Lines Of Symmetry For A Star
News Leon
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
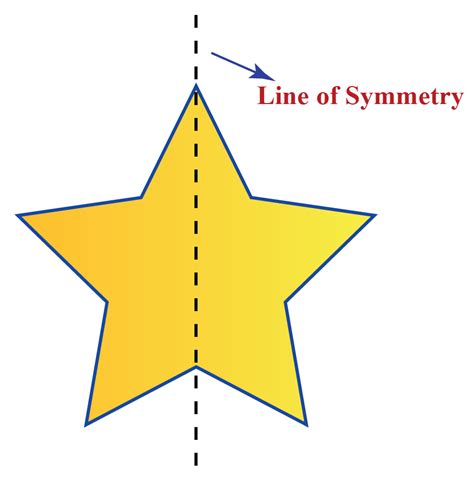
Table of Contents
Lines of Symmetry for a Star: A Comprehensive Exploration
Stars, those celestial wonders that captivate our imaginations, possess a fascinating geometric property: lines of symmetry. Understanding the lines of symmetry in a star, however, depends heavily on the specific type of star we're examining. A simple five-pointed star differs significantly from a more complex, multi-pointed star in terms of its symmetry. This article delves into the mathematical intricacies of determining lines of symmetry in various star shapes, exploring the concepts of rotational symmetry and reflectional symmetry, and providing practical methods for identifying them.
Understanding Symmetry: A Foundation
Before we embark on our star-studded journey into symmetry, let's establish a common understanding of the fundamental types:
1. Reflectional Symmetry (Line Symmetry)
Reflectional symmetry, also known as line symmetry or bilateral symmetry, occurs when a shape can be folded along a line, creating two mirror-image halves. This line is the line of symmetry, and the shape is said to be symmetric about that line. Imagine folding a perfectly symmetrical butterfly in half along its body – the two halves are identical reflections of each other.
2. Rotational Symmetry
Rotational symmetry involves rotating a shape around a central point. If the shape looks exactly the same after a rotation of less than 360 degrees, it possesses rotational symmetry. The number of times the shape looks identical during a 360-degree rotation determines its order of rotational symmetry. For instance, a square has rotational symmetry of order 4 because it looks identical four times during a full rotation.
Lines of Symmetry in Regular Stars
Regular stars, those with equally spaced points and equal-length sides, exhibit a predictable pattern of symmetry. The number of points directly influences the number of lines of symmetry.
The Five-Pointed Star (Pentagram)
The classic five-pointed star, or pentagram, is a rich source of mathematical exploration. It possesses five lines of symmetry. These lines are not just lines connecting points, but lines extending through the vertices to intersect the opposite midpoints. Each line acts as a reflectional axis, dividing the star into two congruent halves.
Visualizing the Pentagram's Symmetry: Imagine drawing lines from each point of the star to the midpoint of the opposite side. You'll find five distinct lines, all intersecting at the center of the star. Each line is a line of symmetry.
Rotational Symmetry of the Pentagram: In addition to reflectional symmetry, the pentagram also boasts rotational symmetry of order 5. Rotating the pentagram by 72 degrees (360/5) will produce an identical image.
The Six-Pointed Star (Hexagram)
A six-pointed star, often associated with the Star of David, presents a different pattern of symmetry. This shape actually comprises two overlapping equilateral triangles. It possesses six lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 6 (rotations of 60 degrees).
Analyzing the Hexagram's Symmetry: Three lines of symmetry connect opposite vertices of the hexagram, while three others bisect opposite sides. Each of these lines produces a perfect mirror image when the shape is folded along them.
Generalizing for n-Pointed Stars (Regular Polygrams)
For a regular n-pointed star, where n is an odd number, the number of lines of symmetry is always n. This holds true for a seven-pointed star (7 lines of symmetry), a nine-pointed star (9 lines of symmetry), and so on.
However, the situation becomes more complex with even-pointed stars. A regular 8-pointed star will have 8 lines of symmetry, but the arrangement is different from those in odd-pointed stars. This pattern continues for all even n values.
Irregular Stars and Lines of Symmetry
Not all stars are regular. Irregular stars, with varying lengths of sides and angles between points, present a more challenging, and often less predictable, symmetry analysis.
An irregular star may possess:
- Zero lines of symmetry: This is the most common case for irregular stars. Their asymmetrical nature prevents the existence of any lines that would divide them into mirror images.
- One or more lines of symmetry: Certain irregular stars might possess a single line of symmetry or, in rarer cases, several. These lines must divide the star into perfectly mirrored halves. The identification of these lines often requires careful observation and possibly the use of geometric tools.
Determining the lines of symmetry in an irregular star requires a careful visual inspection or a more formal geometric analysis, possibly using coordinate geometry or vector methods to establish the reflectional properties across a potential line of symmetry.
Practical Methods for Identifying Lines of Symmetry
Several methods can be employed to identify lines of symmetry in stars:
1. Visual Inspection
The simplest method involves visually inspecting the star and mentally folding it along potential lines of symmetry. If the two halves perfectly overlap, the line is a line of symmetry. This method is effective for simple stars but can become challenging for more complex shapes.
2. Using Tracing Paper
Tracing the star onto tracing paper allows for easy manipulation and experimentation. By folding the tracing paper along various lines, you can readily determine whether a line forms a line of symmetry.
3. Geometric Software
Computer software dedicated to geometric analysis can accurately and efficiently determine the lines of symmetry of any star, regardless of its complexity. These programs often incorporate advanced algorithms for symmetry detection.
Lines of Symmetry and Star Classification
While not directly used in astronomical star classification (which relies on factors like spectral type, luminosity, and size), understanding a star's geometric lines of symmetry can be a helpful tool in representing them mathematically and graphically, simplifying their study and facilitating the development of accurate models. The concept also has implications in art, design, and various other fields.
Conclusion
The lines of symmetry in a star represent a fascinating interplay of mathematics and visual perception. Whether a regular or irregular star, understanding the principles of reflectional and rotational symmetry provides a framework for analyzing and appreciating their geometric beauty. The methods outlined above empower you to delve into the world of star symmetry, unveiling the hidden mathematical harmony within these celestial icons. From the elegant simplicity of a five-pointed star to the complexity of irregular forms, the exploration of lines of symmetry offers a rich and rewarding experience. Remember, the journey of discovery is as important as the destination – enjoy exploring the symmetrical wonders of the cosmos!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Difference Between Earthing And Grounding And Neutral
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Calcium Carbonate Caco3
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does The Square Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Nahco3
Mar 18, 2025
-
This Lung Volume Cannot Be Directly Measured Using A Spirometer
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lines Of Symmetry For A Star . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
