Cell Type Not Found In Areolar Tissue
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
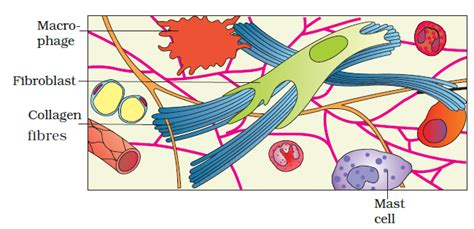
Table of Contents
Cell Types Not Found in Areolar Tissue: A Comprehensive Overview
Areolar connective tissue, also known as loose connective tissue, is a ubiquitous tissue type found throughout the body. Its remarkable versatility stems from its composition, a loose arrangement of various cells embedded within a substantial extracellular matrix. Understanding what isn't present in areolar tissue is just as crucial as knowing what is, as this absence reflects the tissue's specific functional properties. This article delves into a detailed exploration of cell types conspicuously absent from areolar tissue, highlighting the reasons behind these omissions and the implications for the tissue's overall role.
Understanding the Cellular Composition of Areolar Tissue
Before examining the absent cell types, let's briefly review the cellular inhabitants of areolar tissue. This tissue is characterized by a diverse cellular population, including:
-
Fibroblasts: These are the primary resident cells, responsible for synthesizing and maintaining the extracellular matrix components, including collagen and elastin fibers. Their abundance reflects the need for constant matrix remodeling and repair.
-
Fibrocytes: These are quiescent fibroblasts, representing a less active stage of fibroblast function. They are still integral to maintaining the integrity of the matrix.
-
Macrophages: These phagocytic cells play a crucial role in the immune defense system, engulfing cellular debris, pathogens, and foreign substances. Their presence reflects the tissue's role in immune surveillance and response.
-
Mast cells: These cells release histamine and heparin, playing key roles in inflammatory and allergic reactions. Their presence highlights the tissue's role in mediating immune responses.
-
Plasma cells: These antibody-producing cells are part of the adaptive immune response, contributing to the body's specific defense against pathogens. Their presence indicates the tissue's involvement in immune defense.
-
Adipocytes: Fat cells, often found in varying quantities depending on the location of the areolar tissue. They contribute to energy storage and insulation.
-
Leukocytes: Various white blood cells, such as neutrophils and lymphocytes, can migrate into areolar tissue as part of the inflammatory response. Their presence is transient, varying based on the immune status of the tissue.
Cell Types Absent from Areolar Tissue: A Detailed Analysis
The absence of certain cell types in areolar tissue is not accidental; it reflects the tissue's specific physiological role and functional limitations. Let's explore several key examples:
1. Osteocytes and Osteoblasts: The Absence of Bone Formation
Areolar tissue is fundamentally different from bone tissue. Osteocytes, mature bone cells residing within the bone matrix, and osteoblasts, bone-forming cells responsible for synthesizing the bone matrix, are completely absent. The extracellular matrix of areolar tissue lacks the mineralized collagen and the organized structure characteristic of bone. Areolar tissue's primary function is not structural support or mineral storage, which are the hallmarks of bone tissue. Its loose organization allows for flexibility and diffusion, unlike the rigid structure of bone.
2. Chondrocytes: The Lack of Cartilaginous Components
Chondrocytes, the cells responsible for forming and maintaining cartilage, are absent from areolar tissue. Cartilage, with its unique extracellular matrix rich in proteoglycans, provides structural support and flexibility in specific locations like joints. Areolar tissue's lack of this specialized extracellular matrix indicates its role in a different functional context. The presence of collagen and elastin fibers in areolar tissue provides elasticity and support, but their organization and composition are distinctly different from the structure of cartilage.
3. Myocytes (Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth Muscle Cells): The Absence of Contractility
Areolar tissue does not contain myocytes, the cells responsible for muscle contraction. While it may be interwoven with muscle tissue in certain locations, it doesn't inherently possess contractile properties. The absence of these specialized cells is consistent with areolar tissue's role in supporting and connecting different tissues, rather than active movement. Muscle tissue has specialized cellular structures and contractile proteins absent in areolar tissue.
4. Keratinocytes: The Absence of Epithelial Protection
Areolar tissue lacks keratinocytes, the primary cells of the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin. Keratinocytes produce keratin, a structural protein that contributes to the skin's protective barrier function. Areolar tissue is found beneath the epidermis, providing support and connectivity. Its function is not related to protection against environmental stressors, which is the primary role of the epidermis and its keratinocytes.
5. Odontoblasts: The Absence of Tooth Structure
Odontoblasts, the cells responsible for producing dentin, the hard tissue underlying the enamel in teeth, are not found in areolar tissue. Areolar tissue's loose organization is entirely incompatible with the highly specialized and mineralized structure of teeth. The unique cellular organization and matrix composition of dental tissue differ significantly from the structure of areolar connective tissue.
6. Neuroglia: The Absence of Neural Support
While nerves may pass through areolar tissue, neuroglia, the supporting cells of the nervous system, are not a resident cell type. Neuroglia, such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, play crucial roles in maintaining the structural and functional integrity of the nervous system. Areolar tissue's function is not to support or maintain neural cells; rather, it provides a supportive framework through which nerves can travel.
Implications of Absent Cell Types
The absence of these cell types in areolar tissue is directly related to its unique role in the body. Areolar tissue's primary function is to:
-
Provide structural support: Its loose organization allows it to fill spaces between organs and tissues, providing a flexible framework.
-
Facilitate nutrient and waste exchange: The loose arrangement of its fibers and cells permits the diffusion of nutrients and oxygen to surrounding tissues, while also facilitating the removal of waste products.
-
Aid in immune response: The presence of immune cells allows for rapid detection and response to pathogens and injuries.
-
Repair damaged tissues: Fibroblasts actively participate in wound healing and tissue repair.
-
Store energy: Adipocytes contribute to energy storage.
The absence of cells associated with specialized functions, such as bone formation, cartilage formation, or muscle contraction, reinforces the understanding that areolar tissue is a versatile but relatively simple connective tissue, fulfilling crucial supportive and connective roles within the body, without engaging in the specialized processes of other tissue types.
Conclusion
Areolar tissue's unique cellular composition is essential for its diverse functional roles. The absence of specific cell types, such as osteocytes, chondrocytes, myocytes, keratinocytes, odontoblasts, and neuroglia, highlights the tissue's limitations and reinforces its specialized function as a connective and supportive tissue. Understanding both the presence and absence of certain cell types within areolar tissue is fundamental to comprehending its fundamental role in the overall structure and function of the human body. This detailed examination demonstrates the intricate interplay of cellular composition and tissue-specific functions within the context of the human organism. Further research continues to illuminate the complex dynamics of connective tissue and its contribution to overall health and well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Reaction Of Ethanol And Acetic Acid
Mar 26, 2025
-
Proverbs Of The Day With Meaning
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Sodium
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Urinary Bladder Is Composed Of What Epithelium
Mar 26, 2025
-
Sphere Is To Circle As Cube Is To
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cell Type Not Found In Areolar Tissue . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
