What Are The Muscular Ridges Within The Ventricles Called
News Leon
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
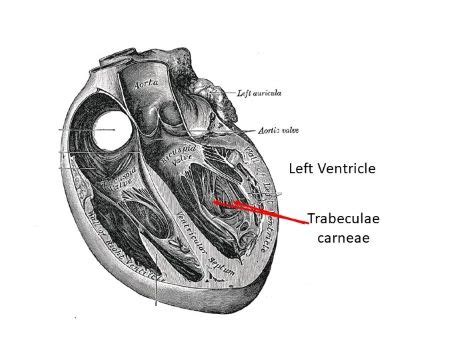
Table of Contents
What Are the Muscular Ridges Within the Ventricles Called? Exploring the Trabeculae Carneae
The heart, a tireless engine driving life's processes, is a marvel of biological engineering. Its intricate structure, particularly that of the ventricles, is crucial for its efficient pumping action. Within the ventricles, you'll find a network of muscular ridges – a key feature that significantly impacts their function. But what are these ridges called? This article dives deep into the anatomy and significance of the trabeculae carneae, exploring their structure, function, and clinical relevance.
Understanding the Ventricles: The Heart's Pumping Chambers
Before we delve into the trabeculae carneae, let's establish a foundational understanding of the ventricles themselves. The heart possesses four chambers: two atria (receiving chambers) and two ventricles (pumping chambers). The ventricles, the right and left, are responsible for propelling oxygen-poor blood (right ventricle) to the lungs and oxygen-rich blood (left ventricle) to the rest of the body. Their muscular walls are significantly thicker than those of the atria, reflecting the greater force required for systemic circulation.
The internal structure of the ventricles is far from smooth. Instead, their inner surfaces are characterized by a complex network of muscular elevations and depressions, a key element of which is the trabeculae carneae.
Trabeculae Carneae: Definition and Structure
The trabeculae carneae, Latin for "fleshy beams," are irregular, muscular ridges that project from the inner surfaces of the ventricles. These ridges are not merely superficial markings; they are integral components of the ventricular myocardium, contributing to the overall thickness and strength of the ventricular walls.
Key characteristics of the trabeculae carneae include:
- Irregular Arrangement: They are not arranged in any specific pattern, creating a somewhat chaotic yet highly effective network.
- Varying Sizes: The size and thickness of the trabeculae carneae vary considerably, with some being quite prominent and others more subtle.
- Attachment: They are attached to the ventricular walls, intertwining and branching extensively.
- Composition: They are composed of cardiac muscle fibers, similar to those forming the bulk of the ventricular walls.
- Functional Significance: This seemingly random arrangement plays a crucial role in efficient ventricular contraction and blood flow.
Differentiating Trabeculae Carneae from Other Structures
It's crucial to distinguish trabeculae carneae from other structures within the ventricles:
-
Papillary Muscles: These are cone-shaped muscular projections that are larger and more prominent than trabeculae carneae. They are anchored to the ventricular walls and play a vital role in coordinating the opening and closing of the atrioventricular valves. While they are also muscular ridges, their size, shape and attachment points clearly distinguish them from the trabeculae carneae. The papillary muscles' function is directly linked to valve regulation, whereas the trabeculae carneae's role is more focused on ventricular contraction efficiency.
-
Moderator Band (Septomarginal Trabecula): This is a prominent trabecula found only in the right ventricle. It's a thick muscular band extending from the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle. It plays a crucial role in conducting electrical impulses within the right ventricle, ensuring coordinated contraction. It's essentially a specialized, larger trabecula with a distinct functional role.
The Functional Role of Trabeculae Carneae
The trabeculae carneae, despite their seemingly disorganized arrangement, serve several important functions:
1. Enhancing Ventricular Contraction Efficiency:
The intricate network of trabeculae carneae allows for a more efficient contraction of the ventricles. By providing additional structural support, they help to prevent bulging or over-stretching of the ventricular walls during contraction, maximizing the force of ejection. The three-dimensional structure created by these muscular ridges effectively increases the overall surface area of the ventricle, allowing more efficient transfer of force during contraction.
