Dsl Is An Example Of What Type Of Internet Access
News Leon
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
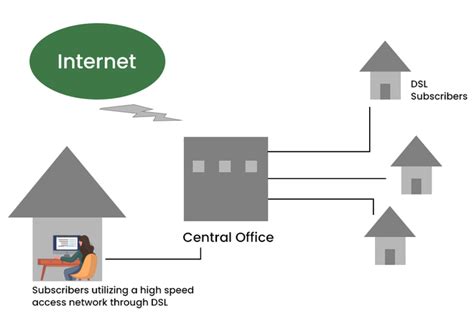
Table of Contents
DSL: A Deep Dive into Digital Subscriber Line Internet Access
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) technology has been a cornerstone of home internet access for many years. But what exactly is DSL, and what type of internet access does it represent? This comprehensive guide will explore DSL in detail, covering its underlying technology, different types of DSL connections, advantages and disadvantages, and its place in the broader landscape of internet access options. We'll also delve into how DSL compares to other technologies and why it remains relevant even in the age of fiber optics and cable internet.
Understanding DSL: A Primer on Digital Subscriber Line Technology
DSL is a family of technologies that use existing telephone lines to provide high-bandwidth internet access. Unlike dial-up internet, which requires you to disconnect your phone line to use the internet, DSL allows you to use both your phone and the internet simultaneously. This is achieved through clever frequency division multiplexing, a technique that allows different signals to occupy different frequency ranges within the same wire.
How does it work? DSL uses the existing copper telephone wires that run to your home. However, it utilizes a much higher frequency range than traditional voice calls. This means that the data signals for your internet connection don't interfere with the voice signals on the same line. A special device called a DSL modem is installed at your premises. This modem separates the voice and data signals, allowing you to make and receive phone calls while simultaneously browsing the internet, streaming videos, or downloading files.
Key Components of a DSL Internet Connection:
- DSL Modem: The heart of the DSL system, converting digital data into analog signals for transmission over the copper wire and vice-versa.
- Telephone Line: The existing copper wiring infrastructure used to transport the data signals.
- DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer): Located at the telephone company's central office, this device aggregates multiple DSL connections and connects them to the wider internet.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP): The company that provides the DSL internet service and manages the connection to the internet.
Types of DSL Connections: ADSL, SDSL, and More
There are several variations of DSL technology, each offering different speeds and capabilities. The most common types include:
-
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line): This is the most prevalent type of DSL. It offers faster download speeds than upload speeds, reflecting the typical internet usage pattern where users download much more data than they upload. This asymmetry is built into the technology, optimizing for the common use case.
-
SDSL (Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line): Unlike ADSL, SDSL provides equal download and upload speeds. This makes it ideal for applications that require high bandwidth in both directions, such as video conferencing, online gaming, and file transfers between computers.
-
HDSL (High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line): This type of DSL provides higher bandwidth than ADSL, suitable for business users requiring greater capacity. It's less common in residential settings.
-
VDSL (Very-high-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line): Offering significantly higher speeds than ADSL, VDSL utilizes advanced modulation techniques to achieve this increased bandwidth. However, its range is typically shorter than ADSL, limiting its reach.
-
ADSL2 and ADSL2+: These are improvements over the original ADSL technology, offering higher speeds and better performance. They are widely deployed and often the standard offering from ISPs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DSL Internet Access
Like any technology, DSL has its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these is crucial to determining if it's the right choice for your needs.
Advantages:
- Always-on Connection: Unlike dial-up, DSL provides a continuous internet connection without requiring you to dial in each time.
- Cost-Effective: DSL is often a more affordable option than cable internet, particularly in areas where cable infrastructure is limited.
- Wide Availability: DSL leverages the existing telephone network, making it readily available in many locations, even those with limited cable or fiber access.
- Simultaneous Voice and Data: DSL allows you to use your phone line and your internet connection concurrently.
- Relatively Simple Setup: Installing and configuring a DSL connection is generally straightforward.
Disadvantages:
- Speed Limitations: DSL speeds can be significantly slower than cable or fiber internet, especially over longer distances from the central office. Speed is heavily dependent on distance and the quality of the copper wiring.
- Distance Sensitivity: The further your home is from the telephone company's central office, the slower your DSL speed will be. This is a major limiting factor for DSL.
- Susceptibility to Noise: DSL connections can be affected by noise on the telephone line, potentially leading to intermittent disruptions or slower speeds.
- Limited Availability in Some Areas: While widely available, DSL isn't available everywhere, particularly in more rural or sparsely populated areas where upgrading the copper infrastructure is not economically viable.
- Technological Limitations: As a technology built upon aging infrastructure, DSL is inherently limited in its potential speed compared to newer technologies like fiber optics.
DSL vs. Other Internet Access Technologies: A Comparison
To understand DSL's place in the market, it's essential to compare it to other popular internet access technologies:
DSL vs. Cable Internet: Cable internet generally offers faster speeds than DSL, particularly for downloads. However, cable internet performance can be affected by network congestion during peak usage times. DSL often provides a more consistent speed, though slower overall. Availability also differs, with cable access depending on the presence of cable infrastructure in your area.
DSL vs. Fiber Internet: Fiber optic internet offers significantly faster speeds and greater bandwidth than DSL. It is also less susceptible to noise and distance limitations. However, fiber internet is typically more expensive and is not yet available in all areas.
DSL vs. Satellite Internet: Satellite internet offers coverage in remote areas where other technologies are unavailable. However, it suffers from higher latency (delay) and is often more expensive than DSL.
The Future of DSL: A Niche Technology?
With the advent of faster technologies like fiber and cable, the future of DSL seems uncertain. However, DSL continues to play a significant role in providing internet access to areas where other options are unavailable or too expensive to implement. Moreover, ongoing upgrades and advancements in DSL technology, such as VDSL2 and G.fast, are helping to improve speeds and extend its reach.
While it's unlikely DSL will become the dominant internet access technology, its role as a cost-effective and readily available option in specific geographical locations will likely persist for the foreseeable future. It serves as a vital bridge, connecting communities to the digital world where higher-bandwidth options are not economically feasible or technically possible. As such, it remains a relevant and important type of internet access.
Conclusion: DSL's Enduring Relevance in the Digital Landscape
In summary, DSL is a type of internet access that utilizes existing telephone lines to provide a high-bandwidth connection. While it faces stiff competition from newer technologies like fiber and cable internet, DSL remains a viable and valuable option for many users, especially in areas with limited infrastructure and budgetary constraints. Its enduring relevance hinges on its affordability, availability, and its ability to offer a reliable internet connection for various residential and small business needs. Understanding the different types of DSL, its advantages and limitations, and how it compares to other technologies is critical for consumers seeking to make informed decisions about their internet service. The continuing evolution of DSL technology suggests that it will maintain a niche but essential role in the global digital landscape for years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 36 And 54
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Layer Of The Skin Does Not Contain Blood Vessels
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Neutrons Does Xenon Have
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Light Years Is Pluto From Earth
Mar 21, 2025
-
Sequence Is True For The Lytic Cycle Of A Virus
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Dsl Is An Example Of What Type Of Internet Access . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
