How Many Neutrons Does Xenon Have
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
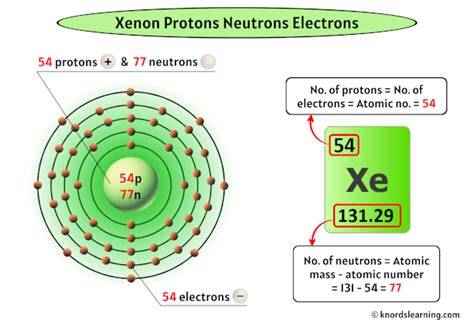
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Xenon Have? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Nuclear Physics
Xenon, a noble gas with the chemical symbol Xe and atomic number 54, doesn't have a single, definitive number of neutrons. This is because xenon exists in nature as a mixture of several isotopes. Each isotope of xenon has the same number of protons (54) but a different number of neutrons. Understanding this requires a delve into the world of nuclear physics and isotopic abundance.
Understanding Isotopes
Before we explore the neutron count in xenon isotopes, let's clarify the concept of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in their number of neutrons. This difference in neutron count affects the atomic mass of the isotope. While the chemical properties of isotopes of an element are largely similar, their physical properties, like mass and radioactivity, can vary significantly.
Key Terms:
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in an atom's nucleus. This defines the element. For xenon, the atomic number is 54.
- Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
- Neutron Number: The number of neutrons in an atom's nucleus. This, combined with the atomic number, determines the specific isotope.
- Isotope Notation: Often represented as ¹²⁶Xe, where 126 is the mass number and Xe is the element symbol.
Xenon Isotopes and Their Neutron Counts
Xenon has a total of 36 known isotopes, ranging from ¹¹⁴Xe to ¹⁴²Xe. Of these, nine are stable, meaning they don't undergo radioactive decay. The remaining isotopes are radioactive, with varying half-lives.
Here's a breakdown of some key xenon isotopes and their respective neutron numbers:
| Isotope | Mass Number | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Abundance (%) | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ¹²⁴Xe | 124 | 54 | 70 | 0.096% | Stable |
| ¹²⁶Xe | 126 | 54 | 72 | 0.090% | Stable |
| ¹²⁸Xe | 128 | 54 | 74 | 1.92% | Stable |
| ¹²⁹Xe | 129 | 54 | 75 | 26.4% | Stable |
| ¹³⁰Xe | 130 | 54 | 76 | 4.1% | Stable |
| ¹³¹Xe | 131 | 54 | 77 | 21.2% | Stable |
| ¹³²Xe | 132 | 54 | 78 | 26.9% | Stable |
| ¹³⁴Xe | 134 | 54 | 80 | 10.4% | Stable |
| ¹³⁶Xe | 136 | 54 | 82 | 8.9% | Stable |
Note: The abundance percentages represent the relative proportion of each isotope found in naturally occurring xenon.
The radioactive isotopes of xenon have significantly shorter lifespans and are not naturally abundant. They are often produced in nuclear reactions or as byproducts of radioactive decay of other elements.
The Significance of Isotopic Abundance
The isotopic abundance of xenon is crucial in various scientific fields:
- Geochronology: Analyzing the relative abundances of xenon isotopes can help determine the age of rocks and minerals, offering insights into geological processes.
- Cosmochemistry: Xenon isotopes play a vital role in understanding the formation and evolution of the solar system. Certain xenon isotopes are indicative of specific nucleosynthetic processes.
- Nuclear Physics: Studying the properties of xenon isotopes provides valuable data for understanding nuclear structure and reactions.
- Atmospheric Science: Xenon isotopes can be used as tracers to study atmospheric processes and circulation patterns.
Factors Affecting Neutron Number
The number of neutrons in an atom's nucleus isn't arbitrary. It's influenced by several factors:
- Nuclear Forces: The strong nuclear force binds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus. The balance between the repulsive electromagnetic force between protons and the strong nuclear force dictates the stability of an atom.
- Neutron-Proton Ratio: Stable isotopes generally have a neutron-to-proton ratio that's close to 1:1 for lighter elements, but this ratio increases for heavier elements like xenon. This is because the increasing number of protons requires more neutrons to overcome the electrostatic repulsion.
- Shell Model of the Nucleus: Similar to electron shells in atoms, the nucleus has energy levels or shells. Isotopes with filled nuclear shells tend to be more stable.
Xenon and Nuclear Reactors
Xenon plays a significant role in nuclear reactor physics. The fission of uranium-235 produces several xenon isotopes, some of which are strong neutron absorbers. This neutron absorption can affect the reactor's power output and control. Specifically, xenon poisoning is a phenomenon where the buildup of these neutron-absorbing isotopes temporarily reduces reactor reactivity. Understanding the isotopic composition of xenon within the reactor is critical for safe and efficient operation.
Applications of Xenon Isotopes
The unique properties of xenon isotopes lead to diverse applications:
- Medical Imaging: Radioactive xenon isotopes are used in medical imaging techniques like ventilation/perfusion scans, providing crucial information about lung function.
- Medical Treatments: Radioactive isotopes are also utilized in certain medical treatments.
- Laser Technology: Certain xenon isotopes are employed in lasers, taking advantage of their spectral properties.
- Analytical Chemistry: Xenon isotopes find use in analytical techniques like mass spectrometry, aiding in the identification and quantification of different substances.
Further Research and Exploration
The study of xenon isotopes continues to be an active area of research. Advances in techniques like mass spectrometry enable ever more precise measurements of isotopic abundances. This improved accuracy contributes to a deeper understanding of fundamental scientific processes and technological applications. The ongoing exploration of xenon isotopes promises to unveil further insights into the cosmos, our planet, and the subatomic world.
Conclusion
To definitively answer "How many neutrons does xenon have?", there isn't one single answer. Xenon exists as a mixture of numerous isotopes, each with a different number of neutrons. The most abundant isotopes range from 70 to 82 neutrons. Understanding the isotopic composition of xenon is vital in various scientific and technological fields, highlighting its importance across disciplines. The variations in neutron number and the resulting isotopic properties underscore the complexity and richness of nuclear physics and its impact on our world. Further research into xenon isotopes will undoubtedly lead to even more exciting discoveries and applications in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Chemical Formula For Sodium And Oxygen
Mar 28, 2025
-
Dark A Bands Are Made From
Mar 28, 2025
-
The Respiratory Center Of The Brain Is Located In The
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Percent Of 12 5 Is 39
Mar 28, 2025
-
In The Figure A Plastic Rod Having A Uniformly
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Xenon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
