Switch S In The Figure Is Closed At Time
News Leon
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
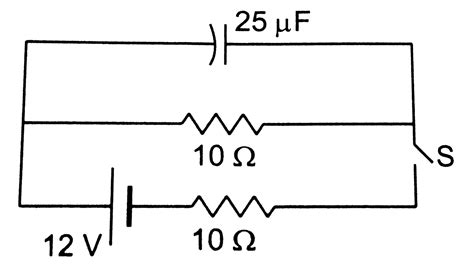
Table of Contents
Switch S in the Figure is Closed at Time t = 0: A Deep Dive into Circuit Analysis
The seemingly simple act of closing a switch in a circuit at a specific time, t=0, opens up a fascinating world of circuit analysis. Understanding the transient behavior of circuits after a switch closure is crucial in various engineering disciplines, from electrical engineering and electronics to control systems and power systems. This article will explore the dynamics of such circuits, covering different circuit configurations, analytical techniques, and practical applications. We'll delve into both simple and more complex scenarios, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental concept.
Understanding the Transient Response
When a switch is closed at t=0 in a circuit containing energy storage elements like capacitors and inductors, the circuit's response isn't instantaneous. Instead, it undergoes a transient period where currents and voltages change dynamically until they reach a steady-state condition. This transient behavior is governed by the circuit's inherent characteristics, specifically the values of its resistors, capacitors, and inductors (RLC components).
The Role of R, L, and C Components
-
Resistors (R): Resistors dissipate energy in the form of heat, influencing the rate at which the transient response decays. A higher resistance generally leads to faster decay.
-
Inductors (L): Inductors store energy in their magnetic fields. They resist changes in current, causing a slower transient response. The inductance value directly impacts the time constant of the circuit.
-
Capacitors (C): Capacitors store energy in their electric fields. They resist changes in voltage, also affecting the transient response. The capacitance value contributes significantly to the circuit's time constant.
The interplay between these components determines the nature of the transient response—whether it's overdamped, critically damped, or underdamped.
Analytical Techniques for Solving Switch Closure Problems
Several mathematical techniques can be employed to analyze the transient behavior of circuits after a switch closure at t=0. The most common include:
1. Differential Equations
For circuits with R, L, and C components, applying Kirchhoff's laws leads to a set of differential equations that describe the circuit's behavior. Solving these equations, often using Laplace transforms, provides expressions for voltage and current as functions of time. This method offers a precise solution but can be computationally intensive for complex circuits.
2. Laplace Transforms
Laplace transforms are a powerful tool for simplifying the solution of differential equations. Transforming the time-domain equations into the s-domain allows for algebraic manipulation, making the solution process significantly easier. The inverse Laplace transform then yields the time-domain solution. This technique is particularly useful for circuits with multiple energy storage elements.
3. Thevenin and Norton Equivalents
Simplifying complex circuits using Thevenin or Norton equivalent circuits can significantly reduce the complexity of the analysis. By reducing the circuit to a simpler equivalent, the transient response can be determined more easily. This is especially helpful when dealing with circuits containing multiple sources and components.
4. State-Space Representation
For higher-order circuits, state-space representation offers a systematic approach to analyze the system's behavior. This method uses a set of first-order differential equations to describe the system's dynamics, making it easier to handle complex circuits and to simulate them using computer software.
Different Circuit Configurations and Their Transient Responses
Let's examine the transient behavior of several common circuit configurations after switch closure at t=0:
1. RC Circuits (Resistor-Capacitor Circuits)
A simple RC circuit consists of a resistor and a capacitor connected in series with a voltage source. When the switch is closed, the capacitor charges exponentially towards the source voltage. The time constant, τ = RC, determines the rate of charging. The voltage across the capacitor as a function of time is given by:
V<sub>C</sub>(t) = V<sub>s</sub>(1 - e<sup>-t/RC</sup>)
where V<sub>s</sub> is the source voltage.
2. RL Circuits (Resistor-Inductor Circuits)
An RL circuit consists of a resistor and an inductor connected in series with a voltage source. Upon switch closure, the current through the inductor increases exponentially towards a steady-state value. The time constant, τ = L/R, governs the rate of current increase. The current through the inductor as a function of time is:
I<sub>L</sub>(t) = (V<sub>s</sub>/R)(1 - e<sup>-Rt/L</sup>)
where V<sub>s</sub> is the source voltage.
3. RLC Circuits (Resistor-Inductor-Capacitor Circuits)
RLC circuits exhibit more complex transient behavior, characterized by oscillations or exponential decay, depending on the relationship between R, L, and C. The response can be:
-
Overdamped: The circuit returns to steady state without oscillating. This occurs when the damping is high (large R).
-
Critically Damped: The circuit returns to steady state in the fastest possible time without oscillating. This is the optimal damping condition.
-
Underdamped: The circuit oscillates before settling to steady state. This occurs when the damping is low (small R).
The characteristic equation for an RLC circuit helps determine the type of damping and the frequency of oscillation in the underdamped case.
Practical Applications of Switch Closure Analysis
Understanding the transient response of circuits after switch closure is crucial in many real-world applications:
-
Power Systems: Analyzing the transient behavior of power systems during switching operations is vital for ensuring system stability and preventing equipment damage.
-
Motor Control: Controlling the speed and torque of electric motors often involves switching techniques. Analyzing the transient response helps in designing efficient and reliable control systems.
-
Digital Electronics: The operation of digital circuits relies on the fast switching of transistors. Understanding transient effects is critical for designing high-speed digital systems.
-
Telecommunications: Switching networks in telecommunications rely on fast and reliable switching mechanisms. Analyzing the transient response is important for ensuring efficient and reliable communication.
-
Medical Equipment: Many medical devices employ switching circuits. Accurate analysis of transient behavior is crucial for safety and proper device functioning.
Advanced Topics and Further Exploration
This article provides a foundational understanding of switch closure analysis. Further exploration can delve into more advanced topics such as:
-
Non-linear circuits: Circuits containing non-linear components like diodes or transistors require more sophisticated analytical techniques.
-
Switching power supplies: The transient behavior of switching power supplies needs careful consideration for efficient operation and regulation.
-
Numerical methods: For complex circuits, numerical methods like simulation software are often necessary to obtain accurate solutions.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple act of closing a switch at t=0 initiates a complex interplay of currents and voltages in a circuit. Understanding this transient behavior is fundamental to various engineering disciplines. By mastering the analytical techniques and understanding the behavior of different circuit configurations, engineers can design and analyze circuits that perform reliably and efficiently in a wide range of applications. This knowledge is essential for building robust and functional systems across diverse fields. Continuous learning and exploration of advanced topics will further enhance one's proficiency in this critical area of circuit analysis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is The Following Relation A Function
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is The Smallest Unit Of Measurement
Mar 26, 2025
-
When Lithium Hydroxide Pellets Are Added
Mar 26, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 36 And 54
Mar 26, 2025
-
Inventory Is Classified On The Balance Sheet As A
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Switch S In The Figure Is Closed At Time . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
