A Capacitor With Initial Charge Q0 Acts As
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
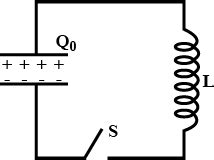
Table of Contents
A Capacitor with Initial Charge q₀: Acting as a Current Source and More
A capacitor, a fundamental passive component in electrical circuits, stores energy in an electric field. While often viewed as simply storing charge, a capacitor with an initial charge (q₀) exhibits dynamic behavior that's crucial to understanding its role in various circuits. This article delves deep into the multifaceted roles of a charged capacitor, exploring its behavior as a current source, its impact on transient response, and its applications in diverse scenarios.
The Capacitor's Dual Nature: Energy Storage and Current Delivery
A capacitor's ability to store energy is intrinsically linked to its behavior as a current source. When a capacitor is charged to an initial voltage V₀ (corresponding to an initial charge q₀ = CV₀, where C is the capacitance), it possesses stored energy. This stored energy can be released, manifesting as a current flow when the capacitor is connected to a circuit.
Capacitor as a Current Source: The Transient Response
Unlike a constant current source, a charged capacitor acts as a time-dependent current source. The current delivered isn't constant but decays over time. This is because the capacitor discharges, losing its stored energy as current flows. The rate of discharge depends on the circuit's resistance and the capacitor's capacitance.
Understanding the Discharge Process:
The fundamental equation governing capacitor discharge in a simple RC circuit (a resistor R connected in series with a capacitor C) is:
i(t) = (q₀/RC) * e^(-t/RC)
Where:
i(t)is the current at time t.q₀is the initial charge on the capacitor.Ris the resistance.Cis the capacitance.eis the base of the natural logarithm (approximately 2.718).RCis the time constant (τ), representing the time it takes for the current to decay to approximately 37% of its initial value.
Key Observations:
- Exponential Decay: The current from the charged capacitor follows an exponential decay. This means the current starts high and gradually decreases to zero as the capacitor discharges.
- Time Constant (τ = RC): The time constant is a crucial parameter. A larger time constant indicates a slower discharge, meaning the capacitor acts as a current source for a longer duration.
- Dependence on R and C: Both the resistance and the capacitance influence the discharge rate. Increasing R or C increases the time constant, extending the duration of the current flow.
Beyond the Simple RC Circuit: More Complex Scenarios
The behavior of a capacitor with an initial charge becomes more intricate in circuits with more complex topologies. For instance:
1. Parallel RC Circuits: In parallel RC circuits, the initial current will be divided among the branches. The discharge rate will still be exponential, but the effective time constant will depend on the parallel combination of resistors.
2. RLC Circuits: Adding an inductor (L) creates an RLC circuit. This introduces oscillations or damped oscillations, depending on the circuit parameters. The initial charge on the capacitor will determine the initial amplitude of these oscillations. The current will be a more complex function, often involving sinusoidal terms along with the exponential decay.
3. More Complex Networks: In complex networks with multiple capacitors and resistors, the analysis becomes significantly more challenging, often requiring techniques like Kirchhoff's laws and nodal/mesh analysis. The initial charge on each capacitor will influence the overall transient behavior of the entire circuit.
Applications Leveraging the Initial Charge
The ability of a charged capacitor to act as a temporary current source has numerous practical applications:
1. Pulse Generation:
A charged capacitor can be discharged rapidly through a resistor to generate a pulse of current. The pulse's duration and amplitude can be controlled by choosing appropriate values of R and C. This principle is used in various applications, including:
- Flash Photography: A capacitor stores a significant charge, then discharges rapidly to provide the high current needed to power the flash lamp.
- Timing Circuits: The discharge time constant of an RC circuit can be used to create precise timing intervals.
2. Energy Storage and Delivery:
Capacitors are vital for storing and delivering energy in various applications. For example:
- Power Supplies: Capacitors smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supplies. The initial charge on the capacitor helps maintain a relatively constant output voltage despite variations in the input.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Capacitors provide backup power in UPS systems during power outages. The stored charge provides a temporary power source until a backup generator kicks in or the main power is restored.
3. Sensor Applications:
Capacitors play a critical role in sensors. A change in capacitance, often due to a physical phenomenon, can be detected as a change in the charge or discharge characteristics. Examples include:
- Capacitive Touchscreens: A finger's proximity changes the capacitance, which is detected as a touch input.
- Pressure Sensors: Pressure changes alter the capacitance of a sensor, providing a measurement of the pressure.
4. Signal Processing:
Capacitors are ubiquitous in signal processing circuits, often used for:
- Filtering: Capacitors act as frequency-selective elements, allowing certain frequencies to pass while blocking others. The initial charge can impact the circuit's transient response to input signals.
- Coupling and Decoupling: Capacitors can isolate DC components while allowing AC signals to pass, or vice versa, influencing the overall signal processing.
Analyzing Circuits with Initially Charged Capacitors
Analyzing circuits containing initially charged capacitors requires careful consideration of initial conditions. Standard circuit analysis techniques like nodal analysis, mesh analysis, or superposition must incorporate the initial voltage across the capacitor (V₀ = q₀/C) at time t = 0. This initial voltage acts as a source in the circuit.
The Importance of Initial Conditions:
Ignoring the initial charge on the capacitor can lead to erroneous results. The initial voltage across the capacitor influences the transient response, particularly in circuits that contain inductors as well, and ignoring it will provide inaccurate calculations of currents and voltages over time.
Solving Techniques:
Several techniques help analyze circuits with initially charged capacitors:
- Differential Equations: The most rigorous approach uses Kirchhoff's laws to derive differential equations that describe the circuit's behavior. The initial charge provides the initial condition for solving these equations.
- Laplace Transforms: Laplace transforms provide a powerful mathematical tool to solve complex circuit differential equations, particularly helpful in systems with multiple energy storage elements. The initial conditions are incorporated into the Laplace transform.
- Simulation Software: Software like LTSpice or Multisim simplifies the analysis by allowing you to simulate the circuit's behavior, including the effect of the initially charged capacitor.
Conclusion: The Versatility of the Charged Capacitor
A capacitor with an initial charge is far more than a passive storage element; it's a dynamic component that can act as a time-dependent current source, influencing the transient response of circuits. Its behavior, characterized by exponential decay in simple RC circuits and more complex waveforms in more intricate networks, makes it indispensable in a vast array of applications, from pulse generation and energy storage to sensor technology and signal processing. Understanding the principles governing the behavior of a charged capacitor is crucial for anyone working with electrical circuits and electronic systems. Proper analysis methods, incorporating the initial conditions, are essential for accurate predictions and efficient circuit design. The versatility of this simple component underscores its fundamental role in modern electronics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cell Type Not Found In Areolar Tissue
Mar 25, 2025
-
Every Computer Has An Operating System
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Browser
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Conjugate Base Of Nh4
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Years Did Rip Van Winkle Sleep
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Capacitor With Initial Charge Q0 Acts As . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
