How Many Neutrons Does Magnesium Have
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
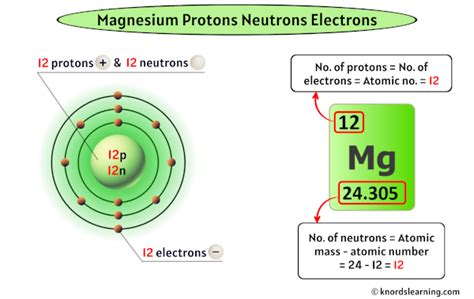
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Magnesium Have? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Nuclear Structure
Magnesium, a vital element for life and a common sight in everyday materials, presents an interesting case study in nuclear physics. Unlike elements with a single, dominant isotope, magnesium boasts three naturally occurring isotopes, each with a varying number of neutrons. This article will explore the intricacies of magnesium's isotopic composition, delving into the concept of atomic number, mass number, and the implications of differing neutron counts on the element's properties.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we dive into the neutron count of magnesium, let's establish a fundamental understanding of atomic structure. Every atom consists of three primary subatomic particles:
-
Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number and its identity on the periodic table. Magnesium's atomic number is 12, meaning every magnesium atom possesses 12 protons.
-
Neutrons: Electrically neutral particles residing alongside protons in the nucleus. Neutrons contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge. The number of neutrons can vary within the same element, leading to the concept of isotopes.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom, maintaining a balanced charge.
Isotopes: Variations on a Theme
Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons. This difference in neutron count results in variations in the atom's mass number (the total number of protons and neutrons). While the chemical properties of isotopes are largely similar due to the identical number of electrons and protons, their physical properties, like mass and radioactive decay behavior, can differ significantly.
Magnesium possesses three naturally occurring stable isotopes:
-
Magnesium-24 (²⁴Mg): This is the most abundant isotope of magnesium, accounting for approximately 79% of naturally occurring magnesium. Its mass number of 24 indicates it has 12 protons (atomic number) and 12 neutrons (24 - 12 = 12). Therefore, Magnesium-24 has 12 neutrons.
-
Magnesium-25 (²⁵Mg): This isotope constitutes about 10% of naturally occurring magnesium. With a mass number of 25, it has 12 protons and 13 neutrons (25 - 12 = 13). Magnesium-25 therefore has 13 neutrons.
-
Magnesium-26 (²⁶Mg): The least abundant of the three stable isotopes, Magnesium-26 makes up approximately 11% of naturally occurring magnesium. Its mass number of 26 reveals 12 protons and 14 neutrons (26 - 12 = 14). Consequently, Magnesium-26 has 14 neutrons.
The Significance of Neutron Number
The number of neutrons in an atom's nucleus significantly influences its stability and properties. While a specific neutron-to-proton ratio contributes to nuclear stability, deviations from this optimal ratio can lead to instability and radioactive decay.
In the case of magnesium, all three naturally occurring isotopes are stable. This stability is largely attributed to the relatively balanced number of protons and neutrons in their nuclei. However, even slight changes in neutron numbers can influence the isotopes' behavior:
-
Mass: The variation in neutron numbers directly affects the atom's mass. Magnesium-26, with its higher neutron count, is heavier than Magnesium-24.
-
Nuclear Spin: Neutrons, along with protons, contribute to the atom's overall nuclear spin. This property affects the magnetic behavior of the nucleus and can be exploited in techniques like nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
-
Radioactive Isotopes: Although magnesium's three naturally occurring isotopes are stable, several radioactive isotopes of magnesium exist. These isotopes have neutron counts deviating significantly from the stable range, resulting in radioactive decay. These radioactive isotopes find applications in various scientific and medical fields.
Magnesium in Nature and Applications
Magnesium's abundance in the Earth's crust and its diverse properties lead to widespread applications across various industries:
-
Biological Importance: Magnesium is an essential element for life, playing a crucial role in numerous biochemical processes. It's a vital component of chlorophyll in plants, and it acts as a cofactor in many enzyme reactions in both plants and animals.
-
Alloying Agent: Magnesium's light weight and relatively high strength make it a valuable alloying agent in the production of lightweight alloys for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries.
-
Chemical Applications: Magnesium compounds are used extensively in various chemical processes, including the production of fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial chemicals.
-
Medical Applications: Magnesium sulfate (Epsom salts) finds application in medicine as a laxative and in treating various medical conditions. Radioactive magnesium isotopes are employed in medical imaging and therapy.
Conclusion: The Neutron Story of Magnesium
In summary, the answer to "How many neutrons does magnesium have?" isn't a single number but rather a range depending on the specific isotope. Magnesium-24 has 12 neutrons, Magnesium-25 has 13, and Magnesium-26 has 14. Understanding the isotopic composition of magnesium provides a crucial insight into the element's properties, its role in various applications, and the fundamental principles of nuclear physics. The variations in neutron numbers within the stable isotopes of magnesium highlight the subtle yet significant impact of nuclear structure on the overall characteristics of an element. This understanding is essential for advancements in materials science, medicine, and other related fields. Further research into the intricacies of magnesium's isotopes continues to uncover new facets of its behavior and potential applications. From its vital role in biological systems to its use in modern technology, magnesium serves as a compelling example of the intricate connections between atomic structure, elemental properties, and practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Tertiary Alcohol
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Neutrons Are In Mg
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Type Of Cartilage Is Found In The Intervertebral Discs
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Word Is Closest In Meaning To The Underlined Word
Mar 15, 2025
-
Increment And Decrement Operators In C
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Magnesium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
