Albr3 K2so4 Kbr Al2 So4 3
News Leon
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
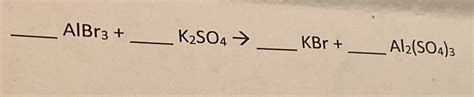
Table of Contents
Delving into the World of Aluminum Bromide, Potassium Sulfate, Potassium Bromide, and Aluminum Sulfate
This article explores the properties, uses, and reactions of four inorganic compounds: Aluminum bromide (AlBr₃), Potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄), Potassium bromide (KBr), and Aluminum sulfate (Al₂(SO₄)₃). We'll examine their individual characteristics, potential reactions between them, and their broader applications in various industries. Understanding these compounds individually and collectively is crucial for comprehending their roles in chemistry and beyond.
Aluminum Bromide (AlBr₃): A Deep Dive
Aluminum bromide is a colorless to pale-yellow crystalline solid with a strong affinity for moisture. Its anhydrous form is crucial for many applications, as the hydrated form can be less stable and more prone to hydrolysis.
Properties of AlBr₃:
- Chemical Formula: AlBr₃
- Molar Mass: 266.69 g/mol
- Melting Point: 97.5 °C
- Boiling Point: 263 °C
- Solubility: Soluble in various organic solvents like benzene and carbon disulfide, but reacts violently with water.
- Structure: Exists as a dimer (Al₂Br₆) in the solid state and as a monomer in the gas phase. The dimeric structure involves bridging bromine atoms.
Uses of AlBr₃:
AlBr₃ finds applications primarily as a:
- Catalyst: In organic chemistry, it serves as a Lewis acid catalyst in Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation reactions. These reactions are vital in synthesizing various organic compounds.
- Reagent: In the synthesis of other aluminum compounds and in some specific organic reactions requiring a Lewis acid.
Potassium Sulfate (K₂SO₄): An Essential Compound
Potassium sulfate, also known as arcanite, is a white crystalline solid, widely used as a fertilizer and in various industrial processes. Its solubility in water makes it a readily available source of potassium and sulfate ions.
Properties of K₂SO₄:
- Chemical Formula: K₂SO₄
- Molar Mass: 174.26 g/mol
- Melting Point: 1069 °C
- Boiling Point: Decomposes
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water.
- Structure: Forms an orthorhombic crystal structure.
Uses of K₂SO₄:
K₂SO₄'s principal applications stem from its potassium and sulfate content:
- Fertilizer: It's a crucial potassium source for plants, especially in crops sensitive to chloride ions (e.g., tobacco, potatoes). The sulfate component also contributes essential nutrients.
- Food Additive: It's used as a food additive in some processed foods to enhance texture and stability.
- Industrial Applications: It finds uses in the manufacturing of glass, ceramics, and other industrial processes.
Potassium Bromide (KBr): Versatile Uses in Various Fields
Potassium bromide is a white crystalline salt, readily soluble in water. It possesses notable properties making it suitable for a range of applications, primarily in medicine and photography.
Properties of KBr:
- Chemical Formula: KBr
- Molar Mass: 119.00 g/mol
- Melting Point: 734 °C
- Boiling Point: 1435 °C
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water.
- Structure: Forms a cubic crystal structure.
Uses of KBr:
KBr's versatility allows for its use in various fields:
- Medicine: Historically used as an anticonvulsant and sedative, though its use has diminished due to the availability of safer alternatives.
- Photography: It was widely employed in photographic emulsions as a light-sensitive component. While less prevalent now, its use persists in niche applications.
- Spectroscopy: KBr pellets are used in infrared (IR) spectroscopy as a matrix for sample preparation, allowing for the analysis of the sample's infrared absorption spectrum.
- Other Applications: KBr finds applications in various other fields, including as a food additive (in some countries) and in certain chemical processes.
Aluminum Sulfate (Al₂(SO₄)₃): A Multifaceted Industrial Chemical
Aluminum sulfate, commonly known as alum, is a white or off-white crystalline solid, extensively used in water treatment, paper manufacturing, and other industrial processes. Its astringent properties and ability to form insoluble hydroxides make it highly versatile.
Properties of Al₂(SO₄)₃:
- Chemical Formula: Al₂(SO₄)₃
- Molar Mass: 342.15 g/mol
- Melting Point: Decomposes
- Solubility: Soluble in water.
- Structure: Exists as a hydrate in various forms, with the anhydrous form being less common.
Uses of Al₂(SO₄)₃:
Aluminum sulfate's applications are extensive:
- Water Treatment: It's a crucial coagulant in water purification, helping to remove suspended solids and impurities.
- Paper Manufacturing: It's used in paper sizing, improving the paper's strength and resistance to water.
- Textile Industry: It acts as a mordant in dyeing processes, improving dye fixation to fabrics.
- Other Applications: It finds uses in leather tanning, cosmetics, and as a fire retardant.
Potential Reactions Between the Compounds
While a direct reaction between all four compounds simultaneously is unlikely to yield a simple, predictable outcome, we can consider potential reactions between pairs or subsets of these compounds.
-
AlBr₃ and Water: AlBr₃ reacts violently with water, undergoing hydrolysis to produce aluminum hydroxide and hydrobromic acid. This reaction highlights the importance of keeping AlBr₃ anhydrous.
-
K₂SO₄ and AlBr₃: A reaction between K₂SO₄ and AlBr₃ is less straightforward and may require specific conditions. It's possible that a double displacement reaction could occur under certain circumstances, potentially yielding potassium bromide and aluminum sulfate, although other products might also form depending on the reaction medium and temperature.
-
KBr and Al₂(SO₄)₃: Similar to the above, a reaction between KBr and Al₂(SO₄)₃ is not immediately obvious and would depend on reaction conditions. A double displacement might be possible under specific conditions. However, the likelihood of a significant reaction is low due to the low reactivity of KBr.
Conclusion: A Diverse Group of Compounds with Broad Applications
Aluminum bromide, potassium sulfate, potassium bromide, and aluminum sulfate represent a diverse group of inorganic compounds with significant applications across various industries. Their individual properties and potential reactions provide a fascinating insight into the richness and complexity of inorganic chemistry. Further research into their specific reactions and applications continues to expand our understanding of their importance in both scientific research and industrial processes. Understanding the characteristics and interactions of these compounds remains crucial for advancements in numerous fields. From water purification and fertilizer production to organic synthesis and photography, these compounds continue to play vital roles in modern society. This exploration only scratches the surface of the vast field of inorganic chemistry, highlighting the importance of further investigation into the numerous compounds and their applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Cant The Subscripts Be Changed In A Chemical Equation
Apr 06, 2025
-
Write An Equation For The Function Graphed Above
Apr 06, 2025
-
Is Sulfur A Metal Metalloid Or Nonmetal
Apr 06, 2025
-
A Group Of Ecosystems With Similar Climates And Organisms
Apr 06, 2025
-
Which Quantum Number Describes The Shape Of An Orbital
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Albr3 K2so4 Kbr Al2 So4 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
