What Are Some Examples Of Pulleys
News Leon
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
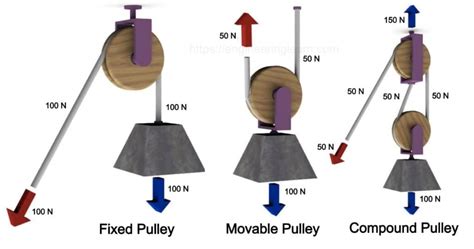
Table of Contents
What Are Some Examples of Pulleys? A Comprehensive Guide
Pulleys are simple machines that use a grooved wheel and a rope, cable, or belt to lift, move, or change the direction of an object. They are incredibly versatile and find applications in countless areas of our daily lives, from simple household tasks to complex industrial machinery. Understanding the different types of pulleys and their applications is crucial for appreciating their impact on our world. This comprehensive guide will delve into various examples of pulleys, exploring their mechanics and practical uses.
Understanding the Basics: Types of Pulleys
Before diving into specific examples, let's briefly review the fundamental types of pulleys:
1. Fixed Pulleys:
A fixed pulley is attached to a stationary object. It changes the direction of the force applied, making it easier to lift heavy objects. However, it doesn't provide any mechanical advantage; the effort required to lift the load is equal to the weight of the load.
2. Movable Pulleys:
A movable pulley moves along with the load. It divides the weight of the load between two supporting ropes, resulting in a mechanical advantage of two. This means you only need to exert half the force to lift the same weight compared to lifting it directly.
3. Compound Pulleys (Block and Tackle):
Compound pulleys, also known as block and tackle systems, combine fixed and movable pulleys to achieve higher mechanical advantages. By adding more pulleys, you can significantly reduce the effort needed to lift or move heavy objects.
Examples of Pulleys in Everyday Life
Pulleys are surprisingly ubiquitous in our daily lives, often unnoticed. Let's explore some common examples:
1. Flagpoles:
Raising and lowering a flag on a tall flagpole is a classic example of a fixed pulley in action. The rope passes over the pulley at the top of the pole, changing the direction of the force and making it easier to hoist the flag.
2. Window Blinds/Curtains:
Many window blinds and curtains use a cord and pulley system. Pulling the cord moves the pulley, which in turn raises or lowers the blinds or curtains. This is a simple yet effective application of a fixed pulley.
3. Well Systems:
Traditional well systems often employ a compound pulley system (block and tackle) to lift buckets of water from deep wells. The multiple pulleys reduce the effort required to haul the heavy bucket. This exemplifies the mechanical advantage offered by compound pulleys.
4. Exercise Machines:
Many weight-training machines use pulley systems to provide resistance. The weight stack is connected to a pulley system, allowing for smooth and controlled movement during exercises. This showcases how pulleys can be used to manipulate and control forces efficiently.
5. Construction Cranes:
Construction cranes rely on sophisticated compound pulley systems to lift heavy materials to great heights. The complex arrangement of pulleys and cables allows for precise control and the ability to lift incredibly heavy loads. This highlights the scalability and power of advanced pulley configurations.
6. Sailboats:
Sailboats utilize pulleys extensively to control the sails. The ropes (sheets and halyards) run through various pulleys to adjust the sail position and harness wind power effectively. This illustrates the application of pulleys in navigating and controlling complex mechanical systems.
Examples of Pulleys in Industry and Technology
The applications of pulleys extend far beyond everyday items. They are essential components in numerous industrial and technological systems:
1. Elevators and Lifts:
Elevators and lifts rely on complex pulley systems to move the cabin vertically. The counterweight system, combined with the pulley arrangement, ensures smooth and safe operation. This shows how pulley systems are integral to critical safety and transportation systems.
2. Conveyor Belts:
Many industrial conveyor belts utilize pulleys to drive the belt and move materials along the system. The pulleys transfer power from a motor to the belt, enabling efficient transportation of goods in factories and warehouses. This showcases the role of pulleys in material handling and logistics.
3. Mining Operations:
Mining operations often employ massive pulley systems to lift ore and other materials from deep shafts. The immense loads and distances involved necessitate robust and reliable pulley configurations for optimal safety and productivity. This underscores the significance of pulleys in heavy-duty industrial applications.
4. Suspension Bridges:
Suspension bridges, while complex structures, rely on fundamental principles of tension and support, which are facilitated by pulley systems in their design and construction. While not directly visible, pulley systems help manage the massive cables and weight distribution in these engineering marvels. This illustrates the subtle, yet crucial role of pulleys in large-scale structural engineering.
5. Automotive Systems:
Pulleys are used in various aspects of automotive mechanics. For instance, the serpentine belt utilizes pulleys to drive various components like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. This demonstrates the use of pulleys in efficient power transmission within complex mechanical systems.
6. Robotics:
Modern robotics often incorporate pulley systems for precise movement and control of robotic arms and other components. The adaptability and ability of pulleys to change the direction and magnitude of forces make them well-suited for robotics applications requiring precise manipulation. This highlights the evolving use of pulleys in advanced technological fields.
Advanced Pulley Systems and Their Applications
Beyond the basic types, there are more sophisticated pulley systems with specialized applications:
1. Differential Pulleys:
Differential pulleys offer a high mechanical advantage with a smaller number of pulleys. They are commonly used in automotive repair shops for lifting heavy vehicles. The complex gear arrangement within the differential pulley creates a high mechanical advantage.
2. Weston Differential Pulley:
The Weston differential pulley is a specific type of differential pulley known for its high mechanical advantage and efficiency. They are frequently employed in heavy-duty lifting applications, such as construction and industrial settings. The design maximizes efficiency in lifting heavy weights.
3. Sheaves and Blocks:
Sheaves are individual pulleys, often used in combination to create block and tackle systems. Different combinations of sheaves create different mechanical advantages. The arrangement of sheaves within blocks forms the basis for complex lifting systems.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Pulleys
From simple household items to complex industrial machinery, pulleys are fundamental components in countless machines and systems. Their ability to alter the direction of force, provide mechanical advantage, and enable precise control makes them indispensable. As technology advances, pulleys continue to play a significant role, showcasing their enduring relevance and versatility across various applications. Understanding the principles behind different types of pulleys and their varied uses allows for a deeper appreciation of their impact on our daily lives and technological advancements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Represents A Genotype
Apr 06, 2025
-
Albr3 K2so4 Kbr Al2 So4 3
Apr 06, 2025
-
Balanced Equation For Hydrochloric Acid And Calcium Carbonate
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Orbitals Are There In The 3d Subshell
Apr 06, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Rna Is True
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Some Examples Of Pulleys . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
