What Is The Molar Mass Of Calcium Carbonate Caco3
News Leon
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
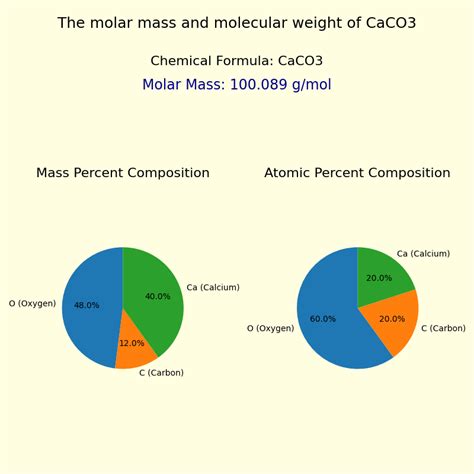
Table of Contents
What is the Molar Mass of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)? A Deep Dive
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a ubiquitous compound found in various forms in nature, from the shells of marine organisms to limestone formations. Understanding its molar mass is fundamental to various scientific disciplines, including chemistry, geology, and environmental science. This comprehensive guide delves into the calculation, applications, and significance of the molar mass of CaCO3.
Understanding Molar Mass
Before we calculate the molar mass of calcium carbonate, let's define what molar mass is. Simply put, molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry, representing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup>) of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.). The molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Calculating the Molar Mass of CaCO3
To determine the molar mass of CaCO3, we need to consider the atomic masses of its constituent elements: calcium (Ca), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). These atomic masses are typically found on the periodic table.
- Calcium (Ca): Approximately 40.08 g/mol
- Carbon (C): Approximately 12.01 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): Approximately 16.00 g/mol
Since CaCO3 contains one calcium atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms, the molar mass is calculated as follows:
(1 x Atomic mass of Ca) + (1 x Atomic mass of C) + (3 x Atomic mass of O)
= (1 x 40.08 g/mol) + (1 x 12.01 g/mol) + (3 x 16.00 g/mol)
= 40.08 g/mol + 12.01 g/mol + 48.00 g/mol
= 100.09 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is approximately 100.09 grams per mole.
Significance of the Molar Mass of CaCO3
The molar mass of CaCO3 is crucial for various calculations and applications in different fields. Here are some key examples:
1. Stoichiometry
In stoichiometric calculations, the molar mass is essential for converting between mass and moles. For instance, if you have a certain mass of CaCO3, you can use its molar mass to determine the number of moles present. This is fundamental for balancing chemical equations and predicting the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
2. Titration Analysis
Molar mass is critical in titrations, where the concentration of a solution is determined by reacting it with a solution of known concentration. The molar mass of CaCO3 is used to calculate the concentration of calcium ions or carbonate ions in a sample. Acid-base titrations are frequently used to analyze CaCO3 content in soil samples, water analysis, and industrial processes.
3. Geochemistry and Geology
In geology, the molar mass of CaCO3 plays a significant role in understanding the formation and composition of rocks like limestone and marble. Knowing the molar mass helps geologists calculate the amounts of CaCO3 present in rock samples and study the geological processes that led to their formation. This understanding is crucial for resource management, geological mapping, and understanding Earth's history.
4. Environmental Science
The molar mass of CaCO3 is vital in environmental studies involving water hardness, soil chemistry, and carbon cycle analysis. CaCO3's presence in water contributes to water hardness. Knowing its molar mass helps scientists determine the level of hardness in water samples and its potential environmental impact. Further, understanding the cycling of carbon within ecosystems requires accurate calculations involving the molar mass of CaCO3. It helps in modeling carbon fluxes and assessing the impact of environmental changes on the carbon cycle.
5. Material Science and Industrial Applications
In material science and industrial applications, the molar mass of CaCO3 is essential in determining the composition and properties of materials containing this compound. For example, in the production of cement, the amount of CaCO3 needed to achieve the desired properties is calculated using its molar mass. This precise calculation ensures that the cement meets quality standards and performs as expected. The molar mass of CaCO3 also plays a crucial role in controlling the properties of other materials like plastics, paper, and paints.
Applications of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)
The widespread use of calcium carbonate stems from its diverse properties and availability. Here are some key applications:
- Construction: Calcium carbonate, in the form of limestone and marble, is a primary component of cement, concrete, and building materials. Its strength and durability make it invaluable in construction.
- Agriculture: It's used as a soil amendment to neutralize acidic soils, improving soil fertility and crop yield.
- Paper Production: It acts as a filler and coating agent in paper manufacturing, improving brightness, opacity, and printability.
- Pharmaceuticals: It's used as a filler and excipient in tablets and capsules, improving their flowability and compressibility.
- Food Industry: It serves as a food additive, acting as an anticaking agent, a dietary supplement (calcium source), and a raising agent.
- Cosmetics: Calcium carbonate is used in various cosmetic products as a pigment, opacifier, and thickener.
- Pollution Control: It can be used in flue-gas desulfurization to remove sulfur dioxide from industrial emissions.
These diverse applications highlight the importance of accurate calculations involving the molar mass of CaCO3 in various industries.
Beyond the Basic Calculation: Isotopes and Variations
While the calculation above provides a general molar mass, it's important to note that the atomic masses of elements are averages reflecting the natural abundance of isotopes. Different isotopes of calcium, carbon, and oxygen have slightly different masses. Therefore, the actual molar mass of a specific sample of CaCO3 can vary slightly based on the isotopic composition. However, for most practical purposes, the average molar mass of 100.09 g/mol is sufficiently accurate.
Conclusion
The molar mass of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), approximately 100.09 g/mol, is a fundamental value with wide-ranging applications across various scientific and industrial fields. From stoichiometric calculations and titration analysis to geological investigations and industrial processes, understanding and applying this value is crucial for accurate measurements, predictions, and process optimization. The versatility of CaCO3 and its importance in numerous applications underscore the significance of its molar mass in scientific and technological advancements. The ability to accurately calculate and utilize molar mass is a cornerstone of chemical understanding and plays a significant role in solving real-world problems across various disciplines. Accurate understanding of molar mass contributes directly to the advancement of scientific knowledge and technological innovation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Part Of The Scapula Articulates With The Clavicle
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Languages Did Helen Keller Know
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Ribs Do Rabbits Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
30 Is What Percent Of 48
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Only Language That A Computer Can Understand
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molar Mass Of Calcium Carbonate Caco3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
