Log X Log X 3 1
News Leon
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
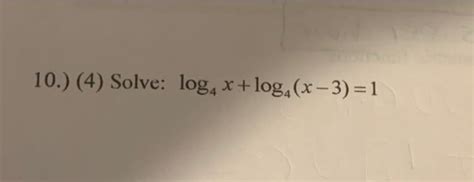
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: A Deep Dive into logₓ(logₓ(3x+1))
The expression logₓ(logₓ(3x+1)) presents a fascinating challenge in mathematical analysis. It's not a standard function often encountered in introductory courses, demanding a nuanced understanding of logarithmic properties and their interplay with polynomial expressions. This article delves deep into this expression, exploring its domain, range, behavior, and potential applications, offering a comprehensive analysis suitable for both students and enthusiasts of mathematics.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Logarithms and their Properties
Before embarking on the analysis of logₓ(logₓ(3x+1)), we must solidify our understanding of logarithms. A logarithm is essentially the inverse operation of exponentiation. The expression logₐ(b) = c is equivalent to aᶜ = b, where 'a' is the base, 'b' is the argument, and 'c' is the logarithm.
Several crucial properties govern logarithmic operations:
- Product Rule: logₐ(xy) = logₐ(x) + logₐ(y)
- Quotient Rule: logₐ(x/y) = logₐ(x) - logₐ(y)
- Power Rule: logₐ(xⁿ) = n logₐ(x)
- Change of Base: logₐ(x) = logₓ(x) / logₓ(a)
These properties are instrumental in simplifying and manipulating logarithmic expressions, and we will utilize them extensively in our analysis.
Defining the Domain: Where the Function Exists
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (x-values) for which the function is defined. In the case of logₓ(logₓ(3x+1)), we have a nested logarithmic function, introducing several constraints:
-
The Argument of the Inner Logarithm: The argument of the inner logarithm,
logₓ(3x+1), must be positive. Therefore,3x + 1 > 0, which impliesx > -1/3. -
The Base of the Logarithms: The base, 'x', must be positive and not equal to 1. This condition is essential because logarithmic functions with bases less than or equal to zero or equal to one are undefined. Therefore,
x > 0andx ≠ 1. -
The Argument of the Outer Logarithm: The argument of the outer logarithm,
logₓ(3x+1), must also be positive. This introduces a further constraint, as the value oflogₓ(3x+1)depends on both 'x' and '3x+1'. We'll need to explore this further using numerical methods or graphical analysis.
Combining these constraints, the preliminary domain appears to be x > 0 and x ≠ 1, but further analysis is needed to refine this considering the nested nature. A graphical approach using computational software can provide a more precise representation of the valid x-values.
Numerical and Graphical Analysis of the Domain
By plotting the function using a graphing calculator or software like MATLAB or Python with libraries like NumPy and Matplotlib, we can visualize the function and determine its domain more precisely. The graph will clearly show where the function is defined and where it becomes undefined due to the logarithmic constraints. This visualization allows for a more intuitive understanding of the domain’s boundary.
The graph will show that there's a region where the inner logarithm is negative, rendering the outer logarithm undefined. Thus, the domain will be a restricted interval within x > 0 and x ≠ 1. Precise numerical methods, potentially involving iterative solutions, might be necessary to identify the exact boundary points.
Investigating the Range: Possible Output Values
Determining the range of logₓ(logₓ(3x+1)) requires a thorough understanding of the behavior of the nested logarithmic function. Since both logarithms are operating on positive values within their respective domains (as established earlier), the range will be influenced by the interplay between the base 'x' and the argument '3x+1'.
As 'x' approaches infinity, the argument 3x+1 also approaches infinity, but the growth rate of the logarithm is slower than that of the linear expression. Consequently, the range might be restricted from negative infinity to a finite value. Numerical analysis and graphing techniques will help to elucidate this.
Exploring the Range through Computational Methods
By analyzing the graph generated from computational software, we can observe the range of values the function takes. Numerical analysis, possibly involving the evaluation of the function at various points within the established domain, can further refine our understanding of its range. We should expect the function to display asymptotic behavior as ‘x’ approaches the boundaries of its domain, thus influencing the range.
Through observation of the graph and numerical analysis, we can deduce if the range is bounded (has a maximum and minimum value) or unbounded (extends to positive or negative infinity). The behavior of the function near the boundary points of the domain is crucial in determining this.
Analyzing the Behavior: Asymptotes and Critical Points
The behavior of logₓ(logₓ(3x+1)) is complex and intricately linked to the constraints imposed by the nested logarithms. We should analyze the function’s behavior as 'x' approaches the boundaries of its domain and identify any potential asymptotes or critical points (where the derivative is zero or undefined).
As 'x' approaches the lower bound of the domain (determined earlier through graphical and numerical analysis), the function likely approaches negative infinity. Similarly, as 'x' approaches infinity, we may observe asymptotic behavior toward a specific finite value or possibly a slow, unbounded increase.
Investigating Asymptotic Behavior and Critical Points
To precisely characterize the asymptotic behavior, we'll need to examine the limits of the function as x approaches the domain's boundaries. L'Hôpital's rule or other advanced calculus techniques might be necessary for a rigorous analysis. Finding critical points involves calculating the derivative of the function (a complex derivative involving the chain rule and logarithmic differentiation) and solving for when the derivative is zero or undefined. This process would require a deep understanding of calculus.
This investigation would illuminate the function's overall shape, identify any extrema (maximum or minimum values), and provide further insight into its range and behavior.
Potential Applications and Extensions
While logₓ(logₓ(3x+1)) isn't a common function found in everyday applications, understanding its properties opens doors to potential applications in more advanced mathematical contexts:
-
Modeling Complex Systems: The function's intricate behavior makes it a potential candidate for modeling systems with nested dependencies, where the rate of change is influenced by the logarithm of another rate of change.
-
Numerical Analysis: The process of analyzing the function's domain, range, and behavior helps refine numerical methods for solving equations involving nested logarithms.
-
Advanced Calculus Problems: The function serves as an excellent case study for exploring complex derivative calculations and asymptotic analysis.
Further Research and Exploration
Further exploration might involve investigating the function's behavior under different bases or exploring variations of the expression, such as introducing parameters or changing the polynomial argument (3x+1). A comparison with related functions might also provide additional insights into the expression's unique properties. Furthermore, the use of symbolic computation software such as Mathematica or Maple could aid in performing complex calculations and visualizations.
Conclusion
Analyzing logₓ(logₓ(3x+1)) provides a compelling illustration of the challenges and rewards inherent in advanced mathematical analysis. The interplay of logarithmic properties and polynomial expressions, alongside the intricacies of nested functions, necessitates a multi-faceted approach combining algebraic manipulation, numerical analysis, and graphical techniques. The process illuminates the importance of rigorous methodology in understanding complex mathematical structures and their potential applications in diverse fields. The exploration continues to unravel the enigmatic nature of this function, showcasing the beauty and complexity within seemingly simple mathematical expressions. This deep dive demonstrates the power of combining theoretical understanding with practical computational methods to gain a comprehensive grasp of complex mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not An Organic Substance
Mar 19, 2025
-
At A Price Below Equilibrium Price There Is
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Cannot Travel In A Vacuum
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Molecular Mass Of Helium
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Add Numbers In Python
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Log X Log X 3 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
