The Process Of Making Yarn From Fibre Is Called
News Leon
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
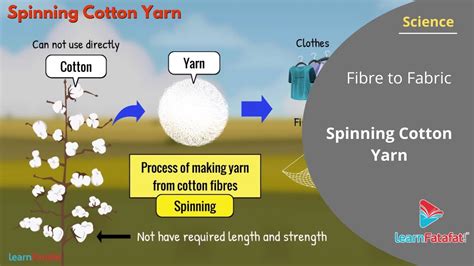
Table of Contents
The Process of Making Yarn from Fiber is Called Spinning: A Comprehensive Guide
The process of transforming raw fibers into yarn is called spinning. This seemingly simple act is a complex interplay of techniques and technologies, stretching back millennia to the very beginnings of textile production. From the hand-spun yarns of ancient civilizations to the high-speed industrial processes of today, spinning remains a crucial step in the creation of textiles, clothing, and countless other fiber-based products. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of yarn spinning, exploring the various stages, techniques, and technologies involved.
Understanding the Raw Materials: Fibers
Before we delve into the spinning process itself, it's essential to understand the nature of the raw materials: fibers. Fibers are the fundamental building blocks of yarn, and their properties significantly influence the final yarn characteristics. Fibers can be broadly categorized as:
1. Natural Fibers:
-
Plant Fibers: These fibers originate from plants and include cotton, flax (linen), hemp, jute, ramie, and sisal. Their properties vary significantly, affecting the resulting yarn's strength, softness, and absorbency. Cotton, for instance, is known for its softness and absorbency, while flax is renowned for its strength and durability.
-
Animal Fibers: Derived from animals, these fibers include wool (from sheep, goats, alpacas, etc.), cashmere (from goats), silk (from silkworms), and mohair (from Angora goats). Animal fibers are generally known for their warmth, softness, and luxurious feel, but their properties can also vary widely depending on the animal breed and the fiber's processing.
2. Synthetic Fibers:
These fibers are manufactured from chemicals and polymers, offering a wide range of properties tailored to specific applications. Examples include nylon, polyester, acrylic, rayon, and spandex. Synthetic fibers are often prized for their durability, resilience, and resistance to shrinking and stretching. They are also frequently blended with natural fibers to enhance certain characteristics of the yarn.
The Stages of Yarn Spinning: From Fiber to Thread
The spinning process, regardless of the fiber type or scale of production, broadly involves these key stages:
1. Fiber Preparation:
This initial stage is crucial and involves several sub-processes designed to prepare the fibers for spinning. The specific steps depend heavily on the type of fiber:
-
Cleaning: Removing impurities such as seeds, leaves, and other debris from natural fibers. This often involves processes like ginning (for cotton) or scutching (for flax).
-
Sorting and Grading: Separating fibers based on length, color, and quality. This ensures uniformity in the final yarn.
-
Opening and Cleaning: Breaking up clumps of fibers and further removing impurities.
-
Carding: A crucial process that disentangles and aligns the fibers, creating a continuous web or sliver. Carding is essential for producing smooth, even yarns.
-
Combing: A more refined process than carding, used for finer fibers to create even smoother and more parallel fibers, resulting in higher-quality yarns. Combing removes shorter fibers, leading to longer, stronger yarns.
2. Fiber Drawing and Attenuation:
This stage involves further aligning and thinning the fiber sliver. The sliver is drawn out and attenuated (made thinner) multiple times, increasing its length and creating a more uniform and parallel arrangement of fibers. This step is crucial for achieving the desired fineness and strength in the final yarn.
3. Spinning:
This is the core of the process, where the prepared fibers are twisted together to form a continuous yarn. Several spinning techniques exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
-
Ring Spinning: This is a widely used method, particularly for cotton and other staple fibers. It involves twisting the fibers with a rotating spindle and guiding the yarn through a ring traveler. Ring spinning is known for its versatility and ability to produce strong, even yarns.
-
Open-End (Rotor) Spinning: A high-speed method that uses a rotor to twist and wind the fibers together. It's highly efficient and produces yarns with a slightly more hairy or fuzzy texture. This is frequently used in making inexpensive yarns.
-
Air-Jet Spinning: Uses high-velocity air jets to twist the fibers, creating very fine and smooth yarns. It is suitable for producing high-quality, lightweight fabrics.
-
Self-Twist Spinning: A method where the fibers are twisted together without the use of a spindle or rotor. This technique produces yarns with a unique texture and drape.
-
Friction Spinning: The fibers are twisted and bonded together using friction. It is used to produce very strong and abrasion-resistant yarns.
4. Winding and Packaging:
Once the yarn is spun, it needs to be wound onto bobbins, cones, or spools for storage and further processing. The yarn may undergo additional treatments like dyeing or finishing before it is finally packaged and ready for use.
Factors Affecting Yarn Quality
Several factors influence the quality of the yarn produced:
-
Fiber Length: Longer fibers generally lead to stronger and smoother yarns.
-
Fiber Fineness: Finer fibers create softer and more delicate yarns.
-
Fiber Strength: Stronger fibers create more durable yarns.
-
Twist: The amount of twist in the yarn affects its strength, elasticity, and texture. Too little twist can lead to weak, easily-broken yarns, while too much twist can make the yarn stiff and harsh.
-
Spinning Method: Different spinning methods produce yarns with different properties.
-
Fiber Blending: Blending different fibers can enhance the yarn's properties, combining strength, softness, and other desirable characteristics.
Advanced Spinning Technologies
Technological advancements have significantly improved yarn spinning efficiency and quality. These include:
-
Automation: Modern spinning mills use highly automated systems for fiber preparation, spinning, and winding.
-
Computerized Control: Precise control of spinning parameters ensures consistent yarn quality.
-
New Fiber Types: Developments in polymer science have led to the creation of new synthetic fibers with unique properties.
-
Precision Monitoring and Analysis: Sophisticated sensors and analysis tools continuously monitor the spinning process, ensuring optimal performance and identifying potential issues early on.
The Importance of Yarn Spinning in the Textile Industry
Yarn spinning is the foundation of the textile industry. The quality of the yarn directly impacts the final fabric's quality, durability, and appearance. The development of new spinning technologies continues to drive innovation in the textile sector, allowing manufacturers to produce higher-quality, more sustainable, and cost-effective yarns for a wide range of applications. Understanding the process of yarn spinning is therefore crucial for anyone involved in the textile industry, from designers and manufacturers to retailers and consumers.
The Future of Yarn Spinning
The future of yarn spinning is likely to be characterized by:
-
Sustainability: Increased focus on using sustainable fibers and environmentally friendly processes.
-
Innovation: Development of new spinning technologies to produce yarns with improved properties and reduced environmental impact.
-
Smart Manufacturing: Greater use of data analytics and artificial intelligence to optimize spinning processes and improve efficiency.
-
Customization: Increased demand for customized yarns with unique properties to meet specific requirements.
In conclusion, the process of making yarn from fiber, known as spinning, is a complex and fascinating journey that transforms raw materials into the fundamental building blocks of countless textiles. From ancient hand-spinning techniques to modern automated processes, the evolution of yarn spinning reflects humanity's ingenuity and enduring need for textiles. Understanding this process is crucial for appreciating the artistry and technology behind the fabrics we use every day.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In Which Kind Of Rock Are Fossils Usually Found
Mar 24, 2025
-
Which Neuroglial Cells Help Form The Blood Brain Barrier
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Capacitor With Initial Charge Q0 Acts As
Mar 24, 2025
-
Calculate The Heat Of Combustion Of Ethene
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Iupac Name For The Following Molecule
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Process Of Making Yarn From Fibre Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
