What Is The Name For The Compound N2o5
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
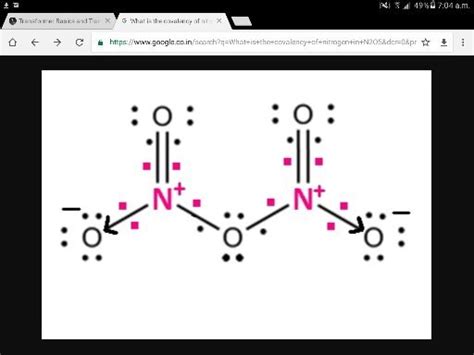
Table of Contents
- What Is The Name For The Compound N2o5
- Table of Contents
- What is the Name for the Compound N₂O₅?
- Understanding Chemical Nomenclature: A Foundation for Naming N₂O₅
- The Physical and Chemical Properties of Dinitrogen Pentoxide
- Physical Properties:
- Chemical Properties:
- Synthesis of Dinitrogen Pentoxide: Methods and Considerations
- Applications of Dinitrogen Pentoxide: A Versatile Compound
- Safety Precautions: Handling Dinitrogen Pentoxide
- Historical Context and Significance
- Conclusion: A Deep Dive into N₂O₅
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is the Name for the Compound N₂O₅?
Dinitrogen pentoxide. That's the name for the chemical compound with the formula N₂O₅. While seemingly simple, this seemingly straightforward answer opens the door to a fascinating exploration of its properties, synthesis, applications, and even its historical significance within the field of chemistry. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of N₂O₅, revealing its multifaceted nature and importance.
Understanding Chemical Nomenclature: A Foundation for Naming N₂O₅
Before we delve deeper into the specifics of dinitrogen pentoxide, let's establish a fundamental understanding of chemical nomenclature. This system of naming chemical compounds is crucial for clear communication among scientists and professionals across the globe. It ensures that everyone understands precisely which chemical substance is being discussed.
The name "dinitrogen pentoxide" adheres to the rules of IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature. Let's break down the name:
-
Dinitrogen: The prefix "di-" indicates two atoms of nitrogen (N). Nitrogen is a non-metal, and in this compound, it is the less electronegative element, hence it is listed first.
-
Pentoxide: The prefix "pent-" signifies five atoms of oxygen (O). The suffix "-oxide" indicates that the compound contains oxygen bonded to another element, in this case, nitrogen.
Therefore, the name "dinitrogen pentoxide" directly and unambiguously describes the composition of the molecule: two nitrogen atoms and five oxygen atoms.
The Physical and Chemical Properties of Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide exists in two forms: a colorless crystalline solid and a colorless gas. Understanding its physical and chemical properties is essential for its safe handling and application.
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Colorless crystalline solid (at low temperatures) or colorless gas (at higher temperatures).
- Melting Point: Around 30°C (86°F). This relatively low melting point indicates its relatively weak intermolecular forces.
- Boiling Point: Decomposes before reaching a boiling point. This decomposition is a crucial characteristic and a key factor influencing its applications.
- Solubility: It's soluble in various solvents, including chloroform and carbon tetrachloride. However, its reaction with water is significant, as we will see later.
- Density: Higher than that of air, meaning it will tend to settle in low-lying areas if released as a gas.
Chemical Properties:
-
Strong Oxidizing Agent: This is arguably one of the most important chemical properties of N₂O₅. It readily accepts electrons from other substances, making it a potent oxidizing agent. This property is vital in its various applications.
-
Reaction with Water: Dinitrogen pentoxide reacts vigorously with water to produce nitric acid (HNO₃):
N₂O₅ + H₂O → 2HNO₃
This reaction is highly exothermic, meaning it releases a significant amount of heat. This aspect must be considered during handling and storage.
-
Thermal Decomposition: As mentioned earlier, dinitrogen pentoxide decomposes at higher temperatures, typically producing nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and oxygen (O₂):
2N₂O₅ → 4NO₂ + O₂
This decomposition is also exothermic and can be quite rapid under specific conditions.
Synthesis of Dinitrogen Pentoxide: Methods and Considerations
Several methods can be used to synthesize dinitrogen pentoxide. The exact method employed often depends on the desired purity, scale of production, and available resources. Some common approaches include:
-
Dehydration of Nitric Acid: This is one of the most established methods. Concentrated nitric acid can be dehydrated using a dehydrating agent like phosphorus pentoxide (P₄O₁₀) to produce N₂O₅. The reaction involves the careful removal of water molecules from the nitric acid, leaving behind the dinitrogen pentoxide.
