How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does The Square Have
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
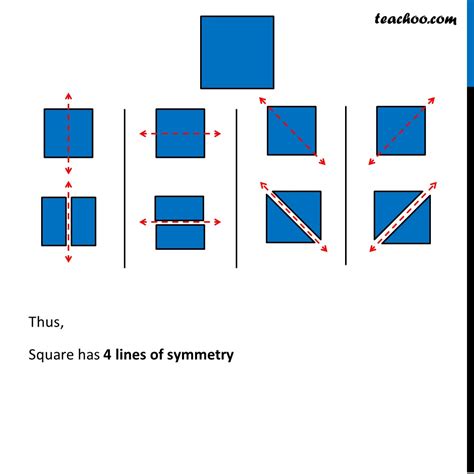
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Square Have? A Comprehensive Exploration
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and art, refers to the harmonious and balanced distribution of elements within a shape or object. Understanding lines of symmetry is crucial in various fields, from geometry to design. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the number of lines of symmetry a square possesses. We will explore different types of symmetry, demonstrate how to identify lines of symmetry, and even touch upon applications in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before we delve into the specifics of a square, let's establish a clear understanding of what a line of symmetry is. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, both halves would perfectly overlap. This concept applies to various shapes, including squares, circles, triangles, and many more complex figures.
Types of Symmetry
Beyond lines of symmetry, there are other types of symmetry to consider:
-
Line Symmetry (Reflectional Symmetry): This is the type of symmetry we are focusing on in this article. It involves reflecting a shape across a line to obtain a mirror image.
-
Rotational Symmetry: This involves rotating a shape around a central point. If the shape looks identical after a rotation of less than 360 degrees, it has rotational symmetry. The order of rotational symmetry is the number of times the shape looks identical during a 360-degree rotation.
-
Translational Symmetry: This type of symmetry is found in patterns that repeat themselves regularly in a specific direction. Think of wallpaper patterns or tiled floors.
-
Point Symmetry: A shape has point symmetry if it looks identical after a 180-degree rotation around a central point. This is a special case of rotational symmetry.
The Square: A Symmetrical Marvel
The square, a simple yet elegant geometric shape, is a treasure trove of symmetry. Its four equal sides and four right angles create a perfect balance that results in multiple lines of symmetry. Let's explore how to identify these lines.
Identifying Lines of Symmetry in a Square
Consider a square ABCD, with vertices A, B, C, and D in clockwise order. We can identify four distinct types of lines of symmetry:
-
Vertical Line of Symmetry: Draw a line connecting the midpoints of sides AB and CD. This line divides the square into two identical rectangles, each a mirror image of the other. This is a vertical line of symmetry.
-
Horizontal Line of Symmetry: Similarly, draw a line connecting the midpoints of sides AD and BC. This line also divides the square into two identical rectangles, creating another line of symmetry, this time horizontal.
-
Diagonal Lines of Symmetry: Now, consider the diagonals of the square. Draw a line from vertex A to vertex C, and another line from vertex B to vertex D. Each of these diagonal lines divides the square into two identical triangles, which are mirror images of one another. This gives us two more lines of symmetry.
The Total Number of Lines of Symmetry in a Square
By carefully analyzing the above, it becomes evident that a square possesses a total of four lines of symmetry. Two are parallel to its sides (vertical and horizontal), and two are the diagonals. This symmetrical nature makes the square a fundamental building block in various applications, from architecture and engineering to design and art.
Demonstrating Lines of Symmetry Practically
Understanding lines of symmetry isn't just about theory; it's about practical application. Here are some ways to demonstrate the four lines of symmetry in a square:
-
Paper Folding: Draw a square on a piece of paper. Fold the paper along each of the four lines of symmetry described above. You'll observe that the two halves perfectly overlap in each case, confirming the presence of a line of symmetry.
-
Digital Manipulation: Use image editing software to digitally manipulate a square image. Reflect the image across each of the four axes described above. You'll find that the reflected image is identical to the original in each case.
Beyond the Square: Exploring Symmetry in Other Shapes
While the square boasts four lines of symmetry, other shapes exhibit different levels of symmetry:
-
Rectangle: A rectangle has two lines of symmetry, one vertical and one horizontal. Unlike the square, it doesn't have diagonal lines of symmetry unless it's a special case of a square.
-
Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Circle: A circle possesses infinite lines of symmetry because any line passing through its center divides it into two identical halves.
-
Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon (five equal sides and five equal angles) has five lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Regular Hexagon: A regular hexagon has six lines of symmetry: three lines connecting opposite vertices, and three lines connecting midpoints of opposite sides.
Applications of Symmetry in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of symmetry has wide-ranging applications across various fields:
-
Architecture and Design: Symmetrical designs are aesthetically pleasing and create a sense of balance and harmony. Many buildings and structures incorporate elements of symmetry in their designs.
-
Engineering: Symmetry plays a crucial role in engineering design, ensuring structural integrity and stability. Symmetrical designs often lead to efficient load distribution and reduced stress.
-
Art and Nature: Symmetry is evident in many works of art, from paintings and sculptures to decorative patterns. It also appears extensively in nature, in snowflakes, flowers, and the human body.
-
Computer Graphics and Animation: Symmetry is used to create realistic and efficient animations and computer-generated imagery (CGI).
-
Physics and Chemistry: Symmetry principles are fundamental to understanding physical laws and molecular structures.
Conclusion: Embracing the Symmetry of the Square
In conclusion, a square possesses four lines of symmetry: two parallel to its sides and two along its diagonals. This rich symmetrical nature makes it a significant shape in mathematics, art, design, and various scientific fields. Understanding lines of symmetry not only enhances our appreciation for geometry but also allows us to analyze and interpret the world around us with a deeper understanding of balance and harmony. This understanding extends beyond the square, encompassing numerous shapes and objects, highlighting the pervasiveness and importance of symmetry in our lives. The seemingly simple square, therefore, serves as a powerful gateway to the broader and fascinating world of symmetrical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Languages Did Helen Keller Know
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Ribs Do Rabbits Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
30 Is What Percent Of 48
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Only Language That A Computer Can Understand
Mar 18, 2025
-
Word That Has Two Different Meanings
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does The Square Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
