How Far Is Moon From Earth In Light Years
News Leon
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
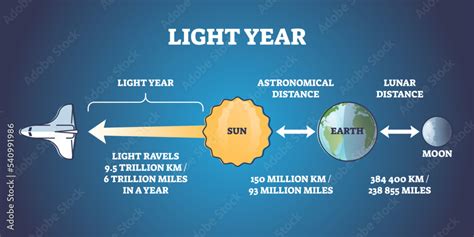
Table of Contents
How Far is the Moon from Earth in Light Years? A Deep Dive into Celestial Distances
The question, "How far is the Moon from Earth in light-years?" might seem straightforward, but it unveils a fascinating exploration of astronomical distances and the very nature of measurement in the cosmos. While the answer itself is deceptively small, understanding the context requires a grasp of different units of distance and the sheer scale of the universe.
Understanding Light Years and Astronomical Units
Before diving into the Moon's distance, let's clarify the units involved. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year, roughly 9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> kilometers (5.879 × 10<sup>12</sup> miles). This is a colossal distance, used for measuring vast interstellar and intergalactic spans.
Conversely, the distance between the Earth and the Moon is typically measured in kilometers or miles, or sometimes in astronomical units (AU). One AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, approximately 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). Using light-years to express the Earth-Moon distance would be like using a sledgehammer to crack a nut.
Calculating the Moon's Distance in Light-Years
The average distance from the Earth to the Moon is about 384,400 kilometers (238,855 miles). To convert this to light-years, we perform a simple calculation:
-
Convert kilometers to light-years: We divide the distance in kilometers by the number of kilometers in a light-year.
-
Calculation: 384,400 km / (9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> km/light-year) ≈ 4.06 × 10<sup>-8</sup> light-years.
Therefore, the Moon is approximately 0.0000000406 light-years away from Earth.
Why Light-Years Aren't Practical for Measuring Lunar Distance
The incredibly small number highlights why light-years are unsuitable for measuring the Earth-Moon distance. The unit is designed for measuring vast cosmic distances, making it impractical and unwieldy for distances within our own solar system. Using kilometers or miles provides a much more manageable and intuitive representation.
Exploring the Variations in Earth-Moon Distance
It's crucial to understand that the Earth-Moon distance isn't constant. The Moon's orbit is elliptical, meaning its distance from Earth varies throughout its orbit.
- Perigee: At its closest point (perigee), the Moon is approximately 363,104 kilometers (225,623 miles) from Earth.
- Apogee: At its farthest point (apogee), the Moon is approximately 405,696 kilometers (252,088 miles) from Earth.
These variations affect the apparent size of the Moon in the sky, with a slightly larger Moon visible during perigee and a slightly smaller Moon during apogee. These variations, while significant in the context of lunar distances, are still minuscule when considering light-years.
The Significance of Understanding Distance Scales
Understanding different distance scales is fundamental to grasping the vastness of space. The seemingly insignificant number representing the Moon's distance in light-years underscores the difference between our immediate celestial neighborhood and the truly enormous distances between stars and galaxies.
Comparing the Moon's Distance to Other Celestial Bodies
To further emphasize the scale, let's compare the Moon's distance to other celestial bodies:
- Sun: The Sun is approximately 1 AU (149.6 million kilometers) away from Earth. This is significantly further than the Moon.
- Mars: The distance to Mars varies greatly depending on the relative positions of Earth and Mars in their orbits. At its closest, Mars is still many millions of kilometers away.
- Nearest Star (Proxima Centauri): Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our Sun, is about 4.24 light-years away. This distance vastly dwarfs the Earth-Moon distance.
The Importance of Accurate Measurements in Astronomy
Precise measurements of celestial distances are crucial for various astronomical endeavors. They enable us to:
- Understand orbital mechanics: Accurate distance measurements are essential for modeling the orbits of celestial bodies and predicting their future positions.
- Study planetary systems: Measuring distances helps us characterize exoplanetary systems and understand the formation and evolution of planets.
- Map the universe: Precise distance measurements are vital for creating three-dimensional maps of the universe, revealing the distribution of galaxies and other large-scale structures.
Technological Advancements in Distance Measurement
Over time, astronomers have developed increasingly sophisticated methods for measuring celestial distances. Early methods relied on triangulation, while modern techniques employ radar, laser ranging (Lunar Laser Ranging – LLR), and sophisticated astronomical observations. LLR, for example, uses lasers bounced off reflectors placed on the Moon during the Apollo missions to measure the Earth-Moon distance with incredible accuracy.
The Future of Lunar Exploration and Distance Measurement
With renewed interest in lunar exploration, accurate measurements of the Earth-Moon distance will become even more critical. Future missions will rely on precise navigation and positioning systems that require an accurate understanding of the Moon's orbit and distance from Earth. Furthermore, advancements in technology will likely lead to even more precise methods for measuring celestial distances, providing astronomers with ever-refined data for their research.
Conclusion: A Grain of Sand in the Cosmic Ocean
The Moon's distance from Earth, when expressed in light-years, appears infinitesimally small: 0.0000000406 light-years. This perspective powerfully illustrates the vastness of the cosmos and the relative proximity of our Moon within our solar system. While light-years are indispensable for charting the universe’s grand scale, kilometers, miles, or even AU are more practical for understanding the dynamic relationship between Earth and its celestial neighbor. The continuous refinement of distance measurement techniques, spurred by ongoing lunar exploration, will undoubtedly deepen our understanding of this vital connection and the wider universe it inhabits.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Reaction Of Ethyl Alcohol With Acetic Acid
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Disappears The Moment You Say It
Mar 29, 2025
-
Microscopic Study Of Tissues Is Called
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Are Characteristics Of A Base
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Phase Is The Reverse Of Prophase
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Far Is Moon From Earth In Light Years . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
