What Is The Number Of Protons For Magnesium
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
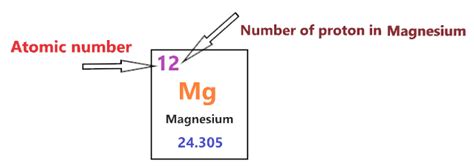
Table of Contents
What is the Number of Protons for Magnesium? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Magnesium, a vital element for human health and a cornerstone of numerous industrial applications, holds a fascinating place in the periodic table. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of protons it possesses, is key to grasping its unique properties and behavior. This article will delve into the specifics of magnesium's atomic structure, exploring its proton count and its implications for chemistry and beyond. We'll also touch upon related concepts to provide a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental element.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we pinpoint the number of protons in magnesium, let's briefly review the fundamental components of an atom:
- Protons: Positively charged subatomic particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the element's atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged subatomic particles also residing in the nucleus. They contribute to an atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged subatomic particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. Their number typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The arrangement of these subatomic particles determines an atom's properties, including its reactivity, bonding behavior, and overall characteristics. Understanding this structure is crucial in various scientific fields, from chemistry and physics to materials science and medicine.
Magnesium's Atomic Number: The Key to its Identity
The atomic number of an element dictates the number of protons in its nucleus. This number uniquely identifies each element on the periodic table. For magnesium, the atomic number is 12. This means that every magnesium atom contains 12 protons in its nucleus. This fundamental fact governs magnesium's chemical behavior and interactions with other elements.
Why is the Number of Protons Important?
The number of protons is paramount because:
- It defines the element: An atom with 12 protons is, by definition, a magnesium atom. Any atom with a different number of protons is a different element entirely.
- It determines the chemical properties: The number of protons dictates the number of electrons in a neutral atom, directly impacting its electron configuration and chemical reactivity. This influences how magnesium forms bonds with other elements.
- It's essential for isotopic identification: While the number of protons remains constant for a given element, the number of neutrons can vary, leading to isotopes. Understanding the proton count helps distinguish between different isotopes of magnesium.
Isotopes of Magnesium: Variations in Neutron Count
While the proton number (12) remains constant for magnesium, the neutron count can vary, resulting in different isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. The most common isotopes of magnesium are:
- Magnesium-24 (²⁴Mg): Contains 12 protons and 12 neutrons. This is the most abundant isotope.
- Magnesium-25 (²⁵Mg): Contains 12 protons and 13 neutrons.
- Magnesium-26 (²⁶Mg): Contains 12 protons and 14 neutrons.
These isotopes exhibit similar chemical properties due to their identical electron configurations, but they have slightly different physical properties due to their varying masses. The abundance of each isotope varies naturally.
The Significance of Magnesium in Biological Systems
Magnesium's role in biological systems is extensive and critical. Its 12 protons contribute to its unique chemical properties, making it an essential element for numerous biological processes. These include:
- Enzyme activation: Magnesium acts as a cofactor for hundreds of enzymes, assisting in crucial metabolic reactions. Its ability to form complexes with various molecules is essential for its catalytic role.
- DNA and RNA synthesis: Magnesium plays a vital part in the replication and transcription of genetic material. Its presence is critical for maintaining the structure and function of DNA and RNA.
- Muscle and nerve function: Magnesium is essential for muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission. It plays a critical role in regulating calcium levels within cells, influencing muscle function and neuronal activity.
- Protein synthesis: Magnesium is involved in the intricate process of protein synthesis, influencing the translation of genetic information into functional proteins.
- Bone health: Magnesium is a crucial component of bone structure, contributing to bone density and overall skeletal health.
The deficiency of magnesium can lead to various health problems, highlighting its indispensable role in maintaining proper physiological functions.
Magnesium's Industrial Applications: Leveraging its Properties
Beyond its biological significance, magnesium's unique properties, driven by its 12 protons, make it valuable in various industrial applications:
- Lightweight alloys: Magnesium's low density makes it ideal for creating lightweight alloys used in automobiles, aircraft, and other transportation vehicles. These alloys combine strength and lightness, improving fuel efficiency and performance.
- Electronics: Magnesium compounds are used in the production of electronics, contributing to the performance and longevity of various components.
- Chemical industry: Magnesium's reactivity makes it a useful reducing agent in various chemical processes.
- Pyrotechnics: Magnesium's bright, white light upon combustion makes it an important component in fireworks and flares.
Exploring Further: Beyond the Basics
The significance of magnesium's 12 protons extends beyond simply identifying the element. It forms the foundation for understanding its:
- Reactivity: The electron configuration determined by the 12 protons influences how magnesium reacts with other elements, forming ionic bonds readily.
- Ionization energy: The energy required to remove an electron from a magnesium atom is directly related to the attractive force exerted by the 12 protons in the nucleus.
- Electronegativity: Magnesium's relatively low electronegativity indicates its tendency to lose electrons and form positive ions (Mg²⁺).
Understanding these properties provides a complete picture of magnesium's behavior in various chemical and physical contexts.
Conclusion: The Importance of a Simple Number
The number 12 – the number of protons in magnesium – may seem insignificant at first glance. However, this simple number holds the key to understanding magnesium's unique properties, its biological significance, and its wide-ranging applications. From the intricate processes within living organisms to the high-tech materials of modern industry, magnesium's 12 protons serve as the foundation for its critical roles. This exploration highlights the importance of fundamental atomic structure in determining the characteristics and uses of elements throughout our world. The precise number of protons fundamentally shapes the behavior and impact of this essential element.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Count Vowels In A String Python
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Elements Is Most Electronegative
Apr 01, 2025
-
For Which Value Of X Is Abcd A Kite
Apr 01, 2025
-
64 To The Power Of 1 2
Apr 01, 2025
-
On The Galapagos Islands Charles Darwin Observed
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Number Of Protons For Magnesium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
