Fungal Cell Walls Consist Primarily Of
News Leon
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
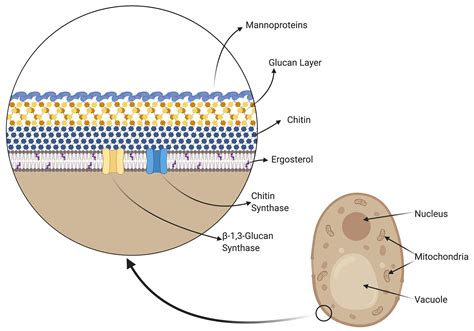
Table of Contents
Fungal Cell Walls: A Deep Dive into their Composition and Significance
Fungal cell walls are complex and dynamic structures that play a crucial role in the survival and pathogenesis of fungi. Unlike plant cell walls, which are primarily composed of cellulose, fungal cell walls are predominantly built from chitin, a strong and flexible polysaccharide. However, this is just the beginning of the story. The composition of fungal cell walls is remarkably diverse, varying significantly across different fungal species and even within different stages of a single fungus's life cycle. This intricate composition is responsible for the remarkable properties of fungal cell walls, including their structural integrity, protection against environmental stress, and ability to interact with the host during infection.
The Core Component: Chitin
The most abundant component of most fungal cell walls is chitin, a linear polymer of β-(1,4)-linked N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) units. This polysaccharide is structurally similar to cellulose, found in plant cell walls, but with a key difference: the presence of an N-acetyl group on each GlcNAc unit. This seemingly small modification significantly alters the properties of the polymer. Chitin's strength and flexibility contribute significantly to the overall structural rigidity of the fungal cell wall, providing mechanical support and protection against osmotic stress. The organization of chitin microfibrils into a complex network further enhances this structural role.
Chitin Synthesis and Regulation
The biosynthesis of chitin is a tightly regulated process involving several enzymes, including chitin synthases. These enzymes are responsible for polymerizing GlcNAc monomers into chitin chains. The precise regulation of chitin synthase activity is crucial for controlling cell wall growth and morphogenesis. Disruptions in chitin synthesis can lead to cell wall defects, making the fungus vulnerable to environmental stress and compromising its ability to survive.
Glucans: The Supporting Cast
Besides chitin, glucans form another major component of fungal cell walls. These are polymers of glucose units, connected in various ways, leading to a diverse range of glucan types. The most common types found in fungal cell walls are β-1,3-glucans and β-1,6-glucans. These glucans contribute significantly to the cell wall's structural integrity, forming a complex network that interweaves with chitin microfibrils.
β-1,3-Glucans: Strength and Defense
β-1,3-glucans form a major structural component of the fungal cell wall, providing strength and rigidity. Their long, linear chains can form extensive hydrogen bonds with each other and with other cell wall components, creating a robust and protective barrier. Furthermore, β-1,3-glucans play a role in fungal defense against environmental stresses and host immune responses. They can act as a physical barrier, protecting the fungus from the action of host immune cells and antimicrobial agents.
β-1,6-Glucans: Branching and Complexity
β-1,6-glucans often branch off from β-1,3-glucan chains, creating a more complex and cross-linked network. This branching pattern contributes to the overall elasticity and flexibility of the cell wall, allowing it to adapt to changes in osmotic pressure and mechanical stress. The branching also influences the interactions between different cell wall components, affecting the overall properties of the cell wall.
Mannoproteins: Beyond Structure
Fungal cell walls also contain significant amounts of mannoproteins. These are glycoproteins containing mannose as the predominant sugar. Mannoproteins contribute not only to the structural integrity of the cell wall but also play a crucial role in several other functions:
- Cell wall organization: Mannoproteins interact with other cell wall components, helping to organize and maintain the structure of the cell wall.
- Cell recognition: Mannoproteins on the outer surface of the cell wall can act as recognition molecules, mediating interactions with other fungi, bacteria, or host cells.