-
Reaction of Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone: Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) can react with ozone (O₃) to form dinitrogen pentoxide. This reaction is often carried out at low temperatures to improve the yield and prevent unwanted side reactions.
-
Reaction of Nitric Acid and Acetic Anhydride: This method involves reacting nitric acid with acetic anhydride, which acts as a dehydrating agent. The reaction yields dinitrogen pentoxide and acetic acid as a byproduct.
Regardless of the synthesis method, careful control of reaction conditions, such as temperature and pressure, is crucial to ensure optimal yield and purity of the product. Safety precautions must also be rigorously followed, given the hazardous nature of the reactants and the product itself.
Applications of Dinitrogen Pentoxide: A Versatile Compound
The potent oxidizing and reactive nature of dinitrogen pentoxide makes it useful in a number of applications, although its instability and hazardous properties necessitate careful handling. Some key applications include:
-
Nitration Reactions: Dinitrogen pentoxide is used as a nitrating agent in organic chemistry. It can introduce nitro (-NO₂) groups into organic molecules, creating nitro compounds that have various applications in the pharmaceutical, explosives, and dye industries. The controlled nitration of organic molecules is a crucial aspect of many chemical synthesis processes.
-
Synthesis of Other Nitrogen Compounds: It serves as a precursor for the synthesis of various other nitrogen-containing compounds. Its reactive nature allows it to participate in reactions that yield valuable chemicals used in diverse fields.
-
Rocket Propellant: While less common now, its strong oxidizing power has historically been explored for use as an oxidizer in rocket propellants. The high energy released during its decomposition makes it a potential candidate, although safety concerns are paramount.
-
Laboratory Reagent: In research settings, dinitrogen pentoxide is used as a reagent in various chemical reactions and experiments. Its unique properties make it an invaluable tool for scientists conducting studies involving nitrogen chemistry.
It is important to reiterate that the handling and use of dinitrogen pentoxide require specialized knowledge, expertise, and stringent safety measures due to its inherent hazards.
Safety Precautions: Handling Dinitrogen Pentoxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide is a highly reactive and potentially hazardous compound. Therefore, meticulous safety precautions are essential during its handling, storage, and disposal. These precautions include:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Appropriate PPE, including gloves, eye protection, and respiratory protection, is crucial to prevent exposure to the compound. This equipment should be selected based on the specific conditions of handling and the potential exposure pathways.
-
Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential to prevent the accumulation of N₂O₅ vapors, which can be toxic and harmful if inhaled. Work should ideally be performed in a well-ventilated fume hood or similar setup.
-
Storage: The compound should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible materials, such as organic solvents or reducing agents. Appropriate containers should be used to prevent leaks or spills.
-
Spill Response: In case of spills, appropriate emergency procedures should be followed. These procedures may include evacuation of the area, the use of absorbent materials, and neutralization of any spilled material.
-
Waste Disposal: Proper waste disposal procedures should be followed, adhering to all relevant regulations and guidelines. Consult with waste management professionals for appropriate disposal methods.
Historical Context and Significance
The discovery and study of dinitrogen pentoxide have contributed significantly to the understanding of nitrogen chemistry. Early research into its properties helped establish fundamental principles in chemical bonding, reactivity, and synthesis. Moreover, its ongoing use in various applications reflects its continued importance in modern chemistry. The exploration of its properties has also led to a deeper understanding of other nitrogen oxides and their roles in atmospheric chemistry and environmental science.
Conclusion: A Deep Dive into N₂O₅
Dinitrogen pentoxide (N₂O₅), while seemingly a simple chemical compound, reveals a rich complexity in its properties, synthesis, applications, and associated safety considerations. From its role as a potent oxidizing agent and nitrating agent to its potential applications (and inherent challenges) in areas like rocket propellant technology, its multifaceted nature underscores its continuing relevance in chemistry. Understanding its chemical properties, synthesis methods, and crucial safety guidelines are paramount for anyone working with or researching this fascinating compound. The careful handling and responsible use of dinitrogen pentoxide are key to ensuring both safety and the continued advancement of scientific knowledge.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Capacitance Of A Parallel Plate Capacitor With Dielectric Slab
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Correct Order For The Scientific Method
Mar 18, 2025
-
Optic Nerve And Blood Vessels Enter The Eye At The
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Major Difference Between Active And Passive Transport
Mar 18, 2025
-
Number Of Valence Electrons In Aluminium
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Name For The Compound N2o5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
