Common Factors Of 36 And 54
News Leon
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
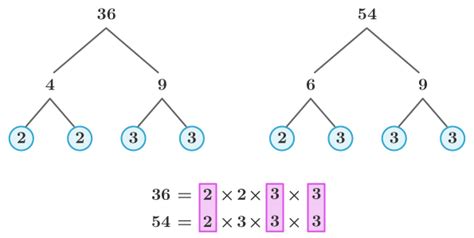
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Common Factors of 36 and 54: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise, but it's a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching implications in various fields, from cryptography to computer science. This article delves deep into the process of identifying the common factors of 36 and 54, exploring different methods, and highlighting the underlying mathematical principles. We'll go beyond simply finding the answer, aiming to build a comprehensive understanding of factors, common factors, greatest common factors (GCF), and their significance.
Understanding Factors and Common Factors
Before we embark on finding the common factors of 36 and 54, let's solidify our understanding of fundamental concepts.
What is a Factor? A factor of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
What are Common Factors? Common factors are numbers that are factors of two or more numbers. They are the shared divisors of the numbers in question. For example, the common factors of 12 and 18 are 1, 2, 3, and 6.
Method 1: Listing Factors
The most straightforward approach to finding the common factors of 36 and 54 is by listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the ones they share.
Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
Factors of 54: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54
By comparing the two lists, we can readily identify the common factors of 36 and 54: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
This method, while simple for smaller numbers like 36 and 54, becomes cumbersome and prone to errors when dealing with larger numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
A more efficient and robust method for finding common factors, especially for larger numbers, involves prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
Let's find the prime factorization of 36 and 54:
- 36: 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
- 54: 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 2 x 3³
Now, to find the common factors, we look for the prime factors that appear in both factorizations. Both numbers have at least one 2 and at least two 3s. Therefore, the common prime factors are 2 and 3.
To find all common factors, we systematically combine these common prime factors:
- 2⁰ x 3⁰ = 1
- 2¹ x 3⁰ = 2
- 2⁰ x 3¹ = 3
- 2¹ x 3¹ = 6
- 2⁰ x 3² = 9
- 2¹ x 3² = 18
Thus, the common factors of 36 and 54, obtained through prime factorization, are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. This confirms the result obtained using the listing method.
The Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
Among the common factors, the greatest common factor (GCF) holds particular significance. The GCF of two numbers is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. In the case of 36 and 54, the GCF is 18.
Understanding the GCF is crucial in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems. For instance, to simplify the fraction 36/54, we divide both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF (18), resulting in the simplified fraction 2/3.
Method 3: Euclidean Algorithm
For larger numbers, the Euclidean algorithm provides an efficient way to determine the GCF. This algorithm is based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers become equal, and that number is the GCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 36 and 54:
- 54 - 36 = 18
- 36 - 18 = 18
- Since both numbers are now 18, the GCF is 18.
The Euclidean algorithm is particularly advantageous for finding the GCF of very large numbers, offering a computationally efficient solution compared to prime factorization or listing factors.
Applications of Common Factors and GCF
The concepts of common factors and the greatest common factor have extensive applications across diverse fields:
- Simplifying Fractions: As shown earlier, the GCF helps reduce fractions to their simplest form.
- Solving Diophantine Equations: These equations involve finding integer solutions to algebraic equations. The GCF plays a vital role in determining the solvability of such equations.
- Cryptography: Number theory concepts, including GCF, are fundamental to modern cryptographic systems that protect sensitive data.
- Computer Science: Algorithms for efficient computation frequently rely on concepts related to factors and GCFs.
- Music Theory: The GCF is used to find the greatest common divisor of two musical intervals, helping in understanding harmonic relationships.
- Geometry: GCF can be used to determine the dimensions of the largest possible square that can tile a given rectangle.
Beyond 36 and 54: Exploring Further
While we've focused on 36 and 54, the methods and principles discussed are applicable to any pair of numbers. The key is to understand the underlying concepts of factors, common factors, and prime factorization to efficiently find the common factors and the GCF for any given numbers. The more complex the numbers, the more beneficial the Euclidean algorithm becomes.
Furthermore, these concepts can be extended to finding the common factors of three or more numbers. In such cases, we would first find the prime factorization of each number and then identify the common prime factors. Combining these common prime factors in all possible ways would then yield all the common factors, with the greatest among them representing the greatest common factor.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
Understanding common factors and the greatest common factor is a cornerstone of number theory and has practical relevance across many disciplines. While listing factors is intuitive for smaller numbers, prime factorization and the Euclidean algorithm provide more efficient and robust methods for larger numbers. By grasping these concepts and mastering the various techniques, we unlock a deeper understanding of the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. This knowledge not only aids in solving mathematical problems but also opens doors to exploring more advanced mathematical concepts and their applications in diverse fields. The journey from finding the common factors of 36 and 54 leads to a richer appreciation of the elegance and power of number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Orbitals Are In The Third Shell
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Continent Is Closest To Antarctica
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is 0 07 As A Percentage
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Unpaired Electrons Does Oxygen Have
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is Not True About The Cell Membrane
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Factors Of 36 And 54 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