2. Improving Blood Flow Dynamics:
The presence of trabeculae carneae influences the flow of blood within the ventricles. They help to prevent the formation of stagnant pools of blood, promoting efficient mixing and reducing the likelihood of clot formation. Their irregular arrangement creates turbulence in the blood flow, enhancing the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood before ejection. This is particularly important in the right ventricle, where blood needs to be thoroughly oxygenated in the pulmonary circulation.
3. Increasing Surface Area for Myocardial Cells:
The extensive network of trabeculae carneae substantially increases the surface area of the ventricular walls. This larger surface area provides more space for the anchoring of myocardial cells, increasing the overall mass of the heart muscle and enabling more robust contractions. The increased surface area also facilitates nutrient and oxygen supply to the cardiac muscle cells.
4. Supporting the Ventricular Endocardium:
The trabeculae carneae provide structural support to the endocardium, the thin inner lining of the heart's chambers. This support helps to maintain the structural integrity of the ventricle, preventing excessive dilation or damage.
Clinical Significance of Trabeculae Carneae
While typically benign, abnormalities involving the trabeculae carneae can be indicative of certain cardiovascular conditions:
-
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): In HCM, a condition characterized by excessive thickening of the ventricular walls, the trabeculae carneae can appear abnormally prominent and thickened. This is a result of the overall increase in myocardial mass. The increased muscle mass and abnormal trabeculae can lead to impaired blood flow and increased risk of arrhythmias.
-
Noncompaction Cardiomyopathy (NCC): This is a rare cardiomyopathy characterized by incomplete compaction of the trabeculae carneae during fetal development. In NCC, the ventricles exhibit a spongy appearance due to the excessively prominent trabeculae carneae. This abnormal structure can lead to impaired ventricular function and increased risk of heart failure.
-
Left Ventricular Noncompaction: This specific type of NCC affects the left ventricle primarily, resulting in a markedly trabeculated left ventricular wall and sometimes associated with other structural heart defects.
-
Imaging Techniques: Advanced imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and CT angiography, are essential for visualizing and characterizing abnormalities in the trabeculae carneae. These techniques provide crucial information for diagnosis and management of associated cardiovascular conditions.
Trabeculae Carneae and Research: Ongoing Investigations
Research on the trabeculae carneae continues to uncover new insights into their complex structure and function. Ongoing studies are investigating their role in:
-
Heart development and embryology: Research is focused on understanding the mechanisms that govern the formation and maturation of trabeculae carneae during fetal development. This helps to shed light on the pathogenesis of conditions like NCC.
-
Electrophysiological properties: Investigating the role of trabeculae carneae in electrical conduction within the ventricles could lead to a better understanding of arrhythmogenesis.
-
Biomechanical modeling: Computer modeling and simulations are used to explore the impact of trabeculae carneae on ventricular mechanics and blood flow dynamics. This assists in understanding the complexities of ventricular function and refining diagnostic and treatment strategies.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Trabeculae Carneae
The trabeculae carneae, those seemingly insignificant muscular ridges within the ventricles, are integral components of the heart's intricate anatomy. Their complex arrangement contributes significantly to the efficient pumping action of the heart, supporting ventricular contraction, influencing blood flow, and increasing surface area for myocardial cells. Understanding their structure, function, and clinical relevance is crucial for diagnosing and managing a range of cardiovascular conditions. Continued research promises to further illuminate the significant role these "fleshy beams" play in maintaining cardiovascular health. From their involvement in the effective pumping mechanism of the heart to their implications in understanding cardiomyopathies, the trabeculae carneae deserve closer attention in our study of the intricate workings of the human heart. Their study allows a deeper understanding of the complexities of the cardiovascular system and aids in developing more precise diagnostic tools and treatments for various heart conditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Toiroidal Solenoid Has A Central Radius Of 0 5m
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Blood Is A Connective Tissue
Mar 25, 2025
-
Is Electric Force A Contact Force
Mar 25, 2025
-
Net Ionic Equation For Naoh Hcl
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Essential Fatty Acid
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Muscular Ridges Within The Ventricles Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
