. This means finding the set of reflections that leave the hexagon unchanged in its position and orientation, even though individual vertices may swap places. This seemingly simple geometrical problem opens a door to deeper understandings of group theory and abstract algebra. Let's delve into the details.
Defining Reflections and Symmetry
Before we tackle the hexagon specifically, let's clarify what a reflection is in the context of geometry. A reflection is a transformation that flips a shape across a line, known as the line of reflection or axis of symmetry. The reflected shape is a mirror image of the original, with each point equidistant from the line of reflection.
A shape exhibits symmetry if it can be mapped onto itself through one or more transformations, including reflections, rotations, and translations. A regular hexagon possesses a high degree of symmetry, meaning it has many lines of reflection and rotational symmetries.
Lines of Reflection in a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has six lines of reflection that map it onto itself. These lines can be categorized:
1. Lines Connecting Opposite Vertices
Three lines of reflection pass through pairs of opposite vertices. For example, a line connecting vertex A to vertex D is a line of reflection. Reflecting the hexagon across this line will leave the hexagon unchanged. The same applies to lines connecting B to E and C to F.
Example: Consider a line through A and D. Vertex A maps to itself, as does vertex D. Vertex B reflects to F, and vertex F reflects to B. Similarly, C reflects to E and E reflects to C. The entire hexagon overlays itself perfectly.
2. Lines Bisecting Opposite Sides
Three additional lines of reflection bisect pairs of opposite sides of the hexagon. These lines are perpendicular to the sides they bisect. For instance, a line perpendicular to and bisecting side AB will also bisect the opposite side DE. Reflection across this line will again map the hexagon onto itself.
Example: Consider the line bisecting AB and DE. Vertex A reflects to B, and B to A. Vertex D reflects to E, and E to D. The vertices C and F remain fixed because they are equidistant from the reflection line.
Therefore, a regular hexagon has a total of six lines of reflection that map it onto itself. These six lines form the reflectional symmetry of the hexagon.
Rotational Symmetry (A Brief Consideration)
While the question focuses on reflections, it's important to briefly acknowledge the rotational symmetry of the hexagon. A regular hexagon can be rotated about its center by angles of 60°, 120°, 180°, 240°, and 300°, and still map onto itself. These rotations, coupled with the six reflections, constitute the full symmetry group of the regular hexagon, often represented as D<sub>6</sub> in group theory.
Understanding the Set of Reflections
The set of reflections that maps the hexagon onto itself is a group in the mathematical sense. This means:
- Closure: Performing two reflections successively is equivalent to another reflection (or potentially a rotation if the reflection axes are not parallel).
- Identity: Reflecting across the same line twice brings the hexagon back to its original position (the identity transformation).
- Inverses: Each reflection has an inverse; reflecting across the same line reverses the original reflection.
- Associativity: The order in which you perform multiple reflections does not affect the final result.
This group structure is crucial for understanding how the reflections interact and collectively generate all the symmetries of the hexagon. Any combination of these six reflections will either result in another reflection within the set, or a rotation in the hexagon's symmetry group.
Visualizing the Reflections
To truly grasp this, visualizing the reflections is paramount. Imagine drawing a regular hexagon on a piece of paper. Then, draw the six lines of reflection. Experiment with reflecting the hexagon across each line, one at a time. Observe how the vertices exchange positions while the overall shape remains identical. Next, try reflecting across multiple lines in succession. Note how this leads to either another reflection or a rotation.
Applications and Further Exploration
The concept of reflections and symmetry in regular polygons, like the hexagon, has far-reaching applications:
- Crystallography: The symmetry operations in crystals are closely related to the symmetries of polygons and other shapes. Understanding these symmetries is vital in material science.
- Computer Graphics: Reflections are fundamental to generating realistic images in computer graphics and animation.
- Art and Design: Symmetrical patterns and designs have been used throughout history in various forms of art and architecture.
Further exploration into this topic can involve:
- Group Theory: Investigating the properties of the symmetry group D<sub>6</sub> and understanding its group multiplication table.
- Abstract Algebra: Connecting the concepts of reflectional symmetry to more abstract algebraic structures.
- Higher-Dimensional Polygons: Extending the analysis to higher-dimensional analogues of hexagons.
Conclusion
The set of reflections that carry a regular hexagon ABCDEF onto itself consists of six reflections. Three of these reflections pass through opposite vertices, and three bisect opposite sides. Understanding these reflections reveals the rich symmetry inherent in this simple geometric shape, opening doors to more complex mathematical concepts and their practical applications in diverse fields. The hexagon’s symmetry, specifically its reflections, is not just a geometric curiosity but a fundamental aspect of its mathematical structure, underpinning concepts in group theory and beyond. By exploring the reflections and their interactions, one gains a deeper appreciation for the beauty and elegance of geometric symmetry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
At A Price Below Equilibrium Price There Is
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Cannot Travel In A Vacuum
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Molecular Mass Of Helium
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Add Numbers In Python
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Inches Are In 4 5 Feet
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Set Of Reflections Would Carry Hexagon Abcdef Onto Itself . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