- Adhesion: Certain mannoproteins help the fungus adhere to surfaces, facilitating colonization and infection.
- Immunomodulation: Mannoproteins can interact with the host immune system, either stimulating or suppressing immune responses. Some mannoproteins act as virulence factors, enhancing the fungus' ability to evade the host's defenses.
Other Cell Wall Components: A Diverse Landscape
While chitin, glucans, and mannoproteins are the major components, several other molecules contribute to the diversity and complexity of fungal cell walls. These include:
- Galactomannans: These polysaccharides, found in some fungal species, can contribute to cell wall rigidity and play a role in interactions with the host.
- Melanin: A dark pigment that contributes to the cell wall's resistance to UV radiation and other environmental stresses. It can also protect the fungus from the action of host immune cells.
- Lipids: Lipids are found embedded within the cell wall matrix, contributing to its structural integrity and permeability.
- Proteins: Various proteins, including enzymes involved in cell wall synthesis and modification, are present within the cell wall.
Variations in Cell Wall Composition: A Species-Specific Tale
The composition of fungal cell walls varies significantly across different fungal species. This diversity reflects the wide range of habitats and lifestyles occupied by fungi. For example, yeasts, which are unicellular fungi, have cell walls with a different composition and organization compared to filamentous fungi, which form multicellular structures. Pathogenic fungi often have cell walls modified to facilitate evasion of the host's immune system, while saprophytic fungi, which live on dead organic matter, have cell walls adapted to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
The Significance of Fungal Cell Walls
Understanding the composition and function of fungal cell walls is crucial for several reasons:
- Antifungal drug development: Fungal cell wall components, such as β-1,3-glucans and chitin, are important targets for antifungal drugs. Many antifungal agents work by disrupting the synthesis or assembly of these components, compromising the integrity of the fungal cell wall and leading to cell death.
- Diagnosis and identification: Differences in cell wall composition can be used to identify and classify different fungal species, which is important for medical and agricultural purposes.
- Understanding fungal pathogenesis: The cell wall plays a vital role in the interaction between pathogenic fungi and their hosts. Understanding cell wall composition and function is critical for developing strategies to combat fungal infections.
- Industrial applications: Fungal cell wall components have several industrial applications, such as in the production of biofuels and biomaterials. Chitin, for instance, finds applications in wound healing and wastewater treatment.
Future Research Directions
Despite considerable advances in understanding fungal cell wall structure and function, many aspects remain poorly understood. Future research will likely focus on:
- Detailed characterization of cell wall components: Advances in analytical techniques will allow for a more precise characterization of the diverse array of molecules making up fungal cell walls.
- Understanding cell wall dynamics: The cell wall is not a static structure but rather a dynamic entity that undergoes continuous modification during fungal growth and development. Future research will need to explore these dynamic changes in more detail.
- Identifying novel antifungal drug targets: A deeper understanding of cell wall synthesis and function will uncover potential new targets for antifungal drug development.
- Exploring the role of cell wall in fungal interactions: More research is needed to understand the complex interactions between the fungal cell wall and other organisms, including other fungi, bacteria, and host cells.
In conclusion, the fungal cell wall is a marvel of biological engineering. Its complex composition and dynamic nature contribute to the survival and pathogenesis of fungi, making it a fascinating subject of study with implications for medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. As our understanding of this intricate structure deepens, we can expect further advancements in controlling fungal growth, treating fungal infections, and harnessing the potential of fungal cell wall components for diverse industrial applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Give The Complete Electron Configuration For Mn
Apr 06, 2025
-
Why Cant The Subscripts Be Changed In A Chemical Equation
Apr 06, 2025
-
Write An Equation For The Function Graphed Above
Apr 06, 2025
-
Is Sulfur A Metal Metalloid Or Nonmetal
Apr 06, 2025
-
A Group Of Ecosystems With Similar Climates And Organisms
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fungal Cell Walls Consist Primarily Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
