Is Calcium Oxide Ionic Or Covalent
News Leon
Mar 31, 2025 · 4 min read
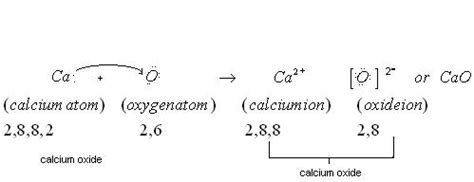
Table of Contents
Is Calcium Oxide Ionic or Covalent? A Deep Dive into Chemical Bonding
Determining the nature of chemical bonds is crucial in understanding the properties and behavior of compounds. This article will delve into the question: Is calcium oxide (CaO) ionic or covalent? We'll explore the concepts of ionic and covalent bonding, examine the electronegativity differences between calcium and oxygen, analyze the properties of calcium oxide, and ultimately conclude on the dominant type of bonding present.
Understanding Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Before classifying calcium oxide's bonding, let's refresh our understanding of ionic and covalent bonds:
Ionic Bonds: The Electrostatic Attraction
Ionic bonds arise from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. This happens when one atom readily donates electrons (becoming a positively charged cation) and another atom readily accepts those electrons (becoming a negatively charged anion). This electron transfer results in a stable electron configuration for both atoms, often resembling that of a noble gas. Ionic compounds generally exhibit high melting and boiling points, are often crystalline solids at room temperature, and are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or molten.
Covalent Bonds: Shared Electrons
Covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve the sharing of electrons between two atoms. This sharing allows both atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration, often fulfilling the octet rule. Covalent compounds generally have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds and are often liquids or gases at room temperature. They are typically poor conductors of electricity.
Polar Covalent Bonds: A Spectrum of Sharing
It's important to note that covalent bonds aren't always perfectly equal. In polar covalent bonds, the shared electrons are not equally shared due to differences in electronegativity between the atoms. The more electronegative atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, resulting in a partial negative charge (δ-) on that atom and a partial positive charge (δ+) on the less electronegative atom. The degree of polarity influences the properties of the compound.
Electronegativity: The Key to Understanding Bond Type
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. The greater the electronegativity difference between two atoms, the more likely it is that an ionic bond will form. A small electronegativity difference suggests a covalent bond, while a significant difference points towards an ionic bond. However, it's not a simple cutoff; there's a spectrum between purely ionic and purely covalent.
Analyzing Calcium and Oxygen: A Tale of Two Elements
Let's examine the electronegativity values of calcium (Ca) and oxygen (O):
- Calcium (Ca): Electronegativity ≈ 1.0
- Oxygen (O): Electronegativity ≈ 3.5
The difference in electronegativity between calcium and oxygen is approximately 2.5 (3.5 - 1.0 = 2.5). This is a significant difference. Generally, an electronegativity difference of 1.7 or greater is considered indicative of an ionic bond. Therefore, based solely on electronegativity, we can anticipate a predominantly ionic bond between calcium and oxygen in calcium oxide.
Properties of Calcium Oxide: Evidence of Ionic Bonding
The properties of calcium oxide strongly support the conclusion of ionic bonding:
-
High Melting Point: Calcium oxide has a very high melting point (2580°C), typical of ionic compounds due to the strong electrostatic forces between the Ca²⁺ and O²⁻ ions. Overcoming these strong attractions requires a significant amount of energy.
-
Crystalline Structure: CaO exists as a crystalline solid at room temperature, a characteristic feature of ionic compounds. The ions arrange themselves in a highly ordered three-dimensional lattice structure to maximize electrostatic attractions and minimize repulsions.
-
Solubility and Conductivity: While not highly soluble in water, calcium oxide reacts with water (a process called slaking) to form calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂, which is a base. The resulting solution conducts electricity, indicating the presence of ions in solution. Molten CaO also conducts electricity, further confirming the ionic nature of the compound.
-
Hardness and Brittleness: Calcium oxide is relatively hard and brittle. These properties are consistent with ionic compounds where the strong electrostatic forces lead to a rigid structure, but the directionality of the forces makes the crystal susceptible to fracture along certain planes.
Addressing Potential Arguments for Covalency
While the evidence overwhelmingly supports ionic bonding, some might argue for a degree of covalent character. This argument is typically based on the concept of polarization. A highly charged cation can distort the electron cloud of the anion, leading to some degree of electron sharing. However, in the case of CaO, the significant electronegativity difference and the observed properties strongly outweigh any minor covalent contribution. The polarization effect is relatively small compared to the dominant ionic character.
Conclusion: Calcium Oxide is Predominantly Ionic
Based on the significant electronegativity difference between calcium and oxygen (2.5), and the observed properties of calcium oxide – high melting point, crystalline structure, and electrical conductivity in solution and molten state – it is definitively concluded that calcium oxide (CaO) is predominantly an ionic compound. While a small degree of covalent character might exist due to polarization effects, the ionic nature is overwhelmingly dominant. The strong electrostatic attractions between the Ca²⁺ and O²⁻ ions are the primary driving force behind the formation and properties of this important compound. Understanding this bonding nature is key to predicting and explaining its behavior in various applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Temperatures Is The Coldest
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Short Term Unsecured Promissory Note Issued By A Company Is
Apr 01, 2025
-
Adjacent Angles Whose Sum In 180 Degrees
Apr 01, 2025
-
Lewis Dot Structure For Magnesium Chloride
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Group Of Related Records Is Called A Table
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Calcium Oxide Ionic Or Covalent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
