Which Neuroglial Cells Help Form The Blood-brain Barrier
News Leon
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
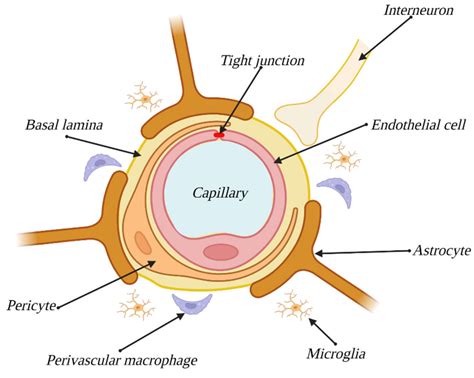
Table of Contents
Which Neuroglial Cells Help Form the Blood-Brain Barrier?
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border composed of specialized endothelial cells that prevents the passage of many substances from the bloodstream into the brain tissue. This critical structure protects the central nervous system (CNS) from harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients and molecules to pass through. While endothelial cells are the primary architects of the BBB, other crucial players exist, notably neuroglial cells. Understanding the specific roles of these neuroglial cells is paramount to comprehending the BBB's intricate functionality and its implications for neurological diseases and drug delivery.
The Endothelial Cell Foundation: The Cornerstone of the BBB
Before delving into the contribution of neuroglial cells, it's essential to acknowledge the foundational role of endothelial cells. These cells form the continuous lining of brain capillaries, exhibiting unique characteristics that distinguish them from endothelial cells in other parts of the body. These characteristics include:
-
Tight Junctions: Endothelial cells in the BBB are interconnected by incredibly tight junctions, effectively sealing the paracellular pathway (the space between cells). This prevents the passage of most molecules and ions, creating a highly selective barrier. Proteins like claudins, occludins, and junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) are key components of these tight junctions.
-
Limited Vesicular Transport: Transcellular transport (movement through the cells) via vesicular trafficking is also limited in BBB endothelial cells compared to other endothelial cells. This minimizes the entry of unwanted substances.
-
Specialized Transporters: BBB endothelial cells express specific transporters that facilitate the selective passage of essential nutrients, such as glucose and amino acids, into the brain. Conversely, they also possess efflux transporters that pump out potentially harmful substances. These transporters are crucial for maintaining the brain's metabolic homeostasis.
-
Basal Lamina: Surrounding the endothelial cells is the basal lamina, a specialized extracellular matrix that provides structural support and further contributes to the barrier's selectivity.
The Neuroglial Cell Support System: Astrocytes and Pericytes
While endothelial cells form the structural core of the BBB, its function and regulation heavily rely on interactions with neighboring neuroglial cells, primarily astrocytes and pericytes. These cells don't physically constitute the barrier itself but actively participate in its development, maintenance, and regulation.
Astrocytes: The Master Regulators
Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells that play a multifaceted role in the CNS. Their contribution to the BBB is substantial, encompassing various aspects:
-
End-Foot Processes: Astrocytes extend numerous processes, called end-feet, which enwrap the brain capillaries and directly contact the endothelial cells. These end-feet are critical for BBB formation and maintenance.
-
Secretion of Paracrine Factors: Astrocytes secrete a variety of paracrine factors, including growth factors, cytokines, and signaling molecules. These factors influence the differentiation and function of endothelial cells, promoting the formation of tight junctions and the expression of specific transporters. Examples include transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and fibroblast growth factors (FGFs).
-
Regulation of Blood Flow: Astrocytes play a significant role in regulating cerebral blood flow. By sensing neuronal activity, they can induce vasodilation or vasoconstriction to adjust blood flow to meet the brain's metabolic demands. This regulation maintains the optimal environment for BBB function.
-
Maintenance of Tight Junctions: Astrocytic end-feet are crucial for the maintenance of the tight junctions between endothelial cells. They actively participate in the regulation of the expression and localization of tight junction proteins.
-
Metabolic Support: Astrocytes provide metabolic support to the neurons and contribute to the overall metabolic homeostasis of the brain. This metabolic interplay indirectly supports the BBB by ensuring its proper function within a stable environment.
