Which Layer Of The Skin Does Not Contain Blood Vessels
News Leon
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
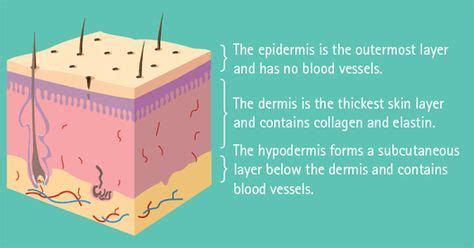
Table of Contents
Which Layer of the Skin Does Not Contain Blood Vessels? Understanding the Stratum Corneum
The human skin, our largest organ, is a complex and fascinating structure. Composed of multiple layers, each with its own unique function, it acts as a protective barrier against the external environment, regulating temperature, and playing a vital role in sensation. While many layers are richly supplied with blood vessels, facilitating nutrient delivery and waste removal, one layer stands out for its avascular nature: the stratum corneum. This article will delve deep into the structure and function of the stratum corneum, explaining why it lacks blood vessels and the implications of this characteristic.
The Structure of the Skin: A Layered Defense
Before focusing on the avascular stratum corneum, it's crucial to understand the overall structure of the skin. Skin is composed of three main layers:
- Epidermis: The outermost layer, responsible for protection against external factors like UV radiation, pathogens, and dehydration. It's further divided into several sublayers, including the stratum corneum.
- Dermis: The middle layer, containing blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. It provides structural support and plays a vital role in thermoregulation and sensation.
- Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Tissue): The deepest layer, composed mainly of adipose tissue (fat). It acts as insulation, cushioning, and energy storage.
Within the epidermis, the stratum corneum is the outermost sublayer, acting as the ultimate barrier between the body and the outside world.
The Stratum Corneum: A Barrier of Dead Cells
Unlike the other layers of the skin, the stratum corneum is entirely composed of dead cells, known as corneocytes. These cells are flattened, keratinized (filled with the protein keratin), and tightly interconnected, forming a tough, waterproof barrier. This tightly packed arrangement of corneocytes, along with the presence of lipids (fats) between them, creates a formidable shield against the environment.
Why the Lack of Blood Vessels?
The absence of blood vessels in the stratum corneum is a key feature that contributes to its protective function. Here's why:
- Barrier Integrity: Blood vessels would compromise the integrity of the skin's protective barrier. The presence of blood vessels would create pathways for the entry of pathogens and harmful substances, weakening the defense against infection and environmental damage.
- Water Retention: The stratum corneum's primary function is to prevent water loss from the body (transepidermal water loss or TEWL). The presence of blood vessels, with their fluid content, would significantly increase TEWL and lead to dehydration.
- Metabolic Efficiency: The dead cells of the stratum corneum have minimal metabolic activity. The lack of blood vessels is energy efficient, as nutrient delivery and waste removal are not required. Nutrients for the stratum corneum are obtained passively from the lower layers of the epidermis.
The Significance of Avascularity
The avascular nature of the stratum corneum has significant implications for various aspects of skin health and function:
- Wound Healing: The lack of blood vessels makes the stratum corneum less prone to bleeding, which is crucial during minor injuries. However, the avascularity also makes healing slower as nutrient delivery is dependent on diffusion from the lower layers.
- Drug Delivery: The stratum corneum's impermeability poses a significant challenge in drug delivery to deeper skin layers. Many topical medications struggle to penetrate the stratum corneum due to its dense structure and lack of direct blood supply. Researchers are constantly exploring innovative methods to enhance drug penetration across this barrier.
- Skin Diseases: Many skin diseases directly affect the stratum corneum's structure and function. Conditions like eczema and psoriasis involve changes in the stratum corneum’s composition, affecting its barrier function and hydration levels. The avascular nature of the layer is a key factor to consider in managing these conditions, as treatment often focuses on restoring the integrity of this barrier.
Nutrient Supply to the Stratum Corneum: Diffusion and Passive Transport
If the stratum corneum lacks blood vessels, how does it receive the necessary nutrients? The answer lies in passive diffusion and the underlying layers of the epidermis. Nutrients, including water and essential lipids, are transported from the dermis and the lower layers of the epidermis through a process of diffusion. This means that substances move from areas of high concentration (in the underlying layers) to areas of lower concentration (in the stratum corneum) across the cell membranes.
The process of diffusion is slow and passive, explaining why the stratum corneum relies on a continuous supply of nutrients from the underlying, vascularized layers. Any disruption to this supply can compromise the integrity and function of the stratum corneum.
The Role of Lipids in the Stratum Corneum
The lipids found between the corneocytes are essential for maintaining the stratum corneum's barrier function. These lipids, including ceramides, cholesterol, and free fatty acids, form a lipid bilayer that prevents water loss and restricts the entry of harmful substances. The composition and organization of these lipids are crucial for maintaining the skin's moisture levels and protecting against environmental stressors. Disruptions to the lipid bilayer can lead to compromised barrier function and various skin conditions.
The Stratum Corneum and Skin Aging
As we age, the structure and function of the stratum corneum change significantly. The rate of cell turnover slows down, leading to a thickening of the stratum corneum and a reduction in its ability to retain moisture. The lipid composition also changes, resulting in a decrease in the barrier function and increased susceptibility to environmental damage. These age-related changes contribute to the dryness, wrinkles, and increased sensitivity often observed in older skin.
Clinical Significance and Implications
The avascular nature of the stratum corneum has significant clinical implications:
- Transdermal drug delivery: The development of effective transdermal drug delivery systems requires strategies to overcome the barrier properties of the stratum corneum.
- Wound healing: Understanding the avascular nature of the stratum corneum is crucial for developing effective wound healing strategies. Promoting blood supply to the underlying layers is essential for efficient healing.
- Skin disease management: Many skin diseases involve alterations in the structure and function of the stratum corneum. Treatments often focus on restoring the integrity of this barrier.
Conclusion: A Vital, Avascular Barrier
The stratum corneum, despite its lack of blood vessels, is a vital layer of the skin. Its avascularity is crucial for its function as a protective barrier against environmental stressors, maintaining hydration, and preventing pathogen entry. Understanding the structure, function, and unique properties of the stratum corneum is fundamental for comprehending skin health and developing effective treatments for skin diseases and conditions affecting this essential layer. Further research into the stratum corneum will continue to shed light on its complex mechanisms and ultimately lead to advancements in skin care and treatment. The intricate interplay of its unique composition, its avascular nature, and its interaction with underlying skin layers make it a fascinating and critical subject of ongoing scientific investigation.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Layer Of The Skin Does Not Contain Blood Vessels . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.