This Lung Volume Cannot Be Directly Measured Using A Spirometer
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
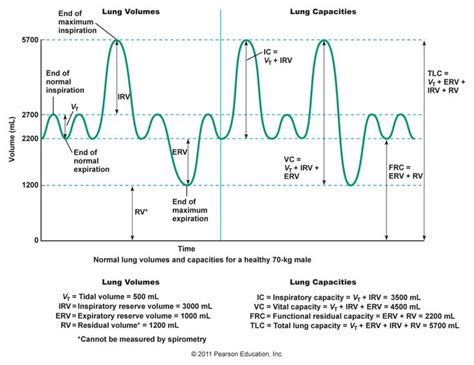
Table of Contents
This Lung Volume Cannot Be Directly Measured Using a Spirometer: Understanding Residual Volume and Functional Residual Capacity
Spirometry, a common and relatively simple pulmonary function test, provides invaluable insights into lung health. It measures various lung volumes and capacities, offering clinicians a window into respiratory function. However, spirometry has its limitations. One crucial aspect of lung function that cannot be directly measured using a spirometer is residual volume (RV). Understanding why this is the case, and the implications of this limitation, is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of respiratory physiology and diagnostics.
What is Residual Volume (RV)?
Residual volume represents the amount of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation. Think of it as the air that's "stuck" in your lungs even after you've completely blown out. This air is crucial for preventing lung collapse (atelectasis) and ensuring continuous gas exchange between breaths. RV is a significant component of the total lung capacity (TLC), which encompasses all the air the lungs can hold.
Why Spirometry Can't Measure RV
Spirometry relies on measuring the volume of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a maximal inhalation. The device measures the air that moves in and out of the lungs, it cannot measure the air that remains within the lungs. By its very nature, a spirometer cannot assess the air trapped within the alveoli and airways after a forced expiration. The air in RV is passively held in the lungs and requires specialized techniques for measurement.
Measuring Residual Volume: Beyond Spirometry
Since spirometry falls short, other methods are employed to determine RV. The most common technique is body plethysmography, also known as a body box.
Body Plethysmography: The Gold Standard
Body plethysmography is considered the gold standard for measuring RV. This technique encloses the subject in an airtight chamber (the "body box"). The individual then performs a series of forced expirations and inhalations against a closed mouthpiece. The changes in pressure within the chamber, coupled with measurements of airflow, allow for the precise calculation of RV. The principle behind this is Boyle's Law, which states that at a constant temperature, the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional. By measuring the changes in pressure and volume within the sealed chamber, the volume of gas trapped in the lungs (RV) can be calculated.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Body Plethysmography
Advantages:
- Accuracy: It provides the most accurate measurement of RV.
- Independent of cooperation: While cooperation is beneficial, it's less dependent on patient effort compared to other techniques.
- Measures other parameters: Besides RV, it can also measure other lung volumes and capacities, including functional residual capacity (FRC).
Disadvantages:
- Claustrophobia: The confined space can be claustrophobic for some individuals.
- Expensive and Specialized: The equipment is expensive and requires specialized training to operate and interpret the results.
- More complex procedure: The procedure is more complex and time consuming compared to spirometry.
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC): Indirectly Measured, Directly Related to RV
Another crucial lung volume, functional residual capacity (FRC), is closely related to RV. FRC represents the amount of air remaining in the lungs after a normal, passive exhalation. While not directly measurable by spirometry alone, FRC can be estimated using spirometry in conjunction with other techniques, often including body plethysmography.
The Relationship Between RV and FRC
FRC is the sum of expiratory reserve volume (ERV) and RV. Spirometry can accurately measure ERV. Therefore, if RV is determined through body plethysmography, FRC can be easily calculated. Conversely, if FRC is determined using other methods (such as nitrogen washout or helium dilution), RV can be calculated by subtracting the measured ERV from the FRC value.
Other Methods for Estimating RV and FRC
While body plethysmography remains the gold standard, several alternative techniques exist for estimating RV and FRC, each with its strengths and limitations:
Helium Dilution
This technique involves the subject breathing a known concentration of helium mixed with air. The helium is rapidly diluted as the subject breathes. By measuring the concentration of helium in the lungs and the original concentration, the total lung capacity can be determined. Since TLC is the sum of RV, FRC, Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Tidal Volume (TV), and Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), and spirometry provides measurements for ERV, IRV, and TV, one can indirectly calculate RV and therefore FRC.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Helium Dilution
Advantages:
- Less claustrophobic: It's less claustrophobic than body plethysmography.
- Relatively simple: The procedure is simpler to perform.
Disadvantages:
- Less accurate: It’s generally less accurate than body plethysmography.
- Assumes homogenous mixing: It assumes homogenous mixing of helium within the lungs, which may not always be true.
Nitrogen Washout
This method relies on the principle of washout of nitrogen from the lungs by breathing 100% oxygen. The rate at which nitrogen is eliminated provides an estimate of the functional residual capacity (FRC) and subsequently RV.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nitrogen Washout
Advantages:
- Relatively simple: The procedure is relatively simple to perform.
Disadvantages:
- Less accurate: The accuracy is less compared to body plethysmography.
- Long procedure: It is a more time-consuming method.
- Patient cooperation essential: Requires patient cooperation and consistent breathing.
Clinical Significance of RV and FRC
Accurate measurement of RV and FRC is critical in various clinical settings:
-
Assessing Lung Disease: Changes in RV and FRC are often indicative of various lung diseases, including COPD, emphysema, and restrictive lung diseases. Increased RV is a hallmark of obstructive lung diseases, where air trapping occurs. Reduced RV suggests restrictive lung disease where lung expansion is limited.
-
Monitoring Disease Progression: Tracking changes in RV and FRC over time can help monitor the progression of lung disease and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
-
Anesthesia and Respiratory Management: Accurate knowledge of RV and FRC is crucial in anesthesia to optimize ventilator settings and avoid over- or under-ventilation during surgery. This information is especially relevant for patients with pre-existing lung conditions.
Conclusion
While spirometry offers a valuable initial assessment of lung function, it cannot directly measure residual volume (RV) or, alone, functional residual capacity (FRC). These crucial lung volumes require more advanced techniques like body plethysmography, helium dilution, or nitrogen washout. Understanding the limitations of spirometry and the importance of these other techniques is vital for accurate diagnosis and management of respiratory conditions. The choice of method depends on factors such as cost, equipment availability, patient tolerance, and the specific clinical context. Accurate measurement of RV and FRC provides crucial insights into the overall health of the lungs and plays a significant role in effective respiratory care. These measurements provide a more complete picture of lung function than spirometry alone, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of respiratory illnesses.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Monomer Of Starch
Mar 18, 2025
-
Balanced Equation For H2so4 And Naoh
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Does 1 1 Ratio Mean
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is 64 As A Fraction
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Way Of The World Analysis
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about This Lung Volume Cannot Be Directly Measured Using A Spirometer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