Pericytes: The Contractile Regulators
Pericytes are contractile cells embedded within the basement membrane of brain capillaries. While less extensively studied compared to astrocytes, their contribution to BBB function is substantial:
-
Regulation of Blood Flow: Pericytes play a vital role in regulating cerebral blood flow by contracting and relaxing, influencing the capillary diameter. This regulation is crucial for maintaining the appropriate delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the brain tissue while removing waste products.
-
Influence on Tight Junction Integrity: Pericytes are believed to influence the integrity and function of tight junctions between endothelial cells. Studies suggest they may interact with astrocytes and endothelial cells to modulate the expression of tight junction proteins.
-
Secretion of Factors: Similar to astrocytes, pericytes secrete factors that affect endothelial cell function and BBB development. These factors can influence the expression of transporters and enzymes that contribute to BBB selectivity.
-
Immune Response Modulation: Pericytes also contribute to the immune response within the CNS. They can modulate the inflammatory response, which is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the BBB during inflammation or injury.
Microglia: The Immune Sentinels and their indirect Role
While not directly involved in the structural formation of the BBB like astrocytes and pericytes, microglia, the resident immune cells of the CNS, indirectly influence the BBB. Their actions primarily manifest during inflammatory conditions or injury:
-
Inflammation and BBB Permeability: During inflammation, activated microglia release inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and chemokines. These mediators can disrupt the tight junctions of the BBB, increasing permeability and potentially allowing harmful substances to enter the brain. This is a significant mechanism in neurological diseases like stroke and multiple sclerosis.
-
Repair and Regeneration: After injury or inflammation, microglia participate in tissue repair and regeneration. This process includes contributing to the restoration of the BBB integrity. They modulate the immune response and promote the regeneration of endothelial cells and other components of the BBB.
-
Modulation of Astrocyte Activity: Microglia interact with astrocytes, influencing their activity and contribution to the BBB. This interaction can either support or impair BBB integrity depending on the context.
Oligodendrocytes: Indirect Influence Through Myelination
Oligodendrocytes are glial cells responsible for the myelination of axons in the CNS. While not directly involved in the structural and functional aspects of the BBB, their contribution is indirectly important for maintaining the healthy environment of the CNS:
-
Myelin Maintenance: The myelin sheath produced by oligodendrocytes is essential for the proper functioning of neurons and the overall health of the CNS. By ensuring efficient neuronal signal transmission, the proper functioning of the brain is supported, indirectly influencing the overall integrity and functionality of the BBB.
-
Metabolic Support: Similar to astrocytes, oligodendrocytes also offer metabolic support to neurons in their vicinity, thus contributing to the maintenance of a stable and healthy environment necessary for proper BBB function.
Clinical Implications: BBB Dysfunction and Neuroglial Cells
Dysfunction of the BBB is a hallmark of many neurological diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and brain tumors. The disruption of the BBB contributes significantly to the progression of these diseases. Understanding the role of neuroglial cells in BBB dysfunction is crucial for the development of effective therapies.
Targeting the interactions between neuroglial cells and endothelial cells could offer novel therapeutic strategies for diseases associated with BBB breakdown. For example, manipulating astrocyte signaling pathways or modulating pericyte contractility may offer ways to restore or reinforce BBB integrity.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Effort
The blood-brain barrier is not simply a single cellular structure; rather, it's a complex and highly regulated interface formed through the intricate interplay of various cell types, predominantly endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes. While endothelial cells form the physical barrier, the neuroglial cells, particularly astrocytes and pericytes, act as master regulators, influencing its formation, maintenance, and response to injury or inflammation. Microglia and oligodendrocytes exert indirect influences, primarily through their roles in immune response and myelin maintenance, respectively. Further research into these complex interactions is essential for fully understanding the BBB and for developing effective treatments for a range of neurological disorders. A deeper understanding of the intricate collaboration between neuroglial cells and endothelial cells will undoubtedly pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies targeting BBB dysfunction.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Substance Loses Electrons In A Chemical Reaction
Mar 25, 2025
-
1 Mg Is How Many Units
Mar 25, 2025
-
Uaa Uga And Uag Are All Codons
Mar 25, 2025
-
Sodium Is A Solid Liquid Or Gas
Mar 25, 2025
-
In The Figure Projectile Particle 1 Is An Alpha
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Neuroglial Cells Help Form The Blood-brain Barrier . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
