Is Electric Force A Contact Force
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
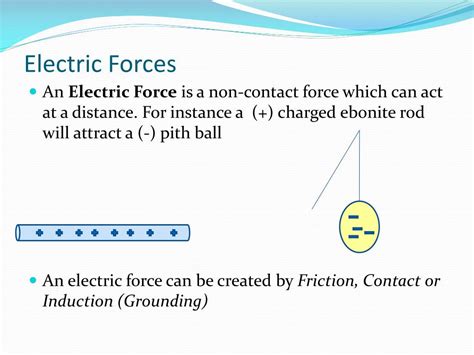
Table of Contents
Is Electric Force a Contact Force? Unraveling the Mysteries of Electromagnetic Interactions
The question of whether electric force is a contact force is a fundamental one in physics, often sparking confusion among students and enthusiasts alike. The short answer is no, electric force is not a contact force. It's a non-contact force, acting over a distance without any physical touch between the interacting objects. Understanding this distinction requires delving into the nature of electric fields and the fundamental principles of electromagnetism. This article will explore this concept in detail, clarifying misconceptions and providing a comprehensive understanding of how electric forces operate.
Understanding Contact Forces
Before we delve into electric forces, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a contact force. A contact force, as the name suggests, requires direct physical contact between two objects for interaction to occur. Examples of contact forces include:
- Normal Force: The force exerted by a surface perpendicular to an object resting on it. Think of a book on a table; the table exerts an upward normal force on the book.
- Frictional Force: The force resisting motion between two surfaces in contact. This force opposes the relative motion of the surfaces.
- Tension Force: The force transmitted through a string, rope, or cable when it's pulled taut.
- Applied Force: A force applied directly to an object, such as pushing a box across the floor.
These forces all share a common characteristic: they require direct physical interaction between the objects involved. The absence of physical contact means the force cannot be categorized as a contact force.
Electric Force: A Non-Contact Force
Electric force, on the other hand, operates under a completely different principle. It's a fundamental force of nature, governed by Coulomb's Law. This law states that the force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Mathematically:
F = k * |q1 * q2| / r²
Where:
- F represents the electric force
- k is Coulomb's constant
- q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges
- r is the distance between the charges
This equation reveals a crucial aspect of electric force: distance. The force exists regardless of whether the charged objects are touching. The force acts across a distance, through a field, making it a non-contact force. This field, known as the electric field, is a region of space surrounding a charged object where another charged object experiences a force.
The Role of the Electric Field
The concept of the electric field is crucial to understanding how electric forces act at a distance. A charged object creates an electric field around itself. This field is not a physical entity, but rather a representation of the influence the charged object has on the surrounding space. When another charged object enters this field, it experiences a force based on its own charge and the strength of the field at its location.
Imagine throwing a stone into a still pond. The stone creates ripples, disturbances that propagate outward. Similarly, a charged object creates disturbances in space – its electric field. These disturbances are not physical objects but represent the potential for interaction with other charged objects. The interaction isn’t a direct “touch” but a response to the field’s influence.
Comparing Electric Force to Gravity
The concept of a non-contact force is also evident in another fundamental force: gravity. Gravity is the attractive force between any two objects with mass. Like electric force, gravity acts at a distance, without requiring direct physical contact. The Earth exerts a gravitational force on objects on its surface and even on the moon, despite the vast distance separating them. This demonstrates that non-contact forces are a fundamental aspect of the universe's workings.
Misconceptions about Electric Force
The confusion surrounding whether electric force is a contact force often stems from everyday experiences. When we touch a doorknob and receive an electric shock, it feels like a direct contact force. However, this is a misinterpretation. The shock results from the flow of electrons between your hand and the doorknob due to a potential difference. The actual electric force causing the electrons to move acts at a distance, even though the effect is felt upon contact.
Another misconception arises from visualizing forces as a push or pull. While this is an adequate representation for some contact forces, it’s misleading when applied to electric forces. The electric field mediates the interaction, not direct physical contact.
Electric Force in Action: Real-World Examples
Numerous phenomena demonstrate the non-contact nature of electric force:
- Lightning: A dramatic display of electric discharge between clouds or between clouds and the ground. The force responsible is purely electric and acts over significant distances.
- Static electricity: The buildup of static charge on surfaces can lead to sparks or attraction/repulsion of objects. This interaction happens without any direct contact.
- Electromagnetic interactions in atoms: The electrons orbiting the nucleus are held in place by the electric force exerted by the positively charged nucleus. This is a prime example of a non-contact force at the atomic level.
- Electric motors: These devices rely on the interaction between magnetic fields (which are intrinsically related to electric fields) and currents to produce mechanical motion. The interaction is non-contact, with the force acting across a gap between components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric force is undeniably a non-contact force. It acts across distances through the intermediary of the electric field, unlike contact forces that require direct physical interaction. Understanding this distinction is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of electromagnetism and its role in various natural phenomena and technological applications. The electric field plays a central role, explaining how charges interact without touching, thereby defying the intuitive notion of force requiring physical contact. The examples provided throughout illustrate the pervasive presence and significance of electric forces as a crucial aspect of our universe. By dispelling common misconceptions and clarifying the function of the electric field, we achieve a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of electromagnetic interactions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Steroid Hormone
Mar 26, 2025
-
Osmosis Refers To The Movement Of
Mar 26, 2025
-
Digit 9 Is Always At Hundreds Place
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Rime Of Ancient Mariner Summary
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Cannot Be A Probability
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Electric Force A Contact Force . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
