Difference Between Associative Property And Commutative Property
News Leon
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
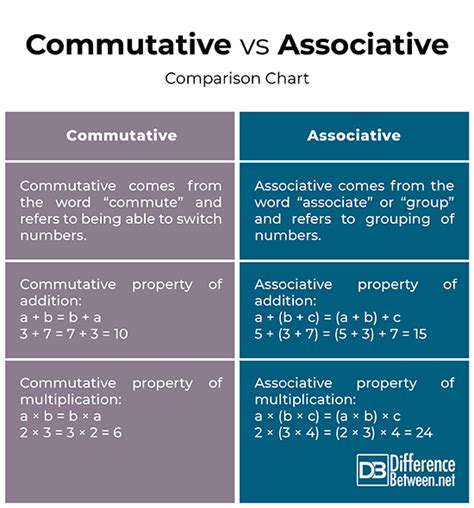
Table of Contents
Decoding the Difference: Associative vs. Commutative Properties
Mathematics, at its core, is a language of structure and relationships. Understanding the fundamental properties governing these relationships is crucial for mastering various mathematical concepts. Among these properties, the associative and commutative properties are frequently encountered, yet often confused. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the nuances of these two properties, clarifying their differences and demonstrating their applications across various mathematical operations.
Understanding the Commutative Property
The commutative property, simply put, states that the order of operands in an operation doesn't affect the outcome. This applies to specific operations, primarily addition and multiplication.
In simpler terms: You can swap the numbers around, and the answer remains the same.
Formally:
- For Addition: a + b = b + a
- For Multiplication: a × b = b × a
Let's illustrate with examples:
- Addition: 5 + 3 = 8, and 3 + 5 = 8. The order of addition doesn't change the sum.
- Multiplication: 6 × 4 = 24, and 4 × 6 = 24. The order of multiplication doesn't change the product.
Where it Doesn't Apply:
Critically, the commutative property does not apply to all operations. Subtraction and division are not commutative.
- Subtraction: 10 - 5 = 5, but 5 - 10 = -5. The order significantly alters the result.
- Division: 12 ÷ 3 = 4, but 3 ÷ 12 = 0.25. Again, the order drastically changes the outcome.
Unveiling the Associative Property
Unlike the commutative property which focuses on the order of operands, the associative property deals with the grouping of operands in an operation involving three or more numbers. It states that you can regroup the numbers without affecting the final result.
In simpler terms: You can change the parentheses, and the answer stays the same.
Formally:
- For Addition: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
- For Multiplication: (a × b) × c = a × (b × c)
Let's illustrate with examples:
- Addition: (2 + 4) + 6 = 12, and 2 + (4 + 6) = 12. The grouping of the numbers doesn't affect the sum.
- Multiplication: (3 × 5) × 2 = 30, and 3 × (5 × 2) = 30. The grouping of the numbers doesn't affect the product.
Where it Doesn't Apply:
Similar to the commutative property, the associative property also has limitations. Subtraction and division are not associative.
- Subtraction: (10 - 5) - 2 = 3, but 10 - (5 - 2) = 7. The grouping drastically changes the result.
- Division: (12 ÷ 3) ÷ 2 = 2, but 12 ÷ (3 ÷ 2) = 8. Again, the grouping leads to different outcomes.
Key Differences: A Head-to-Head Comparison
The core difference lies in what is being changed: order versus grouping.
| Feature | Commutative Property | Associative Property |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Order of operands | Grouping of operands |
| What changes | The sequence of numbers in the operation | The placement of parentheses in the operation |
| Applicable to | Addition and multiplication | Addition and multiplication |
| Not applicable to | Subtraction and division | Subtraction and division |
| Illustrative Example (Addition) | 2 + 3 = 3 + 2 | (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4) |
| Illustrative Example (Multiplication) | 5 × 6 = 6 × 5 | (5 × 6) × 7 = 5 × (6 × 7) |
Practical Applications: Beyond Basic Arithmetic
While the commutative and associative properties might seem elementary at first glance, their implications extend far beyond simple arithmetic. They play a crucial role in:
1. Simplifying Algebraic Expressions:
The commutative and associative properties are invaluable tools for simplifying complex algebraic expressions. By rearranging terms (commutative) and regrouping them (associative), we can often streamline calculations and make problems more manageable. For example:
3x + 5y + 2x + 7y = (3x + 2x) + (5y + 7y) = 5x + 12y
This simplification relies heavily on both the commutative (reordering terms) and associative (regrouping terms) properties.
2. Matrix Algebra:
In linear algebra, matrix addition is both commutative and associative. This property simplifies various matrix manipulations and computations significantly. This fundamental property underpins many advanced mathematical concepts.
3. Computer Science and Programming:
These properties are fundamental in optimizing computer algorithms. By recognizing and applying these properties, programmers can reduce the number of computations needed, leading to faster and more efficient programs. For instance, optimizing database queries often involves leveraging these principles to streamline data retrieval.
4. Set Theory:
In set theory, the union and intersection operations exhibit commutative and associative properties. This facilitates various set manipulations and proofs in set theory.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
The most frequent misunderstanding stems from applying these properties inappropriately. Remember:
- Not all operations are commutative or associative. Always check if the operation allows for reordering or regrouping before applying these properties.
- Combining properties. Often, you'll need to use both the commutative and associative properties together to simplify expressions effectively. Don't try to force one property without considering the other.
Conclusion: Mastering Mathematical Properties
The commutative and associative properties, though seemingly simple, form the bedrock of many advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding their precise definitions, applications, and limitations is crucial for developing a strong mathematical foundation. By mastering these properties, students gain not just a deeper understanding of arithmetic but also acquire powerful problem-solving tools applicable across various mathematical disciplines and computational contexts. This thorough understanding empowers efficient calculations, simplifies complex expressions, and lays a strong base for more advanced mathematical studies. The ability to distinguish and correctly apply these properties showcases a sophisticated understanding of the underlying structures and relationships within mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Feet Is 168 Cm
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Heart Chamber Has The Thickest Wall
Mar 15, 2025
-
Viral Capsids Are Made From Subunits Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Negatively Charged Ion Is Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
Two Different Isotopes Of An Element Have Different
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Associative Property And Commutative Property . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
